Hitachi facts for kids
Hitachi logo used since 2025
|
|

Headquarters in Marunouchi, Chiyoda, Tokyo
|
|
|
Native name
|
株式会社日立製作所
|
|---|---|
|
Romanized name
|
Kabushikigaisha Hitachi Seisaku-sho lit. "Share Company Hitachi Manufacturing Plant" |
| Public | |
| Traded as | |
| Industry | Conglomerate |
| Founded | 1910 Hitachi, Ibaraki, Japan |
| Founder | Namihei Odaira |
| Headquarters |
Marunouchi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo
,
Japan
|
|
Area served
|
Worldwide |
|
Key people
|
Toshiaki Higashihara (Director Executive Chairman Representative Executive Officer) Toshiaki Tokunaga(Representative Executive Officer, President & CEO) |
| Products |
|
| Services |
Former
|
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
|
Number of employees
|
268,655 (as of June 2024) |
Hitachi, Ltd. (Japanese pronunciation: [çi̥taꜜtɕi]) is a big Japanese company. It was started in 1910 and has its main office in Chiyoda, Tokyo. Hitachi makes many different things. These include digital systems, power and renewable energy solutions, and railway systems. They also make healthcare products and financial systems.
The company began as a small part of the Kuhara Mining Plant in Hitachi, Ibaraki. An engineer named Namihei Odaira founded it in 1910. It became its own company in 1920 and was named Hitachi. Hitachi is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. It is one of the biggest companies in Japan. In June 2024, it was the fourth largest Japanese company by market value. Hitachi also does business all over the world. In 2023, about 61% of its money came from other countries.
Contents
What Hitachi Does
Hitachi's main goal is to help society. They do this by creating new and better technology and products. All 12 of the company's leaders, including the founder Namihei Odaira, were engineers.
Hitachi used to make many different products. These included electric generators, consumer electronics, trains, semiconductors, computers, and nuclear reactors. After a big financial crisis in 2008, Hitachi lost a lot of money. The company then sold many parts of its business that were not making money. They started focusing on new areas like digital systems and clean energy. Because of these changes, Hitachi started making a profit again by 2011.
Today, Hitachi's work is split into three main parts. These are Digital Systems and Services, Green Energy and Mobility, and Connective Industries.
Hitachi's Logos and Symbols

Hitachi uses a special symbol made from two Japanese characters. These characters mean 'sun' (日) and 'rise' (立). The founder, Namihei Odaira, created this symbol. It was on most Hitachi products until 1991. In 2000, Hitachi started using the slogan 'Inspire the Next'. The old symbol is still used to represent the company itself.
Since 1975, Hitachi has used pictures of a large, old tree in Hawaii. This tree is called the Hitachi Tree. It is shown in many of their TV commercials. The song played with the tree in the adverts is also famous. Hitachi spends about 50 million yen each year to take care of this special tree.
Hitachi's History
How Hitachi Started (1910–1945)

Hitachi was founded in 1910 by Namihei Odaira. Its first product was a small electric motor. This motor was used for copper mining. Hitachi became an independent company in 1911. Its main office moved to Tokyo in 1918. The name 'Hitachi' means 'sun rise'. Odaira chose this name. He used water power to run his factories. This was new because most factories used steam power back then. Hitachi later made many other electrical items. In 1924, they built Japan's first main electric train. In 1932, Hitachi started making elevators and electric refrigerators.
Growing After the War (1945–1990)
World War II caused problems for Hitachi. Many factories were destroyed. The company's founder, Namihei Odaira, was removed from his position for a time. Hitachi became a public company in 1949. This meant people could buy shares in it on the Tokyo Stock Exchange. Odaira returned to the company in 1951 but passed away later that year.
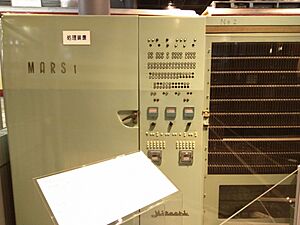
In 1949, Hitachi built its first power shovel. This was the start of Hitachi Construction Machinery. In 1960, Hitachi created the world's first electric train seat booking system. It was called MARS-1. This system allowed people to book train seats across the country. Around this time, Hitachi also started doing business overseas. Hitachi America, Ltd. was set up in 1959. In 1961, Hitachi began selling washing machines that could do everything by themselves. They also finished their first test nuclear reactor.
In 1964, the first high-speed train line, the Shinkansen, opened in Japan. Hitachi helped build the trains for this line. They also helped create the special system that controls the trains automatically. This system made sure trains ran safely and on time. In 1977, Hitachi finished the world's first nuclear power station that used special MOX fuel.
In 1978, Hitachi made a big step in the semiconductor industry. They developed a new type of computer chip that used much less power. This helped Japanese companies become leaders in making computer chips by 1987. Hitachi Europe, Ltd. was started in 1982.
The 2000s

