ABB facts for kids
 |
|
|
Trade name
|
ABB |
|---|---|
| Public | |
| Traded as | |
| Industry | Electrical equipment |
| Predecessors |
|
| Founded | 1988 |
| Headquarters | Zurich, Switzerland |
|
Area served
|
Worldwide |
|
Key people
|
|
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
| Owners |
|
|
Number of employees
|
c. 109,900 (2024) |
| Footnotes / references |
|
ABB Group is a large company from Sweden and Switzerland. It works with electrical engineering all over the world. Its main office is in Zurich, Switzerland. ABB is one of the world's largest companies. It has been listed on the Fortune Global 500 for many years.
ABB was created in 1988. Two older companies joined together: ASEA from Sweden and Brown, Boveri & Cie from Switzerland. Both companies started in the late 1800s. They became big makers of electrical equipment. ABB still works in this area today. Its main activities include making power, sending it out, and distributing it. It also works in industrial automation and robotics.
ABB has grown by buying many other companies. These companies were often in Europe, Asia, and North America. The company has faced some challenges over the years. For example, it had legal issues related to past business practices. In 2002, ABB had its first yearly loss. This was due to legal claims related to a company it had bought. But within three years, ABB successfully reorganized its business. In recent years, ABB has focused on robotics and industrial automation. Before selling its Power Grids part in 2020, ABB was Switzerland's largest industrial employer.
Contents
How ABB Started
The Companies Before ABB
Allmänna Svenska Elektriska Aktiebolaget (ASEA) was founded in 1883. It started in Västerås, Sweden. Ludvig Fredholm created it to make electric lights and generators.
Brown, Boveri & Cie (BBC) was formed in 1891. It was started in Zürich, Switzerland. Charles Eugene Lancelot Brown and Walter Boveri created it. BBC made AC and DC motors, generators, and transformers.
On August 10, 1987, ASEA and BBC announced they would merge. They would form ASEA Brown Boveri (ABB). The new company would have offices in Zurich, Switzerland, and Västerås, Sweden. Each original company would own 50 percent. This merger created a huge industrial group. It had about $15 billion in revenue and 160,000 employees.
When ABB started on January 5, 1988, its main work included:
- Making, sending, and distributing power.
- Electric transportation.
- Industrial automation and robotics.
In its first year, ABB bought about 15 companies. In 1989, ABB bought 40 more companies. This included parts of Westinghouse Electric. It also agreed to buy Combustion Engineering.
ABB in the 1990s
In 1990, ABB bought the robotics business of Cincinnati Milacron in the US. This helped ABB work more with the American car industry. In 1991, ABB introduced the IRB 6000 robot. This robot was modular, meaning it could be changed for different tasks. It was also very fast and accurate for spot-welding.
In the early 1990s, ABB started to grow in Central and Eastern Europe. By the end of 1991, it had 10,000 employees there. The next year, that number doubled. ABB also grew in Asia. By 1994, ABB had 30,000 employees and 100 locations across Asia.
In 1995, ABB merged its rail engineering unit with Daimler-Benz of Germany. This created Adtranz, the world's largest maker of trains.
In 1999, ABB bought Elsag Bailey Process Automation. This company made industrial control systems. This helped ABB grow in high-tech robotics and factory control. It made ABB less reliant on heavy engineering.
Also in 1999, ABB sold its part of the Adtranz train-building business. ABB's work in transportation then focused on motors and electric parts. ABB also merged its power generation business with Alstom. This created ABB Alstom Power.
ABB in the 2000s

In 2000, ABB sold its parts of ABB Alstom Power. It also sold its boiler and fossil-fuel operations. After this, ABB's power business focused on renewable energy and power distribution.
In 2002, ABB announced its first yearly loss. This was due to legal costs related to a company it had bought earlier. ABB worked to fix its financial problems. By 2006, it had settled these legal issues.
In 2004, ABB sold its oil and gas business, ABB Vetco Gray. But ABB still worked in the oil and gas industry with its automation and power technology. In 2007, ABB sold another oil and gas business, ABB Lummus Global.
