Big Lava Bed facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Big Lava Bed |
|
|---|---|

The forested slope in the foreground is part of the Big Lava Bed, a 0.9 cu km lava flow erupted from the cinder cone in the background about 8200 years ago. The lava flow traveled 13 km from the source crater and is the youngest feature of the Indian Heaven volcanic field.
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 4,195 feet (1,279 m) |
| Geography | |
| Location | Skamania County, Washington, U.S. |
| Parent range | Cascade Range |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | 6250 BC ± 100 years, in the late Pleistocene to Holocene |
| Mountain type | Fissure vent, Cinder cone, Explosive eruption, and lava field |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Indian Heaven |
| Last eruption | 8200 years ago |
The Big Lava Bed is a huge area of hardened lava. You can find it in the Gifford Pinchot National Forest in Washington State. It started from a deep crater in its northern part.
It's the newest part of the Indian Heaven volcanic field. About 8,200 years ago, a huge amount of lava burst out. This lava flow was about 0.9 cubic kilometers. It traveled 13 kilometers (about 8 miles) from its starting point.
Contents
What is the Big Lava Bed?
The Big Lava Bed is a large area covered by lava that erupted long ago. It's like a giant, rocky puzzle. This area is part of a bigger group of volcanoes called the Indian Heaven volcanic field. The lava flow came from a cinder cone, which is a type of small, steep volcano.
How Old is the Big Lava Bed?
The lava flow that created the Big Lava Bed is quite old. It happened about 8,200 years ago. This was during a time geologists call the late Pleistocene to Holocene periods. It's the most recent eruption in the Indian Heaven area.
Exploring the Lava Bed
Walking through the Big Lava Bed can be very challenging. There are no easy paths or roads. You will find towering piles of rock, hidden caves, and strange lava shapes. It's a wild and rugged place.
Plants That Grow Here
Even though it's a tough environment, some plants manage to grow. You might see Lodgepole pine trees and alder bushes. These are called pioneer plants. They are among the first plants to grow in new or disturbed areas. They bravely push through the rocky ground.
If you decide to explore deep inside the lava bed, be very careful. It's easy to get lost because the landscape all looks similar. Your compass might not work correctly either. The rocks in the lava bed can affect a compass's magnetic reading. This makes finding your way even harder.
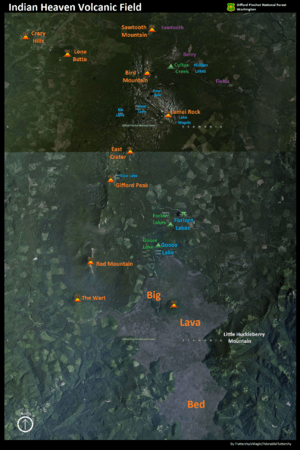
Satellite map showing the various shield volcanoes topped by cinder and spatter cones that characterizes the Indian Heaven Volcanic Field The Big Lava Flow can be seen as the lighter green/brown area at the bottom center. The orange volcano icon in the flow marks the location of the cinder cone, the lava flow's source.
|
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |

