Antium facts for kids
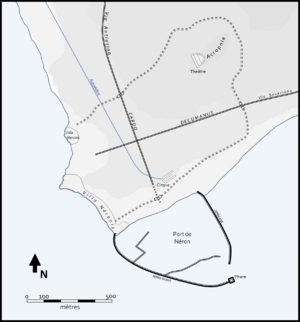
Plan of Antium
|
|
| Location | Anzio and Nettuno, Rome, Italy |
|---|---|
| Region | Lazio |
| Coordinates | 41°26′52.61″N 12°37′44.59″E / 41.4479472°N 12.6290528°E |
| Type | Settlement |
| History | |
| Founded | 11th century BC - beginning 1st millennium BC |
| Abandoned | Middle Ages |
| Cultures | Latial culture, Volsci, Ancient Rome |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Ruined |
| Ownership | Public |
| Public access | Yes |
Antium was an ancient town right on the coast in a region called Latium, south of Rome. It started as a fortified settlement built by people from the Latial culture around 1000 BC. Later, it became a very important city for the Volsci people. Eventually, the powerful Romans took control of it. Some old stories say that Antium was founded by Anteias, who was the son of the famous Greek hero Odysseus. Today, the area where ancient Antium once stood is covered by the modern towns of Anzio and Nettuno.
Contents
Where Was Antium?
The old town of Antium was located on a higher piece of land called Capo d'Anzio. This is where modern Anzio is today. The town was protected by a deep ditch and strong walls. Parts of these walls, made of large stone blocks, were found in 1897.
Antium didn't have a natural harbor. So, it used a nearby port town called Caenon. There are different ideas about exactly where Caenon was located.
Later, when the Romans took over, they built a large town and a big harbor in the Capo d'Anzio area. This was especially true during the time of Emperor Nero. Some historians think that another part of Antium, mainly for farming, might have been where modern Nettuno is now.
Antium's History
The Volsci People
For a long time, Antium was the main city for the Antiates Volsci, a group of people living on the coast.
In 493 BC, a Roman leader named Postumus Cominius Auruncus fought and defeated armies from Antium. He captured several Volscian towns nearby.
A famous Roman general, Coriolanus, was accused of being disloyal to Rome. He went to Antium and found safety with a Volscian noble named Attius Tullus Aufidius. Sadly, Coriolanus was later killed by the Volsci.
In 469 BC, the Roman consul Titus Numicius Priscus destroyed the port town of Caenon.
Just a year later, in 468 BC, the Romans captured Antium itself. The next year, Rome sent a group of its own citizens to live there. This was called a "Latin colony." Three former Roman consuls helped divide the land among these new settlers.
In 464 BC, the people of Antium were thought to be helping Rome's enemies, the Aequi. Roman officials called the leaders of Antium to Rome to explain. Antium was asked to send troops to help Rome fight the Aequi, but their 1,000 soldiers arrived too late.
In 338 BC, the Roman consul Gaius Menius Publius launched a surprise attack. He defeated the armies of several towns, including Antium, near the Astura river. Antium was finally defeated, and its warships were taken by the Romans. Some ships were brought to Rome, and others were burned. The town was forbidden from sailing ships. Gaius Menius took the front parts (called rostra) of the burned ships and used them to decorate the speaker's platform in the Roman Forum. This platform was then called the Rostra.
Roman Antium

After 338 BC, Antium became a Roman colony. Its citizens were given Roman citizenship.
During a civil war in 87 BC, Antium sided with the Roman general Sulla. As a result, it was attacked by the opposing army. Many citizens died, and the town was badly damaged.
As the Roman Republic grew, Antium became a popular place for wealthy Romans. It was far enough from Rome to be peaceful and quiet. Many rich Romans built amazing seaside villas there. You can still see the remains of these grand homes along the coast.
Many famous ancient sculptures were found in the ruins of these villas. These include the Fanciulla d'Anzio (a statue of a young girl), the Borghese Gladiator (now in the Louvre Museum), and the Apollo Belvedere (in the Vatican Museums). When the famous Roman speaker Cicero returned from being exiled, he brought his damaged book collection to Antium to keep it safe.
The most famous villa was the imperial villa, known as the Domus Neroniana (Villa of Nero). This huge villa stretched for about 800 meters along the coast. Many emperors used it, including Augustus. Both Emperor Caligula and Nero were born in Antium. Nero even tore down the old villa to build an even bigger and grander one. He also built a theater in Antium. In 60 AD, Nero started a new colony for retired soldiers and built a new harbor, which you can still see parts of today.
There was also a famous temple dedicated to the goddess Fortuna (Fortune) in Antium. Its exact location is not known, but it's believed to have been near the imperial villa.
Later Years
In the 5th and 6th centuries AD, Antium was attacked by groups like the Vandals and the Goths. Later, in the Middle Ages, it was also attacked by the Saracens. Because of these attacks, people left Antium. They moved to the nearby town of Nettuno, which then carried on the legacy of the ancient city.
Images for kids
-
A beautiful Mosaic from a nymphaeum (a type of water shrine) found in Antium.
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |