Caulophyllum facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Caulophyllum |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
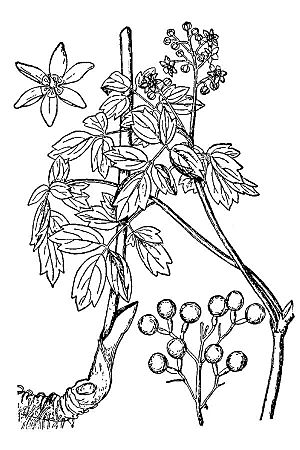
| Caulophyllum thalictroides from Britton & Brown 1913 | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Ranunculales |
| Family: | Berberidaceae |
| Genus: | Caulophyllum Michx. |
| Species | |
|
|
Caulophyllum is a small group of plants that grow year after year. They belong to the Berberidaceae family. You can find them naturally in eastern Asia and eastern North America. These plants are special spring wildflowers. They like to grow in damp, rich forests. Caulophyllum is known for its large, three-part leaves and big, blue, berry-like fruits. Unlike many spring flowers, it stays green for most of the summer. Common names for these plants include blue cohosh, squaw root, and papoose root.
Contents
What is Caulophyllum?
These plants are quite tall, usually growing between 0.3 and 0.9 meters (about 1 to 3 feet). They have one or a few main stems. Each stem usually has one very large leaf, but bigger stems might have two. This large leaf is actually made of three main parts, which then divide again. So, it looks like many smaller leaves on three separate branches. Each small leaflet has three to five distinct tips.
These plants grow special underground stems called rhizomes. Each spring, new leaves grow from these rhizomes. In the fall, when the leaves die, a scar is left on the rhizome. A new bud forms there, ready to grow next spring. These plants can live for a very long time, sometimes more than 50 years! They prefer to live in wooded areas where the soil stays moist.
Flowers and Fruits
In April or May, each grown-up stem produces a spike of flowers. Each flower has six parts that look like petals, called sepals. These sepals can be greenish-yellow or even purple. The male parts (called stamens) and the female part (called the pistil) of the flower mature at different times. This helps make sure the plant gets cross-pollinated by other plants, not just itself.
At the base of each sepal, there are six small, soft glands that make nectar. This nectar attracts pollinators like bees. After a flower is pollinated, it grows into a large, deep-blue, berry-like fruit, about 1 centimeter (0.4 inches) wide. Inside each fruit are two bitter seeds. The seeds have a special blue coating. These fruits stay on the plants until fall.
It can take a few years for the seeds to sprout. When they do, the first leaves (called cotyledons) stay underground. This is known as hypogeal germination. The young plants need several years to grow before they are big enough to produce their own flowers.
Types of Caulophyllum
All the different types, or species, in this plant group look very similar. For a long time, people thought there were only two species. However, the Flora of North America now says that Caulophyllum giganteum is its own species, not just a type of Caulophyllum thalictroides.
Caulophyllum giganteum is a bit larger than Caulophyllum thalictroides. It also grows more to the north, though their areas overlap. It blooms about two weeks earlier and has fewer flowers, which are always purplish.
Here are the main species:
- Caulophyllum thalictroides – Also known as Blue cohosh (found in Eastern North America)
- Caulophyllum giganteum – Called Giant blue cohosh (found in Eastern North America)
- Caulophyllum robustum – Known as Asian blue cohosh (found in Japan and Eastern Asia)
Uses of Caulophyllum
People have found different ways to use these plants throughout history. All three species are generally thought to have similar properties. Sometimes, these plants are grown in woodland gardens because they are attractive.
Important Safety Note: Children should not eat the attractive blue fruits. These plants contain chemicals that can be harmful if eaten. Touching the powdered roots might also irritate your skin.
Food Uses
In the past, the roasted seeds of Caulophyllum were used as a substitute for coffee. This drink does not contain caffeine.
See also
 In Spanish: Caulophyllum para niños
In Spanish: Caulophyllum para niños

