Western Bloc facts for kids
The Western Bloc was a group of countries that were friends with the United States during the Cold War. The Cold War was a long period from 1947 to 1991 when the US and its allies were in a tense standoff with the Soviet Union and its allies.
Many countries in Western Europe and Northern America were key parts of the Western Bloc. But it also included nations from other parts of the world, like Asia, the Middle East, Latin America, and Africa. These countries generally did not like the ideas of the Soviet Union or communism. The Western Bloc was against the political systems and foreign policies of communist countries. These communist countries were mostly led by the Soviet Union and its friends in the Warsaw Pact, and sometimes China.
People often called the Western Bloc the "Free World" or the "First World." This was because they saw themselves as being free from communist control. The group of communist countries was called the Eastern Bloc or the "Communist World."
Contents
What Was the Cold War?
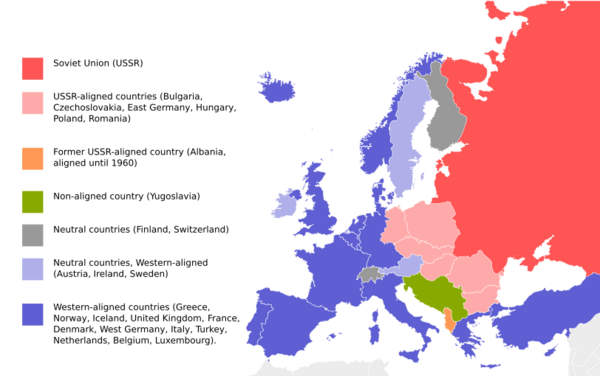
The Cold War was a time of great tension between two major groups of countries. On one side was the United States and its allies, forming the Western Bloc. On the other side was the Soviet Union and its allies, known as the Eastern Bloc. It was called "cold" because there wasn't a direct, large-scale war between these two main powers. However, they supported different sides in smaller wars around the world.
This period was marked by a race to build more weapons, especially nuclear ones. Both sides also tried to spread their political ideas around the globe. The Western Bloc believed in democracy and capitalism. The Eastern Bloc believed in communism, where the government controls most things.
Key Groups in the Western Bloc (1947–1991)
During the Cold War, the Western Bloc was made up of several alliances and partnerships. These groups worked together to protect their shared interests and stand against the Eastern Bloc.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
NATO was a very important military alliance formed in 1949. Its main goal was to protect its members from any attack, especially from the Soviet Union. If one NATO country was attacked, all other members promised to help.
- Founding Members: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, United Kingdom, United States.
- Later Members: Greece (from 1952), Turkey (from 1952), West Germany (from 1955), Spain (from 1982).
Five Eyes Alliance
This was a special intelligence-sharing alliance. It allowed these countries to share secret information with each other.
- Australia
- Canada
- New Zealand
- United Kingdom
- United States
ANZUS Treaty
This was a military alliance focused on security in the Pacific Ocean region.
- Australia
- New Zealand
- United States
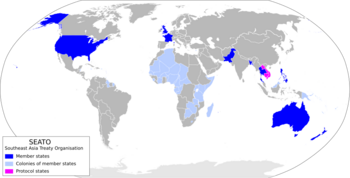
Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO)
SEATO was another alliance created to stop the spread of communism in Southeast Asia.
- Australia
- France
- New Zealand
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Thailand
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Cambodia (until 1956)
- Laos (until 1975)
- South Vietnam (until 1975)
Central Treaty Organization (CENTO)
Also known as the Baghdad Pact, CENTO aimed to prevent Soviet expansion into the Middle East. It lasted until 1979.
- Iran (until 1979)
- Iraq (until 1958)
- Pakistan (until 1979)
- Turkey (until 1979)
- United Kingdom (until 1979)
Rio Treaty
This treaty was about mutual defense among countries in the Americas.
- Argentina
- Bahamas (from 1982)
- Bolivia (until 2005)
- Brazil
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Cuba (until 1959)
- Dominican Republic (until 1990)
- Ecuador (until 2012)
- El Salvador
- Guatemala
- Honduras
- Mexico
- Nicaragua (until 1979)
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Trinidad and Tobago (from 1967)
- United States
- Uruguay
- Venezuela
Western-Aligned Countries After 1991
The Cold War ended in 1991 when the Soviet Union broke apart. After this, the idea of the "Western Bloc" changed. Many former Eastern Bloc countries joined alliances that were once part of the Western Bloc. The United States continued to have strong allies around the world.
NATO Expansion
NATO grew significantly after the Cold War, including many countries that were once under Soviet influence.
- Original Members: Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Germany (reunified), Greece, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Turkey, United Kingdom, United States.
- New Members (after 1991): Albania (2009), Bulgaria (2004), Croatia (2009), Czech Republic (1999), Estonia (2004), Finland (2023), Hungary (1999), Latvia (2004), Lithuania (2004), Montenegro (2017), North Macedonia (2020), Poland (1999), Romania (2004), Slovakia (2004), Slovenia (2004), Sweden (2024).
Major Non-NATO Allies (MNNA)
The United States also has a special group of countries called Major Non-NATO Allies. These countries work closely with the US on defense and security matters, even if they are not part of NATO.
- Australia (from 1987)
- Egypt (from 1987)
- Israel (from 1987)
- Japan (from 1987)
- South Korea (from 1987)
- Jordan (from 1996)
- New Zealand (from 1997)
- Argentina (from 1998)
- Bahrain (from 2002)
- Philippines (from 2003)
- Thailand (from 2003)
- Taiwan (from 2003)
- Kuwait (from 2004)
- Morocco (from 2004)
- Pakistan (from 2004)
- Afghanistan (2012–2021)
- Tunisia (from 2015)
- Brazil (from 2019)
- Colombia (from 2022)
- Qatar (from 2022)
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad)
The Quad is a group focused on security and cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region.
- United States
- India
- Australia
- Japan
See also
 In Spanish: Bloque occidental para niños
In Spanish: Bloque occidental para niños
- Eastern Bloc
- Free World
- First World
- Second World
- Third World
- Western world
Sources
- Matloff, Maurice. Makers of Modern Strategy. Ed. Peter Paret. Princeton: Princeton UP, 1971. 702.
- Kissinger, Henry. Diplomacy. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1994. 447,454.
- Lewkowicz, Nicolas. The United States, the Soviet Union and the Geopolitical Implications of the Origins of the Cold War New York and London: Anthem Press, 2018.