Pantanal facts for kids
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|

Typical Pantanal scenery
|
|
| Location | Brazil |
| Criteria | Natural: (vii), (ix), (x) |
| Inscription | 2000 (24th Session) |
| Area | 187,818 km2 (72,517 sq mi) |
| Official name: Pantanal Matogrossense | |
| Designated: | 24 May 1993 |
| Reference #: | 602 |
| Official name: El Pantanal Boliviano | |
| Designated: | 17 September 2001 |
| Reference #: | 1089 |
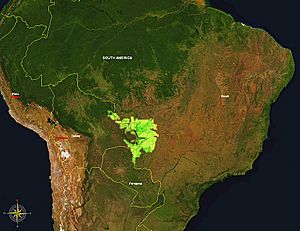
The Pantanal is the world's largest wetland or swamp. It covers a huge area of 140,000 square kilometers. This is bigger than the country of Greece!
The Pantanal is located in South America. It is shared by three countries: Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay. This amazing place is home to countless plants and animals.
Sadly, the Pantanal faces many dangers. These include pollution and mercury from gold mining. Ranching also causes problems. Even though the Pantanal can clean some chemicals, too much pollution is a big worry. In winter, almost 80% of this area gets flooded.
Contents
What is the Pantanal?
The Pantanal is a giant, gently sloped basin. It collects water from higher areas called the Planalto highlands. This water slowly flows out through the Paraguay River and its smaller rivers.
This huge area formed because of a large dip in the Earth's crust. It's like a giant natural bowl. Many rivers from the surrounding plateau flow into it. They bring sediments and dirt, which have filled the area over many years.
The Pantanal is surrounded by different types of forests and savannas. To the west, there are dry forests. To the south, there are both dry and humid forests. To the north and east, you'll find Cerrado savannas.
The Pantanal gets about 1000 to 1400 millimeters of rain each year. The upper Paraguay River also feeds it with water. The average temperature is about 25 degrees Celsius (77 degrees Fahrenheit). But temperatures can change a lot, from 0 to 40 degrees Celsius (32 to 104 degrees Fahrenheit).
How Water Shapes the Pantanal
Wetlands like the Pantanal are special because they have wet and dry seasons. They switch between being covered in water and having dry soil. During the dry season, the water level can be far below the ground.
The soil in the Pantanal varies. Higher areas have lots of sand. Areas near rivers have more clay and silt. The land is mostly flat, ranging from 80 to 150 meters (260 to 490 feet) above sea level.
Most rain falls between November and March. In the Paraguay River part of the Pantanal, water levels can rise by two to five meters (6.5 to 16 feet) each season. In other areas, the water changes less. Floodwaters move slowly, about 2 to 10 centimeters (0.8 to 4 inches) per second. This is because the land is flat and thick plants slow the water down.
When floodwaters first touch dry soil, the water loses its oxygen. This can cause many fish kills. Scientists think this might be due to harmful bacteria growing in the water.
Amazing Plants of the Pantanal
The plants in the Pantanal are a mix from different nearby areas. You can find plants from the Amazon rainforest, dry woodlands, and different types of savannas. Forests usually grow on higher ground. Grasslands cover the areas that flood every year.
The main things that limit plant growth are flooding and lack of water in the dry season. Even with these challenges, the Pantanal is full of life.
Brazilian researchers have found about 2000 different plant types here. Some of these plants may even have important medicinal uses!
Incredible Animals of the Pantanal
The Pantanal is a true animal paradise! It is thought to be home to:
- 1000 different kinds of birds
- 400 types of fish
- 300 kinds of mammals
- 480 types of reptiles
- Over 9000 kinds of invertebrates (animals without backbones)
The Important Apple Snail
The apple snail is a very important animal in the Pantanal. It's called a "keystone species." This means it plays a huge role in the ecosystem.
When the wetlands flood each year, grass and other plants die and start to rot. This process uses up all the oxygen in the shallow water. Most animals that break down dead plants can't survive without oxygen.
But apple snails are special! They have both gills (for breathing underwater) and lungs (for breathing air). This allows them to live in water with no oxygen. They stick a long tube, like a snorkel, to the water surface to get air.
This amazing ability lets them eat all the dead plants. They turn this dead plant matter into rich fertilizer for new plants. The snails themselves are also a food source for many other animals.
Rare and Common Animals
Some of the rarest animals in the Pantanal are the marsh deer (Blastocerus dichotomus) and the giant river otter (Pteroneura brasiliensis).
Other endangered or threatened animals found here include:
- The hyacinth macaw (Anodorhyncus hyacinthinus), a beautiful blue bird often smuggled.
- The crowned solitary eagle.
- The maned wolf (Chrysocyon brachyurus).
- The bush dog (Speothos venaticus).
- The South American tapir (Tapirus terrestris).
- The giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla).
Common animals you might see are the capybara (Hydrochoerus hydrochaeris), the Ocelot (Leopardus pardalis), and the yacare caiman (Caiman yacare). In 1996, there were an estimated 10 million caimans in the Pantanal. This makes it the place with the most crocodilians in the world!
The Pantanal also has one of the largest and healthiest populations of jaguars (Panthera onca) on Earth.
Fish and Reptiles
Most fish in the Pantanal eat tiny bits from sediments and plant surfaces. This is common for fish in South American flood-plains. Fish move between river channels and flooded areas depending on the season. They have special ways to survive in waters with low oxygen.
Besides the caiman, other reptiles living in the Pantanal include:
- The yellow anaconda (Eunectes notaeus).
- The gold tegu (Tupinambis teguixin).
- The red-footed tortoise (Geochelone carbonaria).
- The green iguana (Iguana iguana).
-
Black howler monkeys
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Pantanal para niños
In Spanish: Pantanal para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |