Catalysis facts for kids

Catalysis is when a chemical reaction happens faster or slower because of something called a catalyst. Think of a catalyst as a helper. It changes how quickly a reaction goes, but it doesn't get used up itself. This means a catalyst can help many reactions, over and over again!
Some catalysts make reactions go faster. These are called positive catalysts. Others make reactions go slower. These are called negative catalysts, or inhibitors. There are also "promoters" that make catalysts work even better. And "catalytic poisons" are things that stop catalysts from working.
Contents
What is a Catalyst?
A catalyst is a substance that changes the speed of a chemical reaction. For example, if you add manganese oxide to hydrogen peroxide, the hydrogen peroxide quickly breaks down into water and oxygen. The manganese oxide is the catalyst here.
Catalysts can be found in nature or made by people. They are very useful because they don't leave any unwanted stuff behind in the mixture. Plus, you can often use a catalyst again and again.
How Catalysts Work
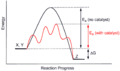
Most catalysts work by lowering the "activation energy" of a reaction. Imagine a hill that chemicals need to climb to react. A catalyst creates a new, easier path around the hill. This means less energy is needed for the reaction to happen, which makes it go much faster.
Our bodies use many natural catalysts called enzymes. These enzymes are super important for all the chemical reactions that keep us alive and healthy.
Slowing Down Reactions
The opposite of a catalyst is an inhibitor. Inhibitors slow down chemical reactions. Some natural substances can act as inhibitors. For example, some chemicals found in certain animal venoms can slow down important reactions in the body, which can be harmful.
Related pages
- Enzymes are special catalysts found in living things.
Images for kids
-
Left: A sugar cube that has started to burn. Right: A sugar cube burning with the help of ash as a catalyst.
See also
 In Spanish: Catálisis para niños
In Spanish: Catálisis para niños