Chalk-browed mockingbird facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Chalk-browed mockingbird |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| In the Pantanal, Brazil | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Mimidae |
| Genus: | Mimus |
| Species: |
M. saturninus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Mimus saturninus (Lichtenstein, MHC, 1823)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The chalk-browed mockingbird (Mimus saturninus) is a cool bird that belongs to the mimidae family. You can find these birds in several South American countries, including Brazil, Bolivia, Argentina, Paraguay, Suriname, and Uruguay. They are known for their interesting looks and varied songs!
Contents
About the Chalk-browed Mockingbird
What Does It Look Like?
The chalk-browed mockingbird is about 23.5 to 26 centimeters (9 to 10 inches) long. It weighs around 55 to 73 grams (1.9 to 2.6 ounces), which is about the weight of a small apple. Male birds are usually a little bigger than females.
Adult birds have a dark brown top of the head. They have a wide white stripe above their eyes, which looks like a "chalk brow." A black line goes through their eyes, and their cheeks are white. Their upper body is brownish with some darker stripes. Their wings are dark, and when folded, you might see two faint bars. The tail is also dark, with most feathers having white tips. The feathers on the very edge of the tail have white edges.
The underside of their body is white, from their throat all the way to their tail. Their chest might have a gray tint, and their sides are buffy (a light yellowish-brown) with faint dark streaks. Young chalk-browed mockingbirds are browner than adults. They have buffier undersides with dark streaks on their chest.
There are a few different types, or subspecies, of the chalk-browed mockingbird. These subspecies have slight differences in their coloring or bill size. For example, some might be browner overall, while others have a larger beak.
Where Do They Live?
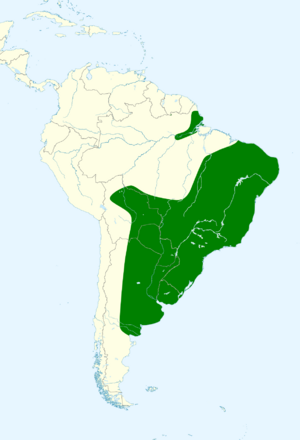
Chalk-browed mockingbirds live in many different open areas. They like places like savannas (grassy plains with scattered trees), the edges of forests, and open woodlands. You can also spot them in pastures with trees and even in gardens in cities and towns.
They usually live in low-lying areas. However, in northern Argentina, they can be found in higher places, up to about 2,500 meters (8,200 feet) above sea level.
How Do Chalk-browed Mockingbirds Live?
What Do They Eat?
The chalk-browed mockingbird is an omnivore, which means it eats both plants and animals. Their diet includes fruits, seeds, and berries. They also enjoy eating insects and other small animals. Sometimes, they might even eat the eggs or baby birds from other birds' nests. They usually look for their food on the ground.
How Do They Raise Their Young?
Chalk-browed mockingbirds usually breed, or have babies, from September to January. They are very protective of their territory and typically stay with one partner. Sometimes, other birds, both family members and non-family, help them protect their home and take care of the young.
Their nest is shaped like a shallow cup. It's made from twigs and lined with softer materials. They usually build their nests in a low tree or a thick bush, often within 3 meters (10 feet) of the ground. Sometimes, they build them higher up. A female chalk-browed mockingbird usually lays three or four eggs.
What Do They Sound Like?
The chalk-browed mockingbird has a loud and varied song. It's a mix of different notes, trills, and phrases. Their calls can sound like a sharp "tshrip" or a snorting "sha-sha-sha." They are also known for being great mimics, meaning they can copy the sounds of other bird species, even some birds of prey!
Is the Chalk-browed Mockingbird Endangered?
The IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) has looked at the chalk-browed mockingbird. They have decided that this bird is of "Least Concern." This means that it is not currently at risk of disappearing.
The chalk-browed mockingbird lives across a very large area, estimated to be about 10.6 million square kilometers (4.1 million square miles). It is also very common in many parts of its range. Scientists believe that the number of these birds is stable. They live in several protected areas, which helps keep them safe. There aren't any major threats to them, even though some of their nests are affected by another bird called the shiny cowbird, which lays its eggs in their nests.
Images for kids