Arena (web browser) facts for kids
 |
|
Arena on
|
|
| Original author(s) | Dave Raggett (1992–1994), Håkon Wium Lie, Henrik Frystyk Nielsen, Yves Lafon |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | CERN/W3C Yggdrasil Computing |
| Initial release | pre 1993 0.91 27 November 1995 |
| Last release |
0.3.62 / 25 November 1998
|
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | NeXT, Linux, Unix SunOS, Solaris, SGI, DEC, FreeBSD, X11(X) |
| Available in | English |
| Type | Web browser, HTML editor |
| License | W3C, some parts GPL |
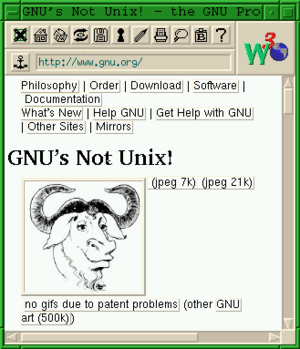
The Arena browser, also known as the Arena WWW Browser, was one of the very first web browsers made for Unix computers. It was started by Dave Raggett in 1993. Later, its development continued at CERN and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
Arena was super important because it helped test new web technologies. These included HTML version 3.0, Cascading Style Sheets (CSS), and Portable Network Graphics (PNG). It was quite popular in the early days of the World Wide Web.
Contents
What was the Arena Browser?
The Arena browser came out before well-known browsers like Netscape Navigator and Microsoft's Internet Explorer. It introduced many cool new features that later became common in other browsers.
Early Web Innovations
Arena was the first browser to support several key features. These included background images, which made web pages look much more interesting. It also supported tables, which helped organize information on a page. Another neat feature was text flowing around images, making pages easier to read. It even supported mathematical equations directly within the web page.
A Testing Ground for the Web
From 1994 to 1996, the Arena browser served as the main testbed browser for the W3C. A testbed is like a special lab where new ideas and technologies are tried out. This means Arena played a big role in shaping how the internet works today. After 1996, the Amaya project took over this important testing role.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Arena (navegador web) para niños
In Spanish: Arena (navegador web) para niños
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |