Double bond facts for kids
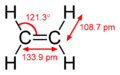
A double bond is a special connection between two atoms in chemistry. Instead of sharing two electrons, they share four! This makes the connection extra strong.
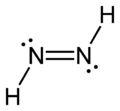
The most common type of double bond is between two carbon atoms. You can find these in molecules called alkenes. But double bonds can also form between different atoms. For example, a carbon atom and an oxygen atom can form a double bond in a group called a carbonyl. Other examples include nitrogen-nitrogen (N=N), carbon-nitrogen (C=N), and sulfur-oxygen (S=O) double bonds.
When chemists draw molecules, they use something called skeletal formula. A double bond is shown as two parallel lines (=) between the two atoms. It looks just like an equals sign!
What Makes Double Bonds Special?
Double bonds are stronger than single bonds. They are also shorter in length. Think of it like holding hands with two people instead of one – it's a tighter grip!
These bonds are also "electron-rich." This means they have lots of electrons ready to react. Because of this, molecules with double bonds are often more reactive. They like to join with other atoms or molecules.
The Two Parts of a Double Bond
A double bond isn't just one big connection. It's actually made of two different parts:
- Sigma bond (σ): This is the first and strongest part. It's like a direct handshake between the two atoms. The electrons are found right in the space between the atom centers.
- Pi bond (π): This is the second part. It's a bit different. The electrons in a pi bond are found in cloud-like areas above and below the main connection. It's like a high-five above and below the handshake.
Together, these two parts make up the strong and reactive double bond.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Enlace doble para niños
In Spanish: Enlace doble para niños