Atlantic Coast leopard frog facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Atlantic Coast leopard frog |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification | |
 |
|
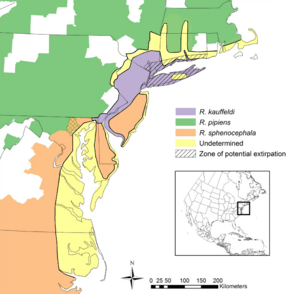
| Known (purple) and potential (yellow) range of L. kauffeldi | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Rana kauffeldi Feinberg et al., 2014 |
The Atlantic Coast leopard frog (scientific name: Lithobates kauffeldi) is a type of frog found only in the United States. It's a "true frog," which means it has smooth skin and a slim body. This frog lives along the Eastern Seaboard, from Connecticut down to North Carolina. It gets its name from the spots on its legs and back, which look a lot like a leopard's pattern!
This frog is one of several kinds of leopard frogs. Scientists figured out it was a unique species because of its special mating call, its genes, where it lives, and how it looks.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The Atlantic Coast leopard frog is named kauffeldi after a scientist named Carl Frederick Kauffeld. In 1936, he thought there might be a third type of leopard frog living in the New York Tri-State Area, especially on Staten Island. The scientists who officially described this frog in 2014 named it after him to honor his early ideas.
Where Do They Live?
You can find the Atlantic Coast leopard frog along the northeastern coast of the United States. Its home stretches from central Connecticut all the way to northeastern North Carolina. This area is about 780 kilometers (485 miles) long. It's also about 100 kilometers (60 miles) wide, reaching from the Atlantic Ocean inland.
As you go south, the area where they live gets narrower. Scientists believe these frogs live in ten different states. However, they are still learning the exact places where all these frogs can be found.
For a long time, this frog was hard to find. It looks very similar to the northern leopard frog and the southern leopard frog. It also lives in similar places. This made it tricky for scientists to tell them apart!
What Do They Look Like?
These frogs can be different colors, from a mint-gray to a light olive green. They also have brown spots scattered all over their backs and legs. You might notice dark lines running along their snouts. They have big eyes and strong legs, which are great for leaping!
Their color can even change! They might look darker at night and lighter during the day. Their colors can also change with the seasons.
Male frogs have large sacs on the sides of their heads. They use these to make a special mating call. This call is a single, clear "chuck" sound. It's different from the "ak-ak-ak" sound that other related frogs make.
How Do They Breed?
Atlantic Coast leopard frogs breed around the same time as other leopard frog species. They start moving to their breeding spots in February and March. When the weather gets warmer in March and April, the male frogs begin to call out at night. Sometimes, they even call during the day.
They float in shallow water in groups of five or more. They call to attract females. Their calls don't travel very far, which might be why they gather in dense groups.
Breeding continues through the spring and early summer. It's busiest for about 2-3 weeks in late March and early April in New York. The female frogs lay their eggs in clusters.
Where Do They Hang Out?
L. kauffeldi frogs like to live in large wetland areas. This includes places like marshes, wet meadows, or slow-moving water. They prefer clear, shallow water. You'll often find them in or near open areas with lots of plants. They like plants such as cattails, reeds, or river shrubs.

