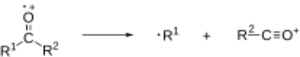Alpha cleavage facts for kids
Alpha cleavage (also called α-cleavage) is a special way that molecules can break apart in organic chemistry. It happens when a chemical bond breaks right next to a carbon atom that is connected to a special group of atoms called a functional group. Think of it like cutting a string right next to a knot!
Contents
What is Alpha Cleavage?
Alpha cleavage is when a carbon-carbon bond breaks. This bond is always next to a carbon atom that has a specific functional group attached to it. A functional group is like a special part of a molecule that gives it certain properties or makes it react in particular ways.
How Alpha Cleavage Helps Scientists?
Scientists use alpha cleavage to understand molecules, especially with a tool called mass spectrometry.
Finding Clues with Mass Spectrometry
In mass spectrometry, scientists shoot tiny particles at molecules to break them into smaller pieces. A machine then measures the size and weight of these pieces. This is like smashing a LEGO model and then weighing all the different bricks to figure out what the original model looked like.
When molecules break apart inside the mass spectrometer, alpha cleavage is one common way they split. By studying the sizes of the broken pieces, chemists can often guess the structure of the original molecule. Many different molecules break using alpha cleavage, and understanding this helps scientists make sense of the results they get from the mass spectrometer.
How Molecules Break Apart: The Process
Imagine a molecule where an electron is knocked off an atom. This creates a special kind of charged particle called a radical cation. Electrons are usually removed from certain places first:
- First, from "lone pair" electrons (electrons that aren't shared in a bond).
- Next, from "pi bond" electrons (found in double or triple bonds).
- Last, from "sigma bond" electrons (found in single bonds).
Once an electron is removed, things get interesting! One of the lone pair electrons can move to form a new bond with an electron from a nearby (alpha) bond. The other electron from that nearby bond then moves to a different atom, creating another radical. This process forms a double bond next to the atom that lost the lone pair electron (like oxygen), and it breaks (cleaves) the original bond that lost its two electrons.
Sometimes, in molecules that have a special group called a carbonyl group (a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom), alpha cleavage might happen at the same time as another type of breaking called a McLafferty rearrangement.
Alpha Cleavage in Light Reactions
In photochemistry, which is the study of how light affects chemical reactions, alpha cleavage also happens. Here, it means a bond breaks evenly, with each part of the broken bond getting one electron. This is called homolytic cleavage, and it happens close to a specific group in the molecule when light energy is involved.