Étienne François Geoffroy facts for kids
Étienne François Geoffroy (born February 13, 1672 – died January 6, 1731) was a French doctor and chemist. He is most famous for his "affinity tables" from 1718. These tables helped explain how different chemicals react with each other. Geoffroy first thought about becoming a pharmacist. But he later decided to become a doctor instead. People sometimes called him Geoffroy the Elder.
About Étienne François Geoffroy
Étienne François Geoffroy was born in Paris, France. He studied at the University of Montpellier. In 1698, he traveled to London with Marshal Tallard. After that, he visited the Netherlands and Italy.
When he returned to Paris, he became a professor. He taught chemistry at the Jardin du Roi. He also taught pharmacy and medicine at the Collège Royal. Later, he became the dean of the medical faculty. Geoffroy passed away in Paris on January 6, 1731.
His brother, Claude Joseph, was also a chemist. People called him Geoffroy the younger.
Geoffroy's Important Work
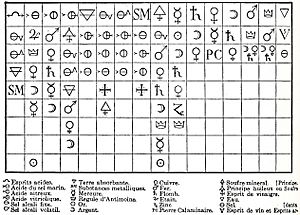
Geoffroy is best known for his "affinity tables." He presented these tables to the French Academy of Sciences in 1718 and 1720.
These tables were lists that showed how substances reacted with each other. They explained how different bodies had varying "affinities" for different reagents. This means they showed how strongly different chemicals wanted to combine. These tables were very popular for the rest of the 1700s. Later, new ideas from scientists like C. L. Berthollet replaced them.
Geoffroy also wrote a paper about the idea of the philosopher's stone. This was a mythical substance that people believed could turn metals into gold. Even though he wrote about this, Geoffroy still believed that iron could be made artificially when plants burned. His book, Tractatus de materia medico, was published after he died in 1741. It was well-known for a long time.
See also
- Chemical affinity
- Pharmacy
- Pharmacist
 | George Robert Carruthers |
 | Patricia Bath |
 | Jan Ernst Matzeliger |
 | Alexander Miles |