W and Z bosons facts for kids
W and Z bosons are tiny particles that help make up everything around us. They are a type of boson, which means they have a special property called spin (like a tiny internal rotation). Scientists first found these particles in experiments in 1983.
W and Z bosons are important because they carry the "weak force." This force is one of the four basic forces in the universe. It's called "weak" because it's not as strong as the strong force, which holds atomic nuclei together.
There are two types of W bosons: W+ and W–. They have different electric charges. Z bosons are special because they are their own antiparticle, meaning they are identical to their antimatter version.
Contents
What Are W and Z Bosons Called?
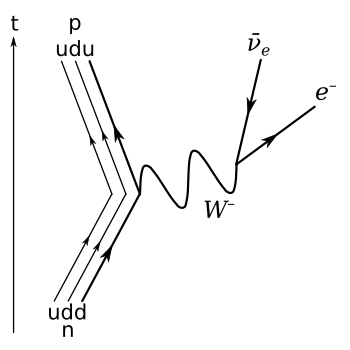
W bosons get their name from the weak force they carry. This force is involved in how some radioactive elements break down. This process is called Beta decay.
In the late 1970s, scientists realized that the weak force and electromagnetism are actually connected. They combined them into one idea called the electroweak force. This helped them understand how these particles work.
How W and Z Bosons Are Made
W and Z bosons are usually created during a process called Beta decay. This is a type of radioactive decay where an unstable atom changes into a more stable one.
Understanding Beta Decay
Beta decay happens when an atom's center has too many neutrons. You can think of a neutron as being made of smaller parts. When there are too many neutrons, one of them can change. It splits and forms a proton and an electron. The new proton stays in the atom's center. The electron shoots out of the atom very fast. This fast-moving electron is what makes Beta radiation harmful.
To be more exact, protons and neutrons are both made of even smaller particles called quarks. A proton has two up quarks and one down quark. An up quark has a charge of +2/3, and a down quark has a charge of -1/3. So, a proton has a total charge of +1. A neutron has one up quark and two down quarks, giving it a total charge of 0.
The weak force can change the "flavor" of a quark. For example, it can turn a down quark inside a neutron into an up quark. When this happens, the neutron's charge changes to +1. It then becomes a proton. So, Beta decay causes a neutron to become a proton, along with other particles.
What Happens When W Bosons Decay?
When a quark changes its flavor, like in Beta decay, it releases a W boson. W bosons don't last long at all! They exist for only about 3x10-25 seconds before they decay into other particles. This is why it took so long for scientists to find them.
Even though they are so short-lived, W bosons are surprisingly heavy. They weigh about 80 times more than a proton. It might seem strange that a heavy particle comes from a lighter one. But in the world of tiny particles, extra mass can come from stored energy, as explained by Einstein's famous formula, E=mc2.
After its super-short life, a W boson decays into one electron and one neutrino. Neutrinos almost never interact with other matter, so we can often ignore them. The electron that is produced is shot out of the atom at high speed. The proton that was formed during Beta decay stays in the atom's center. This increases the atom's atomic number by one, changing it into a different element.
What Happens When Z Bosons Decay?
Z bosons are also part of the Standard Model of physics. This model successfully predicted that W bosons exist. Z bosons decay into a particle and its antiparticle. These can be particles like electrons or quarks.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bosones W y Z para niños
In Spanish: Bosones W y Z para niños