Belgian Congo facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Belgian Congo
Congo belge (French)
Belgisch-Kongo (Dutch) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1908–1960 | |||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
Motto: Travail et Progrès
(“Work and Progress”) |
|||||||||
|
Anthem: National=The Brabançonne
|
|||||||||
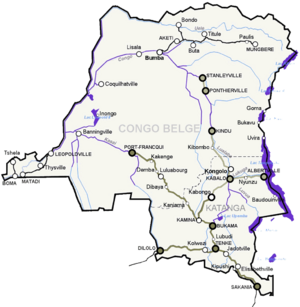
The Belgian Congo
|
|||||||||
| Status | Belgian colony | ||||||||
| Capital | Léopoldville/Leopoldstad | ||||||||
| Common languages | French (de facto official) Dutch (majority of whites) more than 200 indigenous languages |
||||||||
| King of the Belgians | |||||||||
|
• 1908–09
|
Léopold II | ||||||||
|
• 1909–34
|
Albert I | ||||||||
|
• 1934–51
|
Léopold III | ||||||||
| Governor-general | |||||||||
|
• 1908–10
|
Théophile Wahis | ||||||||
|
• 1946–51
|
Eugène Jungers | ||||||||
|
• 1958–60
|
Henri Cornelis | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
|
• Established
|
15 November 1908 | ||||||||
|
• Independence
|
30 June 1960 | ||||||||
|
• Secessions¹
|
July–August 1960 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1960 | 2,344,858 km2 (905,355 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
|
• 1960
|
16610000 | ||||||||
| Currency | Congolese franc | ||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | CG | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
|
¹ Secession of Katanga on 11 July and South Kasai on 8 August 1960
|
|||||||||
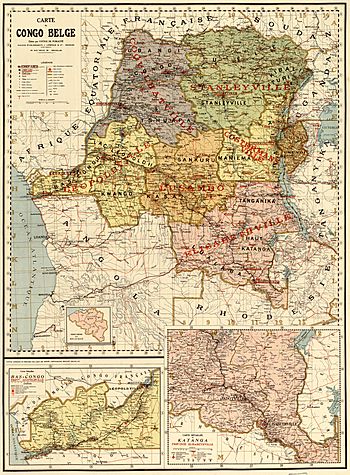
The Belgian Congo was a large country in central Africa. It was a colony of Belgium from 1908 to 1960. Before 1908, this land was the Congo Free State. This was a private kingdom owned by King Léopold II of Belgium. After 1908, the Belgian government took control. The Belgian Congo became independent on June 30, 1960. Today, it is known as the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Contents
How Did the Belgian Congo Start?
From Private Land to Colony
Before 1908, the land was called the Congo Free State. It was not a colony of Belgium. Instead, it was the personal property of King Léopold II. He ruled it from 1885 to 1908. During this time, there were many reports of harsh treatment of the local people. Because of these reports, the Belgian government decided to take over.
On November 15, 1908, the Belgian government officially took control. This changed the Congo Free State into the Belgian Congo. It became a regular colony, managed by the Belgian government.
Life in the Belgian Congo
Who Ruled the Colony?
The Belgian Congo was ruled by a Governor-General. This person was chosen by the King of the Belgians. The capital city was Léopoldville (now Kinshasa). The colony had its own laws and a system of administration.
What Was Life Like for People?
Life in the Belgian Congo was very different for Europeans and Africans. Europeans, mostly Belgians, held all the power. They worked in government, mining, and trade. Africans were mostly farmers or worked in mines and plantations.
The Belgian government focused on making money from the Congo's rich natural resources. These included rubber, copper, and later, uranium.
Education and Health
Missionaries played a big role in education and healthcare. They set up schools and hospitals. However, education for Africans was often basic. It focused on practical skills rather than higher learning.
Building Infrastructure
The Belgians built many roads, railways, and ports. These were mainly to help transport resources out of the country. For example, the Congo River was important for moving goods.
The Congo During World Wars
World War I (1914-1918)
During World War I, the Belgian Congo was involved in fighting. Its army, called the Force Publique, fought against German forces in East Africa. They won some important battles.
World War II (1939-1945)
The Congo was very important during World War II. It supplied a lot of raw materials to the Allies. This included rubber, tin, and copper. Most importantly, the Congo provided uranium for the Manhattan Project. This was the secret project that developed the first atomic bombs. The uranium came from the Shinkolobwe mine.
Road to Independence
Growing Calls for Freedom
After World War II, many African countries started to seek independence. The people of the Belgian Congo also began to demand more rights and self-rule. Political parties started to form.
Independence Day
On June 30, 1960, the Belgian Congo became an independent country. It was renamed the Republic of the Congo. Patrice Lumumba became its first Prime Minister. This was a very important day for the Congolese people.
Images for kids
-
Leopold II, King of the Belgians and de facto owner of the Congo Free State from 1885 to 1908
-
Ruandan migrant workers at the Kisanga mine in Katanga, ca. 1920
-
King Albert I and Queen Elisabeth inspecting the military camp of Léopoldville during their visit to the Belgian Congo, 1928
-
Equestrian statue of Leopold II in Kinshasa
See also
 In Spanish: Congo Belga para niños
In Spanish: Congo Belga para niños
 | George Robert Carruthers |
 | Patricia Bath |
 | Jan Ernst Matzeliger |
 | Alexander Miles |