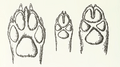Canids facts for kids
Quick facts for kids CanidsTemporal range: Palaeogene - Recent
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Coyote (Canis latrans) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: | |
| Family: |
Canidae
G. Fischer de Waldheim, 1817
|
Canids are a group of mammals that include dogs, wolves, foxes, coyotes, and jackals. They belong to a scientific group called a "family," which is like a big animal club. This family is known as Canidae.
Most canids are meat-eaters, but some are omnivores, meaning they eat both plants and meat. They are part of the larger group of animals called carnivores, which includes bears, cats, and seals.
The Canidae family is split into two main groups, like two different teams:
- Vulpini: These are the "true foxes."
- Canini: These are the "true dogs," which include wolves, domestic dogs, and coyotes.
Sometimes people mistakenly call all canids "canines," but that's not quite right. "Canines" only refers to the "true dog" group.
Contents
What are Canids?
Canids are known for their strong bodies, sharp teeth, and excellent senses. They have great hearing and a powerful sense of smell, which helps them find food and stay safe. Most canids are good runners and can chase down their prey.
They live in many different parts of the world, from cold Arctic regions to hot deserts. Canids can be found in forests, grasslands, mountains, and even near human cities.
Canid Groups
The Canidae family is divided into two main groups, or "tribes," based on their characteristics.
True Foxes (Vulpini)
This group includes many types of foxes. They are often smaller than true dogs and have flatter skulls. Many foxes have bushy tails and pointed ears. They are usually solitary, meaning they live alone or in small family groups.
Some examples of true foxes are:
- The Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes), which is found in many parts of the world.
- The Fennec Fox (Vulpes zerda), known for its huge ears that help it stay cool in the desert.
- The Arctic Fox (Alopex lagopus), which changes its fur color with the seasons.
- The Gray Fox (Urocyon cinereoargenteus), which can climb trees!
- The Bat-eared Fox (Otocyon megalotis), which uses its large ears to listen for insects underground.
True Dogs (Canini)
This group includes wolves, coyotes, jackals, and domestic dogs. They are generally larger than foxes and often live in social groups called packs. Living in packs helps them hunt bigger animals and protect their territory.
Some examples of true dogs are:
- The Grey Wolf (Canis lupus), which is the ancestor of our pet dogs.
- Domestic dogs (Canis lupus familiaris), which are the most common canids and live with humans.
- The Coyote (Canis latrans), a clever animal found across North America.
- The Golden Jackal (Canis aureus), found in parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- The African wild dog (Lycaon pictus), known for its colorful fur and strong hunting skills.
- The Dhole (Cuon alpinus), a wild dog from Asia that hunts in packs.
- The Maned Wolf (Chrysocyon brachyurus), a tall, long-legged canid from South America that looks a bit like a fox on stilts.
Images for kids
-
Representatives of three canid subfamilies: Hesperocyon (Hesperocyoninae), Aelurodon (Borophaginae) and Canis aureus (Caninae)
-
A look at the paws of a gray wolf, Eurasian golden jackal, and dhole.
-
The skeleton of a black-backed jackal (Lupulella mesomelas) on display.
-
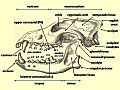
A skull of an Eurasian wolf.
-
Dholes working together to hunt a sambar in Bandipur National Park.
See also
 In Spanish: Canidae para niños
In Spanish: Canidae para niños