In 2001, a special card system called Suica was launched in Tokyo. This card lets people pay for train fares by just tapping it. Hitachi built the computer system behind this card. Other similar cards were later made across Japan, and Hitachi helped with these too. These cards are now used for many other payments, not just trains. In 2007, Hitachi showed the first computer hard drive that could store 1 terabyte of data.
In 2008, Hitachi lost a lot of money. This was the biggest loss for a Japanese company at that time. Hitachi was a very large company, and it was hard to make big changes. This made it difficult to deal with the financial crisis. Because of this, Hitachi decided to change its business. They sold many parts of the company. From 2008 to 2018, Hitachi greatly reduced the number of companies it owned. Hitachi plans to focus on IT and maintaining big systems in the future.
The 2010s
In 2011, Hitachi agreed to sell its hard disk drive business to Western Digital. Some parts of this business were later sold to Toshiba. In 2012, Hitachi stopped making televisions in Japan. They also announced a new way to store data using quartz glass. This method could keep information safe for millions of years. In October 2012, Hitachi bought a nuclear energy company in the UK called Horizon Nuclear Power.
In 2014, Hitachi and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries combined their power generation businesses. In 2015, Hitachi joined with Johnson Controls to make air conditioning systems. Hitachi also invested a lot of money in IoT technology in 2016. Hitachi's train business grew in Europe, especially in the UK. A new factory opened in Newton Aycliffe in 2015.
In 2017, Hitachi and Honda started working together to make motors for electric cars. Hitachi also sold its power tools business, which was renamed HiKOKI. In 2018, Hitachi stopped selling televisions in Japan. In December 2018, Hitachi bought most of ABB's power grid business. This new company was first called Hitachi-ABB Power Grids. In 2019, Hitachi sold its medical imaging business to Fujifilm. Hitachi also stopped its plans to build new nuclear power plants in the UK. In October 2019, Honda and Hitachi started talks to combine their car parts businesses. This led to a new company called Hitachi Astemo in 2021.
The 2020s

In March 2020, Hitachi made the first magnetically levitated train for the Chuo Shinkansen line. In September 2020, Hitachi stopped plans for nuclear power plants in the UK due to funding issues. Hitachi Capital, the company's financial business, was bought by Mitsubishi UFJ Lease. In November 2020, Hitachi announced plans to separate Hitachi Metals and Hitachi Construction Machinery from the main group. In December 2020, Hitachi sold most of its home appliance business outside Japan to Arcelik. In December 2021, GE-Hitachi was chosen to build new small nuclear reactors in Canada.
Hitachi has become much more profitable since 2009. This is because it now focuses on energy, information technology, and big infrastructure projects. In July 2024, Bosch announced it would buy the Johnson Controls–Hitachi Air Conditioning business. This deal includes many factories and engineering centers around the world. Bosch will continue to sell products under the Hitachi brand in Asia.
Hitachi's Businesses Today
Hitachi's work is divided into three main areas: Digital Systems and Services, Green Energy and Mobility, and Connective Industries.
Digital Systems and Services
This part of Hitachi helps businesses use digital tools. They use a system called Lumada to improve how companies work. This section made up about 21.9% of Hitachi's total money in 2022.
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Hitachi Lumada
- Data storage and analytics
- Software
- Outsourcing services
- Telecommunications equipment
- ATMs
Hitachi Vantara
Hitachi Vantara is a Hitachi company that helps other companies manage their digital data. They offer hardware, software, and services. Their main products help store and manage large amounts of data. In 2017, Hitachi Data Systems became part of Hitachi Vantara. Hitachi Consulting also joined Hitachi Vantara in 2019. In November 2023, Hitachi Vantara's digital solutions business became a new company, Hitachi Digital Services. Hitachi Vantara now focuses on data storage and cloud services.
- Servers
- Disk array systems
GlobalLogic
GlobalLogic is a Hitachi company based in the United States. It was bought by Hitachi in 2021. This was Hitachi's most expensive purchase at the time. GlobalLogic helps Hitachi improve its software development. They provide services to other companies for making software and hardware.
Green Energy and Mobility
This part of Hitachi focuses on power systems. This includes making electricity, sending it out, and distributing it. In the train industry, Hitachi makes rolling stock (the trains themselves). They also make systems for controlling trains and maintaining train depots. This section made up about 22.9% of Hitachi's total money in 2022.
Hitachi Rail
Hitachi built its first steam train in 1920. Since then, it has grown to build almost everything for trains. This includes the trains, power systems, signaling, and seat booking systems. Hitachi's train business has main offices in Japan and London, England. They also have a factory in Newton Aycliffe, UK.
Hitachi Energy
In July 2020, Hitachi bought most of ABB’s power grid business. In December 2022, they bought the rest. This company, now called Hitachi Energy, is a big supplier of high-voltage power systems.
Nuclear Power
Hitachi has been involved in nuclear power since the 1950s. They have built and maintained nuclear reactors since the 1970s. In 2007, Hitachi's nuclear business joined with General Electric. This new company, GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy, builds advanced reactors. They are also developing smaller, newer reactors. Hitachi also owns Horizon Nuclear Power, which had planned to build nuclear power stations in the UK.
Connective Industries

This part of Hitachi makes building systems like elevators and escalators. They also work in healthcare, focusing on cancer treatments and medical equipment. They make industrial equipment like air compressors and transformers. This segment also helps with water management. This section made up about 27.3% of Hitachi's total money in 2022.
Hitachi Global Life Solutions
This company makes home appliances. These include refrigerators, washing machines, and vacuum cleaners. Hitachi stopped making televisions in 2012.
- Air conditioning systems (now with Johnson Controls Hitachi)
- Refrigerators
- Washing machines and washer-dryers
- Vacuum cleaners
Hitachi Building Systems
Hitachi Building Systems is one of the biggest makers of elevators in Japan.
- Elevators
- Escalators
- Building security systems
- Air conditioning systems for buildings
Hitachi High-Tech
This company makes special equipment for testing and measuring. They also make electron microscopes. These microscopes help scientists see very tiny things. They also make equipment for treating cancer and for cell research.
- Test and measurement equipment
- Electron microscopes
- Particle therapy equipment
- Cell culture equipment
Hitachi's Other Companies
Hitachi Astemo

Hitachi Astemo makes advanced parts for cars and other vehicles. It is a joint company between Hitachi, Honda, and JIC Capital. Hitachi and Honda combined their car parts businesses to create this company. They want to make new technology and software for cars. Hitachi Astemo is a very large supplier of car parts.
- Car Information Systems
- Drive Control
- Electric Powertrain Systems
- Engine Management Systems
Hitachi Construction Machinery
Hitachi Construction Machinery is one of the world's largest makers of construction equipment. This company became separate from Hitachi in 1970. Hitachi sold some of its shares in this company in 2022.
- Hydraulic Excavators
- Forestry Equipment
- Cranes
- Mining Dump Trucks
- Wheel Loaders
Past Businesses
Hitachi has sold or stopped many other businesses over the years. These include:
- Hitachi Capital: This was Hitachi's financial business. It was bought by Mitsubishi UFJ Lease.
- Hitachi Metals: This company made special materials for things like aircraft engines and car parts. Hitachi sold all its shares in this company in 2021.
- Hitachi Works: Parts of this business were transferred to Mitsubishi Power.
- Televisions: Hitachi stopped making plasma and LCD televisions.
- Memory chips: This business was spun off into Elpida Memory.
- Personal computers: Hitachi stopped making these.
- Mobile phones: This business was combined with other companies.
- Hard disk drives: This business was sold to Western Digital.
- Power tools: This business was sold and renamed HiKOKI.
- Car navigation systems: This business was sold to Faurecia.
- Chemical products: This business was sold to Showa Denko.
- Medical diagnostic equipment: This business was sold to Fujifilm.
- Thermal power generation systems: Hitachi transferred its shares to Mitsubishi.
- Hitachi Transport System, Ltd.: This company was sold to KKR.
Learning and Research
Hitachi works with several universities to do research. They fund research centers at places like the University of Tokyo and the University of Cambridge. These centers study things like how to make society more efficient using data. They also research quantum computation and magnetism. Hitachi also has similar projects with other universities in Japan.
See also
 In Spanish: Hitachi para niños
In Spanish: Hitachi para niños
- ATM Industry Association (ATMIA)
 | Claudette Colvin |
 | Myrlie Evers-Williams |
 | Alberta Odell Jones |