Quick facts for kids Earleaf acacia |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Acacia
|
| Species: |
auriculiformis
|
 |
|
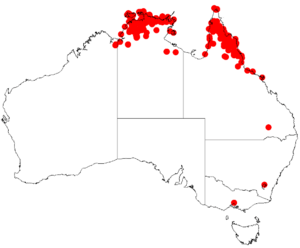
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
The Earleaf Acacia (scientific name: Acacia auriculiformis) is a type of tree that grows very quickly. It's also known by names like auri, earpod wattle, or northern black wattle. In Bengali, it's called akashmoni. This tree belongs to the Fabaceae family, which includes peas and beans.
You can find the Earleaf Acacia naturally in Australia, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea. It can grow quite tall, reaching up to 30 meters (about 98 feet). Each kilogram of its seeds contains around 47,000 tiny seeds!
Contents
What it Looks Like
The Earleaf Acacia is an evergreen tree, meaning it stays green all year. It usually grows between 15 to 30 meters tall. Its trunk can be up to 12 meters long and 50 centimeters wide. The trunk often looks a bit bent or "crooked," and its bark has vertical cracks. The tree's roots are shallow but spread out widely.
This tree has lots of leaves that form a wide, spreading top, called a crown. The leaves are thick, feel like leather, and are curved. They are about 10 to 16 centimeters long and 1.5 to 2.5 centimeters wide, with several parallel lines running through them.
The flowers are creamy yellow and smell sweet. They grow in pairs and are about 8 centimeters long. After flowering, the tree produces flat, leathery pods that are about 6.5 x 1.5 centimeters. At first, these pods are straight, but as they get older, they twist into irregular spirals. Inside the pods are broadly oval seeds, about 4 to 6 millimeters long. In some parts of India, birds like jungle crows and mynas eat these seeds, which helps spread them around.
The name Acacia comes from a Greek word meaning "point" or "barb." The second part of its name, auriculiformis, comes from Latin words meaning "external ear" and "form" or "shape." This refers to the unique shape of its pods, which look a bit like ears!
Here are some local names for the Earleaf Acacia:
- Telugu: Minnumaanu, Kondamanu, Seema Babul, Maha Babul
- Bengali: Akaashmoni
- Tamil: Kaththi Karuvel
- Thai: กระถินณรงค์
How People Use It
The Earleaf Acacia is a very useful tree. People plant it as an ornamental plant to make places look nice, or as a shade tree to provide cool spots. It's also grown on large plantations in places like Southeast Asia and Sudan to be used as fuelwood.
Its wood is good for many things, including making paper, furniture, and tools. The tree's bark contains a substance called tannin, which is used to treat animal hides to make leather. In India, the wood and charcoal from this tree are widely used for fuel. The tree also produces a sticky substance called gum, which is sold commercially, though it's not as useful as another type of gum called gum arabic.
In Thailand, people sometimes eat the small, fresh leaves of the Earleaf Acacia, often with chili sauce or papaya salad. Indigenous Australians have also used parts of the tree to make a medicine that helps with pain.
Scientists have found that extracts from the inner wood of the Earleaf Acacia can stop fungi that attack wood. Also, extracts from the tree have been shown to slow down the development of the melon fly, a type of insect that can harm crops.
Products from the Tree
- Fuel: This tree is a major source of firewood because its wood is dense and produces a lot of energy when burned. It also makes very good charcoal that glows well, produces little smoke, and doesn't spark.
- Paper: The wood is widely used to make paper pulp. Trees grown on plantations have shown great promise for making strong, unbleached paper and high-quality semi-chemical pulp.
- Timber: The wood has a yellow outer layer (sapwood) and a light brown to dark red inner layer (heartwood). It's strong, has a nice grain, and lasts a long time. It's excellent for making things like toys, chess pieces, and handicrafts. It's also used for furniture, tool handles, and even for construction if the trees are big enough.
- Tannin and Dye: The bark of the tree contains enough tannin (13-25%) to be used commercially. It also has a natural dye (6-14%) that's good for the soga-batik industry, which makes patterned fabrics. In Indonesia, this natural dye is used in the batik textile industry.
Benefits for the Environment
- Erosion Control: The Earleaf Acacia has a root system that spreads out widely and forms a dense mat. This makes it great for holding soil in place and stopping erosion, especially on land that's been damaged.
- Shade and Shelter: Its thick, dark-green leaves stay on the tree even during dry seasons, making it an excellent tree for providing shade. It's also planted to offer shelter on beaches and along coastlines.
- Land Reclamation: Because its roots stabilize the soil, and it grows quickly even in poor soil, it's popular for helping land recover after mining or other disturbances. It can grow in both very acidic and very alkaline soils.
- Soil Improvement: Plantations of Earleaf Acacia help improve the soil by adding organic matter, nitrogen, and potassium when its leaves fall. Its leaf-like structures (called phyllodes) also make a good, long-lasting mulch.
- Nitrogen Fixing: This tree can "fix" nitrogen from the air into the soil, which is a natural way to fertilize the ground. It does this with the help of tiny bacteria in its roots.
Pests and Diseases
Generally, the Earleaf Acacia doesn't suffer much from pests and diseases. However, in Indonesia, a rust fungus called Uromyces digitatus has slowed down its growth. In India, a fungus called Ganoderma lucidum has been reported to cause root rot. Also, a type of beetle called Sinoxylon spp. can damage young stems and branches, causing them to break. If the main stem is damaged, the tree might grow multiple tops instead of one tall trunk, which can make it less useful for timber.
Images for kids
-
Flowers and leaves in Kolkata, West Bengal, India.