In 2008, ABB bought Kuhlman Electric Corporation. This US company made transformers. ABB also bought Ber-Mac Electrical and Instrumentation. This helped ABB grow in Canada's oil and gas industries.
ABB in the 2010s

In 2010, ABB bought K-TEK, a company that made measurement tools. ABB also received a grant from the US government. This was to develop magnets that store energy.
In 2011, ABB invested in ECOtality. This company developed charging stations for electric vehicles. ABB also bought Epyon B.V., a leader in EV charging in Europe.
In early 2011, ABB bought Baldor Electric. This helped ABB grow in the North American industrial motors market. In 2012, ABB bought Thomas & Betts. This company made low voltage products. ABB also bought Tropos, which specialized in wireless technology.
In 2013, ABB bought Power-One. This made ABB a top maker of solar inverters. That same year, Fastned chose ABB to supply over 200 fast-charging stations in the Netherlands.
In 2016, ABB won a contract for the TANAP gas pipeline project in Turkey. ABB provided the communication, security, and control systems for the pipeline.
In 2017, ABB bought Bernecker + Rainer Industrie-Elektronik (B&R). This company was a big provider of industrial automation software.
In 2018, ABB became the main partner of the ABB FIA Formula E Championship. This is the world's first fully electric car racing series. In 2018, ABB also bought GE Industrial Solutions. This was General Electric's global electrification business.
In December 2018, ABB agreed to sell most of its Power Grids business to Hitachi. This part of ABB became part of the Hitachi Group. It was later renamed Hitachi Energy. Hitachi acquired the rest of the business in December 2022.
ABB in the 2020s
In March 2020, ABB agreed to sell its solar inverter business to Fimer. This included factories and employees in Finland, Italy, and India.
In 2021, ABB announced it was helping build the first permanent electric road. This road powers cars, trucks, and buses.
In December 2022, ABB opened a new robotics factory in Shanghai. This was a $150 million investment.
In June 2023, ABB agreed to buy Eve Systems. This company makes smart home automation products.
In September 2023, ABB announced a partnership with the Well Done Foundation. They will monitor methane and greenhouse gas emissions from old, unused oil and gas wells in the US.
In January 2024, ABB bought Real Tech. This Canadian company makes optical sensor technology for water monitoring. It also acquired Meshmind, an engineering firm, to improve its AI and software skills.
In May 2024, ABB agreed to buy the wiring accessories business of Siemens in China. This deal gives ABB access to a large distribution network in China.
As of 2025, ABB plans to rename its residential electrical products from GE to the ABB ReliaHome brand.
What ABB Makes
New Products and Ideas
In 1990, ABB launched Azipod. This is an electric system that helps large ships move and steer. It helps ships save fuel and makes them easier to control.
In 1998, ABB launched the FlexPicker. This robot has three arms. It is great for picking and packing items in factories.
In 2000, ABB created the world's first system for ships to get electricity from shore. This was at the port of Gothenburg, Sweden. It lets ships turn off their engines in port. This reduces noise and pollution.
In 2004, ABB launched its Extended Automation System 800xA. This is an industrial system for factories. Today, ABB is a global leader in these control systems.
In 2013, ABB Sécheron SA worked on a new charging system for trolleybuses in Geneva. This system charges buses at stops using overhead devices.
In 2014, ABB showed YuMi. This is a robot with two arms that can work safely next to people. It helps with assembly tasks in factories.
In 2018, ABB showed the Terra High Power charger for electric vehicles. It can charge an electric car enough to travel 200 kilometers in just eight minutes.
Electrification
ABB's Electrification business makes products and services for electricity. This includes everything from power stations to home outlets. Their customers are industries, power companies, and buildings. This business is growing fast in areas like:
- Renewable energy.
- Electric vehicle charging.
- Data centers.
- Smart buildings.
Their products include:
- Electric vehicle chargers.
- Modular substations.
- Distribution automation.
- Products to protect people and equipment from too much electricity.
- Measuring devices, control products, and wiring accessories.
This business also offers KNX systems. These systems connect and automate a building's electrical systems, ventilation, and security. The purchase of GE Industrial Solutions in 2018 made ABB even stronger in electrification.
