Celestial navigation facts for kids
Celestial navigation is a special way to find your location and direction using objects in the sky. Imagine you're on a ship far out at sea, with no land in sight. How do you know where you are or which way to go? For thousands of years, sailors and explorers used the sun, moon, stars, and planets to guide them. By carefully measuring the angles of these celestial bodies, they could figure out their exact position on Earth. This amazing skill helped people explore the world long before modern tools like GPS existed!
Contents
Celestial navigation is like using the sky as a giant map. It involves looking at the positions of the sun, moon, stars, and planets. By measuring how high these objects are above the horizon, and knowing the exact time, you can calculate your latitude and longitude. This tells you exactly where you are on Earth.
How Does it Work?
The basic idea is simple: as the Earth spins, the sun, moon, and stars appear to move across the sky. Their positions are predictable. If you know the exact time and the exact position of a celestial body, you can draw a "line of position" on a map. This line shows all the possible places you could be. By taking measurements from two or more different celestial bodies, these lines will cross. Where they cross is your location!
Measuring Angles
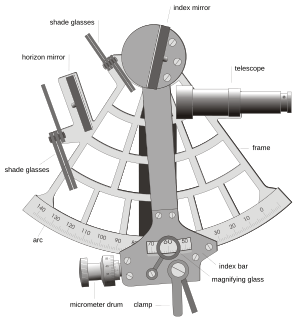
The main tool for measuring angles is called a sextant. A sextant lets you measure the angle between the horizon and a celestial object, like the sun or a star. This angle is called the "altitude." The higher an object is in the sky, the closer it is to being directly overhead.
Using Time and Charts
To make celestial navigation work, you also need to know the precise time. This is because the positions of celestial bodies change constantly as the Earth rotates. Sailors used very accurate clocks called chronometers. They also used special books called nautical almanacs. These almanacs contain tables that list the exact positions of the sun, moon, and stars for every hour of every day. By combining the sextant measurement, the time, and the almanac data, a navigator can calculate their position.
People have used the stars to navigate for thousands of years. Early sailors, like the Polynesians, were masters of reading the sky. They used stars to cross vast oceans, discovering new islands.
Early Tools and Discoveries
- Ancient Times: Sailors used simple tools like the astrolabe or quadrant to measure star heights. They also relied on their knowledge of constellations.
- 15th-18th Centuries: During the Age of Exploration, celestial navigation became vital. Explorers like Christopher Columbus and Ferdinand Magellan used it to cross oceans and discover new lands. However, finding longitude was very difficult until accurate chronometers were invented in the 18th century.
- 18th Century: The invention of the chronometer by John Harrison was a huge breakthrough. It allowed sailors to keep accurate time at sea, which was essential for calculating longitude. The sextant was also developed around this time, making angle measurements much more precise.
Even with modern GPS systems, celestial navigation is still taught and practiced. It serves as an important backup method in case electronic systems fail. Many sailors and aviators learn it for its historical importance and as a valuable skill. It connects us to the ancient art of exploration and discovery.
- Sextant: This is the most important tool. It's used to measure the angle (altitude) of celestial bodies above the horizon.
- Chronometer: A very accurate clock. Knowing the precise time is crucial for calculations.
- Nautical Almanac: A book published yearly that lists the positions of celestial bodies for every day and hour.
- Sight Reduction Tables: Books of pre-calculated values that help navigators quickly solve the complex math problems involved.
- Charts and Plotting Tools: Sea maps and tools like parallel rulers and dividers are used to plot the calculated position.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Historia de la navegación astronómica para niños
In Spanish: Historia de la navegación astronómica para niños
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |