Apocynaceae facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Apocynaceae |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Vinca major | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: |
Apocynaceae
|
| Genera | |
|
See text. |
|
The Apocynaceae family, also known as the dogbane family, is a group of flowering plants. This family includes many different kinds of plants, such as trees, shrubs, herbs, and lianas (climbing vines). Most plants in this family have a milky sap. There are about 200 different groups of plants (called genera) and 2,000 different kinds (called species) in the Apocynaceae family.
Contents
What Makes Apocynaceae Plants Special?
How They Grow
The dogbane family has plants that grow in many ways. Some are annual plants, meaning they live for only one year. Others are perennial herbs, which means they grow back year after year. There are also stem succulents (plants with thick, fleshy stems), woody shrubs, trees, and vines that climb. If you cut or injure most of these plants, they will ooze a milky sap. This sap often contains a substance called latex.
Leaves and Stems
The leaves of these plants are usually simple, meaning each leaf is a single, undivided blade. Leaves can grow in different patterns. Sometimes, they appear one at a time on alternating sides of the stem. This is called an alternate arrangement. More often, leaves grow in pairs on opposite sides of the stem. They can also grow in groups of three or more, forming a circle around the stem. This is called a whorl. When leaves are paired, each pair often grows at a 90-degree angle to the pair below it.
Most plants in this family do not have stipules. Stipules are small, leaf-like parts found at the base of the leaf stem in some plants. If they are present in Apocynaceae, they are usually very small.
Flowers and Fruits
The flowers of the dogbane family are usually very colorful and noticeable. They have a round shape, meaning they look the same if you cut them in half in any direction. These flowers often grow in clusters called cymes or racemes. Sometimes, they grow in tight bundles or even by themselves.
Each flower has both male and female parts. They have five sepals, which are like small leaves that protect the bud. These sepals are joined together at the bottom. There are also five petals that are joined to form a tube. Inside the flower, there are four or five stamens, which are the male parts that make pollen. These stamens are attached to the petals.
The top part of the female organ, called the style, is often wide and thick just below the stigma. The ovary, which holds the seeds, is usually located above the other flower parts. It often has two parts that are joined at the top by a shared style and stigma.
The fruit of these plants can be different types. It might be a drupe, which is a fleshy fruit with a hard pit inside, like a peach. It could also be a berry, a capsule (a dry fruit that splits open), or a follicle (a dry fruit that splits along one side).
Images for kids
-
Alstonia scholaris, showing how leaves are arranged.
-
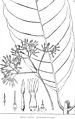
Rhigospira quadrangularis, part of a plant. 1) the flower cluster and 2) a flower, to scale; 3) flower petals in bud, showing their shape and 4) the same cut open when expanded, showing how they overlap and where the stamens are, both magnified; 5) the sepals, disk, very short style, and stigma, to scale; 6) the same, magnified; 7) a stamen, much magnified.
-
Asclepias syriaca dehiscent follicles (before unfurling of pappi)
-
Asclepias curassavica dehiscent follicles shedding seeds with unfurled pappi
-
Saba senegalensis unripe fruit
-
Saba senegalensis: dissection of ripe, edible fruit
See also
 In Spanish: Apocynaceae para niños
In Spanish: Apocynaceae para niños