Chicoutimi facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Chicoutimi
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Borough
|
||

Downtown Chicoutimi
|
||
|
||
| Nicknames:
Queen of the North, Saguenay Queen, Saguenay metropolis, Saguenay kingdom capital, Conventions city
(Reine du Nord, Reine du Saguenay, Métropole du Saguenay, Capitale du royaume du Saguenay, Ville des congrès) |
||
 |
||
| Country | Canada | |
| Province | Quebec | |
| Region | Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean | |
| City | Saguenay | |
| Website | Borough Council of Chicoutimi | |
Chicoutimi (/ʃɪˈkuːtɪmi/ SHIH-koo-TIM-ee) is a large area, called a borough, within the city of Saguenay in Quebec, Canada. It is the most populated borough in Saguenay.
Chicoutimi is located where the Saguenay and Chicoutimi rivers meet. For most of the 1900s, it was the main place for business and government in the Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean region. In 2002, Chicoutimi became part of the new city of Saguenay. It is now the heart of Quebec's fifth-largest urban area. In 2021, about 69,004 people lived there.
Contents
History of Chicoutimi
The area that is now Chicoutimi was first settled by French colonists in 1676. They set up a trading post there to trade furs. Before this, the Montagnais tribes had used the Saguenay and Chicoutimi rivers for centuries. The name Chicoutimi comes from an Indigenous language and means "the end of the deep water." After the British took control of Lower Canada, the fur trading post closed in 1782 because the fur trade moved further west.
The city of Chicoutimi was officially created in 1845. Peter McLeod, a timber contractor, built a sawmill there in 1842. In 1855, Chicoutimi became the main town for Chicoutimi County. It also became the center for the Roman Catholic Diocese of Chicoutimi in 1878.
When the Canadian National Railway arrived in 1893, it helped Chicoutimi's pulp and paper industries grow a lot. The railway also built Chicoutimi station, which served the city until 1988. The Chicoutimi Pulp Co. was started in 1896 by French-Canadian investors. By 1910, the Chicoutimi Pulp Mill was the biggest producer of mechanical pulp in Canada.
Since the Great Depression, Chicoutimi has become a major center for government and business. New schools and cultural places were built. These include the Conservatoire de musique de Saguenay in 1967 and the Université du Québec à Chicoutimi in 1969. The city also hosted the Quebec Summer Games in 1972.
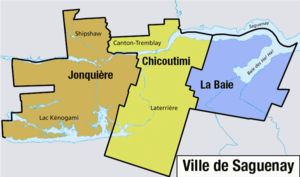
In 1976, Chicoutimi grew by adding the nearby towns of Chicoutimi-Nord and Rivière-du-Moulin. In 2002, a much bigger change happened. The cities of Chicoutimi, Jonquière, La Baie, Lac-Kénogami, Laterrière, Shipshaw, and part of Tremblay all joined together. They formed the new city of Saguenay. Chicoutimi then became one of Saguenay's boroughs.
In the summer of 1996, there was a huge amount of rain in the region. This caused major flooding in downtown Chicoutimi and other areas. Many dams overflowed, and bridges were destroyed. The total cost of the damage was about 1.5 billion Canadian dollars. Sadly, seven people also lost their lives in the flood.
Chicoutimi has a sister city relationship with Camrose, Alberta.
Geography and Cityscape
Chicoutimi is located in the Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean region. It is at the western end of the Saguenay Fjord. Most of the borough, including the downtown area, is on the south side of the Saguenay River. It is the central part of the city of Saguenay. The boroughs of Jonquière and La Baie are next to it on the west and east sides.
Chicoutimi is about 200 kilometers (124 miles) north of Quebec City. It is also about 126 kilometers (78 miles) northwest upriver from Tadoussac. The former cities that now make up Chicoutimi borough are Chicoutimi, Laterrière, Canton-Tremblay, Chicoutimi-Nord, and Rivière-du-Moulin. These names are still used for different areas within the combined city.
The landscape of Chicoutimi has hills, valleys, and flat areas. The land gets steeper closer to the Saguenay River. Its two main natural features are the Saguenay Graben and the Saguenay Fjord. The Saguenay Graben is a rift valley in the Laurentian Highlands where the city is spread out. The Saguenay Fjord has steep shores carved by glaciers along the Saguenay River. Mount Valin, at 980 meters (3,215 feet), is the tallest mountain in the region. It overlooks Chicoutimi about 30 kilometers (19 miles) to the north-east. The Chicoutimi, Du Moulin, and Valin rivers all flow into the Saguenay River in Chicoutimi.
Culture
Sports in Chicoutimi
The city has been home to the QMJHL's Chicoutimi Saguenéens hockey team since 1973. They play their games at the Centre Georges-Vézina.
Cycles Devinci, a company that makes bicycles, started here in 1987.
Professional Hockey Players from Chicoutimi
- Luc Dufour
- Johnny Gagnon
- Leo Gaudreault
- Sylvain Locas
- John Smrke
- Georges Vezina
Education
International Relations
Twin Towns – Sister Cities
Chicoutimi is twinned with:
 Angoulême, France
Angoulême, France
Notable People
- Marilyn Bergeron
- Johnny Gagnon
- Christian Genest, Professor of Statistics, McGill University
- John Kricfalusi
- Kevin Lambert, writer
- René Simard
- Charles Sirois
- Thomas-Louis Tremblay
- Georges Vézina
- Arthur Villeneuve
- Élisabeth Vonarburg, author
- Jeanick Fournier, singer and winner of Canada's Got Talent (season 2)
See also
 In Spanish: Chicoutimi para niños
In Spanish: Chicoutimi para niños