Motion
ABB's Motion business makes electric motors, generators, and drives. It also offers digital solutions. Motion is the top company in this market worldwide. In September 2023, ABB Motion bought a small part of WindESCo. This company makes software to analyze wind turbines.
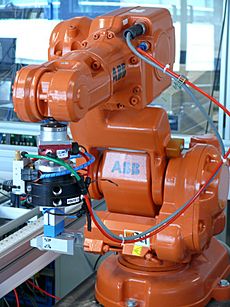
Robotics and Automation
ABB's Robotics & Discrete Automation business combines factory automation systems from B&R with its robots. ABB bought B&R in 2017.
ABB has installed over 300,000 robots around the world. This business helps create the "factory of the future." It provides services for flexible manufacturing and smart machines.
ABB is the second largest company globally in this area. It is number one in robotics in China. ABB is growing its robot making and innovation in Shanghai.
Process Automation
The Process Automation business helps different industries. It offers:
- Integrated automation.
- Electrification and digital services.
- Control technologies.
- Software and advanced services.
- Measurement and analytics tools.
- Marine and turbocharging products.
Former Parts of ABB
Power Grids
The Power Grids business made parts for sending and distributing electricity. This included:
- Transformers.
- Switchgear.
- Circuit breakers.
- High voltage equipment.
It also offered maintenance services. A key part of Power Grids was providing complete systems for power grids and power plants. This included electrical substations and automation systems.
In 2018, ABB and Hitachi announced that Hitachi would take over ABB's Power Grids division. Hitachi officially bought most of the business in July 2020. It was first called Hitachi ABB Power Grids. Then it was renamed Hitachi Energy in October 2021. Hitachi bought the rest of the company from ABB in 2022.
In July 2021, ABB sold its mechanical power transmission business, Dodge, to RBC Bearings Incorporated.
Train Manufacturing

ABB Group started making trains in 1989. It bought a part of British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL). ABB took over two train factories in the UK.
The first trains made under ABB were for Glasgow's railways in 1990. ABB also made trains for the Stansted Express service. Between 1990 and 1994, ABB made many trains for services around London and Kent. It also built diesel trains for other routes.
ABB also made trains for the Waterloo & City line in London. In 1995, ABB made freight trains for the Royal Mail. ABB also worked with Brush Traction to build electric locomotives for the Channel Tunnel.
ABB closed its York factory in 1996. All train manufacturing moved to the Derby factory. This factory became part of Adtranz, a joint company with DaimlerChrysler.
In 1997, Adtranz showed the Class 168 train. This design later became the successful Turbostar and Electrostar trains. In 1999, ABB sold its part of Adtranz to Daimler. This meant ABB stopped making complete trains. Daimler then sold Adtranz to Bombardier Transportation.
Old Brands Now Part of ABB
Bailey Controls
Ervin G. Bailey founded Bailey Controls in 1916. It made the first steam boiler meter. It became a leader in controlling automated processes. In 1989, it merged with Elsag Group. ABB bought Elsag Bailey Process Automation in 1999.
Fischer & Porter
The Fischer & Porter Company started in 1937. It was a leader in measuring flow in pipes. It also made devices to measure pressure, temperature, and other things. In 1994, Elsag Bailey Process Automation bought Fischer & Porter. ABB then bought Elsag Bailey in 1999.
Leadership
In September 2013, Ulrich Spiesshofer became ABB's CEO.
In August 2019, ABB announced that Björn Rosengren would become CEO in March 2020. Before that, he was CEO of Sandvik. In the meantime, ABB Chairman Peter Voser was the interim CEO from April 2019. He took over from Ulrich Spiesshofer. Peter Voser became chairman in April 2015.
Who Owns ABB
The largest owner of ABB is the Swedish investment company Investor AB. This company is controlled by the Wallenberg family. They own 12.9% of ABB. Another large owner is Cevian.
See also
 In Spanish: ABB para niños
In Spanish: ABB para niños
- GREEN Cell Shipping
- Legrand
- Strömberg
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |