Gum arabic facts for kids
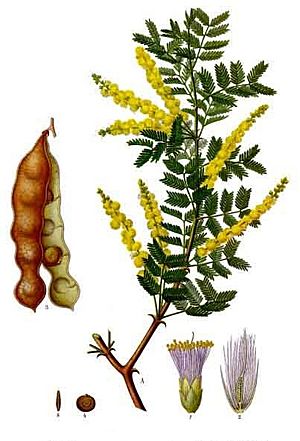
Gum arabic, also called acacia gum or meska, is a natural gum. It comes from the hardened sap of two types of acacia trees: Senegalia senegal and Vachellia seyal. This gum is collected from wild trees across the Sahel region in Africa, stretching from Senegal to Somalia. Long ago, it was also grown in Arabia and western Asia. Gum arabic is made of different natural substances, including sugars. In the past, important sugars like arabinose and ribose were first found and separated from it.
Contents
How Gum Arabic is Made
People have been collecting acacia gum in Arabia, Sudan, and western Asia for a very long time. Gum from sub-Saharan Africa has always been a valuable product to sell to other countries.
Traditionally, desert tribes who moved around a lot would collect the hardened gum during their travels. They usually start collecting it in July, which is the middle of the rainy season. Then, they export it in November, when the dry season begins.
From the 1950s to the early 1990s, Sudan produced about 80% of the world's gum arabic. Today, Sudan still produces the most, but it's less than 50% of the total. Hundreds of thousands of people in Sudan rely on gum arabic for their living. The Sudanese government closely controls how much gum arabic is produced.
What Gum Arabic is Used For
Gum arabic is a very useful natural product. It is used in many different ways, from food to art supplies.
In Food
In food, gum arabic is used as a stabilizer. This means it helps keep ingredients mixed together and prevents them from separating. It is safe to eat and has the E number E414. People in Arab countries use this natural gum to make a cold, sweet, and flavored dessert that is like gelato.
In Ink
Gum arabic has been a part of black ink since ancient times. The main part of this ink is carbon soot from lamps or burnt plants. Besides water and gum arabic, ancient Egyptian ink did not have many other ingredients. This ink, written on paper or papyrus, has lasted for over three thousand years.
Gum arabic is also a key ingredient in traditional lithography, which is a type of printing. It is used in making paints, glues, cosmetics, and other industrial products. For example, it helps control how thick inks are and is used in the textile industry. However, today, cheaper materials are often used instead of gum arabic for many of these purposes.
In Painting and Art

Gum arabic is used as a binder for watercolor painting. This is because it dissolves easily in water. Artists mix any color pigment with acacia gum to make watercolor paint. Water helps to thin the paint and move it onto a surface like paper.
When the water dries, the acacia gum holds the pigment firmly to the paper. After the water evaporates, the gum arabic in the paint makes the colors brighter. It also helps stop the colors from becoming lighter. Gum arabic allows artists to control their paint strokes more precisely. It also makes the water evaporate slower, giving artists a bit more time to work.
In Photography
In old photography methods, gum arabic was mixed with ammonium or potassium dichromate and pigment. This mixture created a colored photographic emulsion. When this emulsion was exposed to ultraviolet light, it became less soluble in water. In the final photo print, the acacia gum permanently binds the pigments onto the paper.
Images for kids
-
Gum arabic exuding from Acacia nilotica
See also
 In Spanish: Goma arábiga para niños
In Spanish: Goma arábiga para niños
 | Isaac Myers |
 | D. Hamilton Jackson |
 | A. Philip Randolph |