Vahanga facts for kids

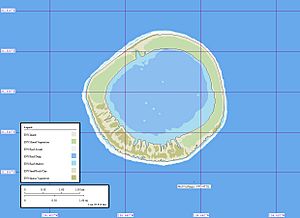
NASA picture of Vahanga Atoll
|
|
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 21°19′S 136°39′W / 21.317°S 136.650°W |
| Archipelago | Tuamotus |
| Area | 12.6 km2 (4.9 sq mi) (lagoon) 3.8 km2 (1.5 sq mi) (above water) |
| Width | 3.6 km (2.24 mi) |
| Administration | |
|
France
|
|
| Overseas collectivity | French Polynesia |
| Administrative subdivision | Tuamotus |
| Commune | Gambier Islands |
| Demographics | |
| Population | Uninhabited (2012) |
Vahanga is a small, empty island in the Pacific Ocean. It is an atoll, which is a ring-shaped coral reef island. Vahanga is part of the Acteon Group in the Tuamotu chain. It belongs to French Polynesia and is managed by the Gambier Islands area. No one lives on Vahanga.
Contents
Exploring Vahanga's Geography
Vahanga is located about 9 kilometers (5.6 miles) west of another island called Tenarunga. It is much further from Tahiti, about 1362 kilometers (846 miles) to the southeast. The atoll is round, like a circle. It measures 3.6 kilometers (2.2 miles) across. The land area of Vahanga is 3.8 square kilometers (1.5 square miles). If you include the water inside the atoll (the lagoon), its total area is 12.6 square kilometers (4.9 square miles). Vahanga is a low-lying island. There is a place on the northwest side where boats can land. You can see a small white house there. However, you cannot get into the lagoon from this landing spot.
Vahanga's Past: A Look at Its History
The first time Vahanga was officially seen was on February 5, 1606. This was during a Spanish trip led by a Portuguese explorer named Pedro Fernández de Quirós. He called the islands Las Cuatro Coronadas, meaning "the four crowned" islands. This name came from the many coconut trees that looked like crowns. However, his notes about seeing the island were not very clear.
The first time the island was clearly seen and recorded was in 1833. This was by a sailor named Thomas Ebrill on his ship, the Amphitrite. Then, in 1837, Lord Edward Russell saw it again. He was the commander of the ship H.M.S Actaeon. The group of islands, including Vahanga, was later named the Acteon Group after his ship. Vahanga used to be owned by a person called Captain Nicholas. But in 1934, the ownership was changed.
Plants and Animals of Vahanga
Vahanga is home to many different plants. You can find coconut trees growing there. Other plants include Portulaca lutea, Cassytha filiformis, and plants from the Amaranthaceae family. One example is Achyranthes aspera var. velutina.
In 2007, a special project took place on Vahanga. Experts from the University of Auckland and the Ornithological Society of Polynesia worked together. Their goal was to get rid of the Polynesian rats on the atoll. These rats had moved onto the island and were causing problems for the local wildlife. The project aimed to help the island's ecosystem get back to normal. This would protect native bird species. These birds include the Polynesian ground-dove and the Tuamotu sandpiper. A similar effort in 2000 had not worked.
Later, in 2015, another conservation project was successful. This time, the rats were completely removed from the island. This helped the native birds and other animals to thrive.
See also
 In Spanish: Vahanga para niños
In Spanish: Vahanga para niños
- Matureivavao
- Tenararo
- Tenarunga
- Acteon Group
- Desert island
- List of islands
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |