Wind shear facts for kids
Wind shear happens when the wind speed or its direction changes a lot over a short distance in the air. Think of it like different layers of air moving at different speeds or in different directions. There are two main types: horizontal (side-to-side) and vertical (up-and-down) wind shear.
Contents
What is Wind Shear?
Wind shear is a sudden change in how fast the wind is blowing or which way it's going. This change happens over a very short distance. It can be a big deal for things like airplanes and even sailboats.
There are two main kinds of wind shear:
- Horizontal wind shear: This is when the wind changes speed or direction as you move from one side to another. Imagine walking across a field and feeling the wind suddenly get stronger or shift direction.
- Vertical wind shear: This is when the wind changes speed or direction as you move up or down through the air. For example, the wind might be gentle near the ground but much stronger higher up.
When Does Wind Shear Happen?
Wind shear can happen in several weather situations. It's often linked to strong weather systems or changes in the landscape.
Around Weather Fronts
Wind shear often occurs near weather fronts. These are places where two different air masses meet. If the temperature difference across the front is 5 °C (9 °F) or more, and the front is moving fast (15 knots or more), you can expect strong wind shear.
Near Low-Level Jets
A low-level jet is a fast-moving current of air that flows close to the ground, usually at night. Significant vertical wind shear can develop right near the bottom of these fast air currents.
Over Mountains
When winds blow over mountains, they can create strong wind shear. On the side of the mountain that the wind blows away from (called the lee side), the air can become very turbulent. This creates vertical shear.
During Temperature Inversions
An inversion happens on clear, calm nights. The air near the ground cools down a lot, becoming colder than the air above it. This creates a stable layer. Wind shear can form at the top of this cool layer, where the wind speed might suddenly increase.
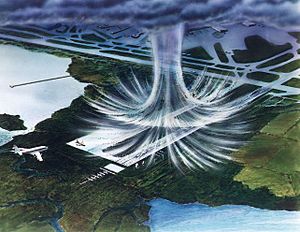
From Downbursts
Downbursts are strong downdrafts of air from thunderstorms. When this air hits the ground, it spreads out very quickly in all directions. This spreading air creates an "outflow boundary" that moves away from the storm. The edge of this boundary often has strong wind shear.
Impact on Sailing
Wind shear also affects sailboats. A sailboat's mast sticks up high into the air. Because of vertical wind shear, the wind at the top of the mast might be blowing at a different speed or from a different direction than the wind closer to the water. Sailors need to understand this to control their boats well.
How Wind Shear Affects Airplanes
Wind shear is very important for pilots. A sudden change in wind speed or direction can cause an airplane to suddenly gain or lose speed, or even drop or rise unexpectedly. This can be dangerous, especially during takeoff and landing. Pilots are trained to detect and react to wind shear to keep flights safe.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Down draft winds with associated virga allow these clouds in the eastern sky at civil twilight to mimic aurora borealis in the Mojave desert
-
Wreckage of Delta Air Lines Flight 191 tail section after a microburst slammed the aircraft into the ground. Another aircraft can be seen flying in the background past the crash scene.
-
Cirrus uncinus ice crystal plumes showing high level wind shear, with changes in wind speed and direction.
-
Strong wind shear in the high troposphere forms the anvil-shaped top of this mature cumulonimbus cloud, or thunderstorm.
-
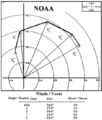
Hodograph plot of wind vectors at various heights in the troposphere. Meteorologists can use this plot to evaluate vertical wind shear in weather forecasting. (Source: NOAA)
See also
 In Spanish: Cizalladura para niños
In Spanish: Cizalladura para niños
 | Georgia Louise Harris Brown |
 | Julian Abele |
 | Norma Merrick Sklarek |
 | William Sidney Pittman |