Volcanic impacts on the oceans facts for kids
When volcanoes erupt with great force, they can change the global climate in several ways. One big way is by sending tiny particles high into the sky. These particles can make the Earth cooler, especially the oceans.
Contents
How Volcanoes Cool the Ocean Surface
Very strong volcanic eruptions shoot special gases, like sulfur gases, high up into the Earth's atmosphere. This high part is called the stratosphere. Up there, these gases turn into tiny, shiny particles called sulfate aerosols.
These tiny particles then spread all over the world. They act like a giant mirror, reflecting some of the sun's energy back into space. This means less sunlight reaches the Earth's surface, which makes things cooler. This cooling effect on the ocean surface usually lasts for a few years, because the particles stay in the air for about 2 to 3 years.
For very large volcanoes (those with a VEI of 5 or more), the average sea surface temperature (SST) around the world can drop by about 0.2 to 0.3 degrees Celsius. This cooling is a bit less than the overall drop in air temperature, which can be 0.3 to 0.5 degrees Celsius. It usually takes several years for the ocean temperatures to return to normal after a big eruption.
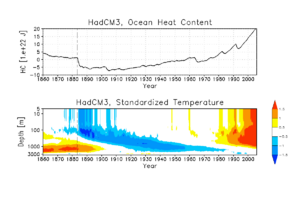
Volcanoes and Ocean Heat
Volcanic eruptions can also affect how much heat the ocean holds. This cooling effect can last much longer than the particles stay in the air, sometimes for decades!
For example, studies have shown that the huge 1883 eruption of Krakatau affected the ocean's heat for as long as a century. However, the effects of more recent volcanoes, like Mount Pinatubo in 1991, seem to last for a shorter time. This is partly because the Earth's climate is getting warmer due to greenhouse gases. Even so, the cooling from Pinatubo reached deep into the ocean, about 1,000 meters down.
A study from 2022 found that after a volcano erupts, the eastern part of the Pacific Ocean near the equator can actually get warmer. But volcanoes closer to the North or South Poles tend to make the ocean colder in those areas.
How Volcanoes Change Sea Level
The amount of heat in the ocean affects sea level. When the ocean gets colder, the water shrinks a little (this is called thermal expansion). So, less heat in the ocean should lead to a small drop in global mean sea level over time.
However, some scientists believe that right after a volcanic eruption, sea level might actually rise a little first, before it starts to drop. One idea for this is how water moves around the Earth. After an eruption, the ocean surface cools, which means less water evaporates from the ocean into the air.
This quick drop in evaporation, combined with a slower change in how much water flows into the ocean from rivers, can cause sea level to go up. But after about one or two years, less rain falls and less sea ice melts. This means less water flows into the ocean from rivers, which then causes the sea level to drop.
Ocean Oxygen and Carbon Levels
In 2023, scientists looked at the eruption of Mount Pinatubo in June 1991. They found that this eruption led to more oxygen and carbon in the ocean. These changes lasted for many years after the eruption.