Western Australian Legislative Assembly facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Legislative Assembly |
|
|---|---|
| 42nd Parliament | |
 |
|
| Type | |
| Type |
Lower house of the Parliament of Western Australia
|
| History | |
| Founded | 30 December 1890 |
| Leadership | |
|
Speaker
|
Stephen Price, Labor
Since 8 April 2025 |
|
Deputy Speaker
|
Ali Kent, Labor
Since 8 April 2025 |
|
Leader of the House
|
David Michael, Labor
Since 8 April 2025 |
|
Manager of Opposition Business
|
Libby Mettam, Liberal
Since 8 April 2025 |
|
Government Whip
|
Terry Healy, Labor
Since 8 April 2025 |
|
Opposition Whip
|
Liam Staltari, Liberal
Since 8 April 2025 |
| Structure | |
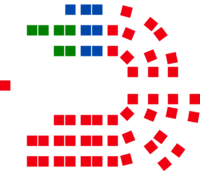
| Seats | 59 |
 |
|
|
Political groups
|
Government (46) Labor (46) Opposition (13) Liberal (7) National (6) |
|
Length of term
|
4 years |
| Elections | |
| Full preferential voting | |
|
Last election
|
8 March 2025 |
|
Next election
|
March 2029 |
| Meeting place | |
 |
|
| Legislative Assembly Chamber Parliament House, Perth Western Australia, Australia |
|
| Website | |
| WA Legislative Assembly | |
The Western Australian Legislative Assembly is one of the two main parts of the Parliament of Western Australia. It is often called the "lower house." This is where many important decisions are made for the state of Western Australia.
The Parliament meets in Parliament House in Perth, the capital city. The Legislative Assembly currently has 59 members. These members are chosen by voters for four-year terms. Each member represents a specific area, called an electoral district. People vote using a system called preferential voting. In Australia, voting is required for all citizens aged 18 and older.
Contents
How the Legislative Assembly Works
Most new laws in Western Australia start in the Legislative Assembly. The political party or group that wins the most seats in the Assembly gets to form the government. The Governor officially invites them to do this.
Forming the Government
The leader of the winning party or group becomes the Premier of Western Australia. The Premier is like the head of the state government. This leader then chooses other members to be ministers. These ministers are in charge of different areas, like education, health, or transport. They can be from either the Legislative Assembly or the Legislative Council.
Passing Laws
In Australia, political parties usually vote together on issues. This means that most laws suggested by the government usually pass through the Legislative Assembly.
History of the Assembly
The Legislative Assembly was the first elected group of lawmakers in Western Australia. It was created in 1890 when Western Australia became self-governing.
Early Days and Voting Rights
When it first started, the Assembly had 30 elected members. However, only men who owned land could vote. Before this, the Governor made most laws, with advice from the appointed Legislative Council.
In 1893, all adult men gained the right to vote. However, Indigenous Australians were specifically not allowed to vote at that time.
Women's Right to Vote
Women in Western Australia gained the right to vote in 1899. This made Western Australia the second Australian colony to allow women to vote, after South Australia. A big moment happened in 1921 when Edith Cowan became the first woman ever elected to any parliament in Australia. She won the West Perth seat in the Legislative Assembly.
Fairer Voting Areas
For many years, Western Australia used a special system for voting areas. This system meant that country areas had fewer voters per member than city areas. This was different from most other Australian states, where each voting area has about the same number of voters.
Changes to Electoral Districts
Until 2008, a member of parliament in Perth represented about 28,519 voters. But a country member represented only about 14,551 voters. This meant that a country vote had more "power" than a city vote. Many people, especially from the Labor Party, wanted a system where every vote counted equally. This idea is called "one vote, one value."
Over time, changes were made to make the system fairer. In 2005, a new law removed the difference between country and city voting areas for the Legislative Assembly. However, the changes did not fully take effect until the 2008 Western Australian state election on September 6, 2008.
Current Electoral Map
After these changes, the Western Australian Electoral Commission redrew the voting areas in 2007. Now, 42 seats are in Perth, and 17 are in country areas. The number of voters in each area is much more equal. For very large country areas (over 100,000 square kilometres), there can still be a slightly different number of voters, but the goal is still fair representation.
Current Members in the Assembly
Here is how the 59 seats in the Legislative Assembly are currently divided among the political parties:
| Party | Seats held | |
|---|---|---|
| Labor | 46 |
|
| Liberal | 7 |
|
| National | 6 |
|
| Total | 59 | |
To pass a new law, at least 30 votes are needed to form a majority.
See also
- 2025 Western Australian state election
- Members of the Western Australian Legislative Assembly
- Members of the Western Australian Legislative Assembly, 2025–2029
- Speaker of the Western Australian Legislative Assembly
- Electoral districts of Western Australia
- Western Australian Legislative Council
- Parliaments of the Australian states and territories



