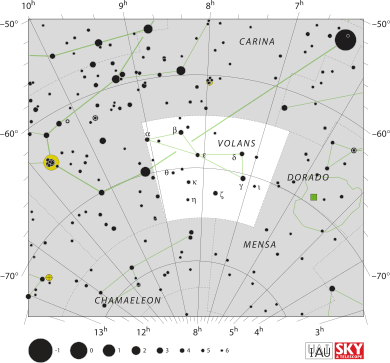
Volans facts for kids
| Constellation | |
List of stars in Volans
|
|
| Abbreviation | Vol |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Volantis |
| Pronunciation | genitive |
| Symbolism | the Flying Fish |
| Right ascension | 8 |
| Declination | −70 |
| Quadrant | SQ2 |
| Area | 141 sq. deg. (76th) |
| Main stars | 6 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars |
12 |
| Stars with planets | 1 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00m | 0 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 1 |
| Brightest star | β Vol (3.77m) |
| Messier objects | 0 |
| Meteor showers | 0 |
| Bordering constellations |
Carina Pictor Dorado Mensa Chamaeleon |
| Visible at latitudes between +15° and −90°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of March. |
|
The constellation Volans is a group of stars you can see in the southern part of the sky. It looks like a flying fish. The name Volans is actually a shorter version of its first name, Piscis Volans.
Volans was one of twelve new constellations created by Petrus Plancius. He used notes from two explorers, Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman, to make them. Volans first appeared on a special map of the sky called a celestial globe. This globe was published in 1597 or 1598 in Amsterdam. The first time Volans was shown in a book of sky maps was in Johann Bayer's Uranometria in 1603.
What Stars and Galaxies Can You See in Volans?
In the Volans constellation, there are two double stars you can see with a small telescope. These are called Gamma Volantis and Epsilon Volantis. A double star is actually two stars that look very close together from Earth. Sometimes they even orbit each other!
Gamma Volantis has stars that are the fourth and sixth brightest you can see. Epsilon Volantis has stars that are the fourth and eighth brightest.
There are also two galaxies in Volans. Galaxies are huge groups of stars, gas, and dust. These two galaxies are named NGC 2442 and NGC 2434. They might be a bit harder to spot clearly with a small telescope.
See also
 In Spanish: Volans para niños
In Spanish: Volans para niños
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |



