Virginia jointvetch facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Virginia jointvetch |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Aeschynomene
|
| Species: |
A. virginica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aeschynomene virginica (L.) Britton, Poggenb. & Sterns
|
|
The Virginia jointvetch (Aeschynomene virginica) is a rare and special flowering plant. It is also called the sensitive jointvetch. This plant belongs to the legume family, which includes peas and beans.
It grows only in a small part of the eastern United States. There are about 20 groups of these plants, and their numbers change each year. For example, New Jersey has thousands of plants, while Maryland has only a few hundred. In Virginia, there are about 5,000 plants. Sadly, changes to its natural home have made it harder for this plant to grow. Because it is so rare, the United States government listed it as a threatened species in 1992.
Sometimes, people get this plant confused with another one. Some books mistakenly say the Virginia jointvetch is a harmful weed found in soybean and rice fields. However, the weed they are talking about is actually Aeschynomene indica. The Virginia jointvetch (A. virginica) is a rare and protected plant, not a weed.
Contents
What the Virginia Jointvetch Looks Like
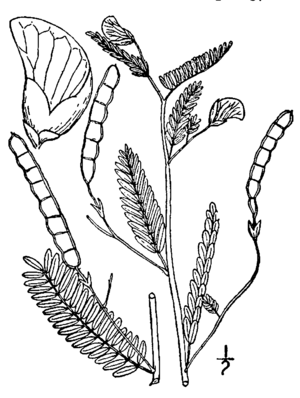
The Virginia jointvetch is an annual plant, meaning it lives for only one year. It grows straight up and can reach a height of two meters, which is about six and a half feet. Its leaves grow in an alternating pattern along the stem. Each leaf has many small, hairy leaflets. These leaflets are special because they are sensitive to touch. If you gently touch them, they will fold up!
Flowers and Seeds
This plant blooms in the summer and early fall. Its flowers look like small peas and are about one centimeter long. They are bright yellow with clear red lines, making them quite pretty. Tiny insects help pollinate these flowers. Some of these helpers include the Least Skipper butterfly and leaf-cutter bees.
After the flowers are pollinated, the plant produces a fruit called a legume pod. This pod can be up to seven centimeters long. It has narrow sections between each seed. The pod easily breaks apart into these segments. These segments can float on water, helping the seeds spread to new places. Sometimes, parts of the pods get caught in floating plant bits. They can then be carried by water and dropped off in new areas, helping the plant grow in different spots.
Where the Virginia Jointvetch Lives
This plant likes to grow in freshwater tidal marshes. These are wet areas near rivers or coasts where the water level changes with the tide. The water in these marshes has very low salinity, meaning it's not salty like the ocean.
The Virginia jointvetch prefers bare, open areas. It does not like places with lots of other plants. You might find it on new shorelines or in spots recently dug up by animals like muskrats. It needs wet soil to start growing, but it cannot grow if it is completely underwater. It also does not do well in areas with thick plant growth.
Challenges for the Plant
Even though it can grow in places affected by tides, the Virginia jointvetch cannot handle big changes. For example, it struggles with too much sediment (dirt and sand) building up. Human activities also harm this plant. Things like new buildings, pollution, or erosion caused by boat wakes can damage its habitat. Protecting these special marshes is important for the survival of the Virginia jointvetch.