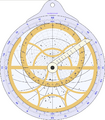
Astrolabe facts for kids
An astrolabe is an old tool that used the positions of the stars or the sun. People used it a long time ago for navigation. Sailors and explorers used it to find out where they were. They could measure how far north or south they were from the equator. They did this by checking how high the sun or stars were above the horizon. Astronomers also used astrolabes, often bigger ones, to study the sky.
Contents
History of the Astrolabe
The first astrolabe was made around 150 BC. This happened in the ancient Greek world, known as the Hellenistic world. Many people believe that a Greek astronomer named Hipparchus created it.
How it Was Made
The astrolabe combined two older tools. One was the planisphere, which was like a flat map of the stars. The other was the dioptra, a tool used to measure angles. Together, they made a powerful calculator. This calculator could solve many different problems in astronomy.
Famous Users
A scholar named Theon of Alexandria wrote a detailed book about the astrolabe. It is also thought that Ptolemy, another famous ancient astronomer, used an astrolabe. He used it to make important observations about the stars and planets.
What an Astrolabe Does
Astrolabes were very useful for many things.
- Finding Your Location: Sailors used them to find their latitude. This is how far north or south they were from the equator.
- Telling Time: They could also be used to tell the time of day or night. This was done by looking at the sun or stars.
- Studying the Sky: Astronomers used astrolabes to measure the positions of stars. They could also predict where planets would be.
- Measuring Heights: Some astrolabes could even be used to measure the height of buildings or mountains.
Images for kids
-
A modern astrolabe made in Tabriz, Iran in 2013.
-
Amerigo Vespucci observing the Southern Cross with an Astrolabium, by Jan Collaert II. Museum Plantin-Moretus, Antwerp, Belgium.
-
A 16th-century astrolabe showing a tulip rete and rule
See also
 In Spanish: Astrolabio para niños
In Spanish: Astrolabio para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |