Coastal taipan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Coastal taipan |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Elapidae |
| Genus: | Oxyuranus |
| Species: |
O. scutellatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Oxyuranus scutellatus (W. Peters, 1867)
|
|
 |
|
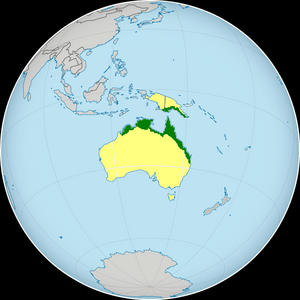
| Distribution of Oxyuranus scutellatus in green | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The coastal taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) is also known as the common taipan. It is a very large and extremely venomous snake. This snake belongs to the family called Elapidae.
Coastal taipans live along the coasts of northern and eastern Australia. They also live on the island of New Guinea. Many studies show that this snake is the third most venomous land snake in the world. Only the inland taipan and eastern brown snake are more venomous.
Contents
About Its Name
A German scientist named Wilhelm Peters first described the coastal taipan in 1867. He gave it the scientific name Pseudechis scutellatus.
Scientists recognize two main types, or subspecies, of the coastal taipan:
- Oxyuranus scutellatus canni (Papuan taipan): This type lives in the southern part of New Guinea.
- Oxyuranus scutellatus scutellatus (Coastal taipan): This type lives in coastal Queensland, the northern Northern Territory, and northeastern Western Australia in Australia.
What It Looks Like
The coastal taipan is the longest venomous snake in Australia. Adult snakes usually grow to about 1.2 meters (4 feet) long. Older snakes can be between 1.5 and 2.0 meters (5 to 6.5 feet) long.
A coastal taipan that is 2 meters (6.5 feet) long usually weighs about 3 kilograms (6.6 pounds). The longest one ever recorded was 2.9 meters (9.5 feet) long and weighed 6.5 kilograms (14.3 pounds). Some people believe even larger ones exist, up to 3.3 meters (10.8 feet) long!
Only a few other venomous snakes are longer than the taipan. These include the king cobra from Asia and the black mamba from Africa.
The coastal taipan has a long, narrow head. It looks a bit like the head of an African black mamba. Its face is often lighter in color. The snake's body is slender and its color can change. It is often light olive or reddish-brown. Some can be dark gray or black. The sides of its body are lighter. Its belly is usually creamy-white or pale yellow. It might have orange or pink spots.
These snakes can even change color with the seasons. They become darker in winter and lighter in summer. Their eyes are large and round. They are usually light brown or hazel with big pupils.
Its Scales
The number and pattern of a snake's scales help scientists identify its species. The coastal taipan has specific scale patterns on its head and body. For example, it has 21 to 23 rows of scales around the middle of its body. The scale under its tail is divided into two parts.
Where It Lives
The coastal taipan lives in Australia and on the island of New Guinea. New Guinea is split between two Indonesian provinces and the country of Papua New Guinea.
In Australia, you can find the coastal taipan in the north and east. This includes north-western Western Australia, the Northern Territory, and eastern Queensland. It can go as far south as Grafton in northern New South Wales. However, it does not live in places where the winter temperature drops below 20°C (68°F).
The Papuan taipan (the other subspecies) lives all over New Guinea. It is more common in Papua New Guinea.
Its Home
Coastal taipans live in many different places. They like warm, wet areas near the coast. They can be found in monsoon forests and different types of woodlands. They also live in grassy areas, like fields.
In Queensland, they have learned to live well in sugarcane fields. They find lots of rats and mice there to eat. They often hide in old animal burrows, hollow logs, or piles of plants and trash.
How It Behaves and What It Eats
The coastal taipan is mostly active during the day. It likes to hunt in the early to mid-morning. If the weather is very hot, it might hunt at night instead.
When it hunts, it uses its good eyesight to look for food. It often moves with its head slightly raised. Once it sees prey, it stops moving. Then, it quickly lunges forward and bites several times. It lets go of its prey and waits for it to move away. This way, the snake avoids getting hurt by animals like rats, which can bite back.
The coastal taipan is not usually aggressive. It prefers to escape if it feels threatened. But if it feels trapped, it can become very aggressive. It might strike many times.
What It Eats
The coastal taipan eats only small animals. Its diet includes rats, mice, bandicoots, and different kinds of birds.
Its Venom
The coastal taipan is the world's third-most venomous land snake. Its venom is extremely powerful. On average, one bite delivers about 120 milligrams of venom. The most ever recorded from a single bite was 400 milligrams.
The venom contains a special toxin called Taipoxin. This is one of the most powerful toxins found in snake venom. It means that, in terms of pure toxins, the coastal taipan is considered one of the most venomous animals on Earth.
The venom mainly contains a strong neurotoxin called taicatoxin. This toxin affects the nervous system. It also stops the blood from clotting properly. If someone is bitten, they might get a headache, feel sick, collapse, or have seizures. They could also experience paralysis, internal bleeding, or kidney damage.
In serious cases, a person could die as quickly as 30 minutes after a bite. The average time to death is about 2.5 hours. The time depends on how severe the bite is and the person's body.
Sadly, without treatment, all coastal taipan bites are fatal. An average bite delivers much more venom than needed to kill a human adult. Doctors say that anyone bitten by a coastal taipan needs medical help right away, even if the bite seems small.
Before 1956, when a special antivenom was created, almost everyone who was bitten died. In a book called Venom, the author Brendan James Murray writes about a man named George Rosendale. He was bitten in 1949 and is believed to be the only person to survive a taipan bite without antivenom. Nurses said his blood was completely black after the bite, showing how serious it was.
See also
 In Spanish: Taipán de la costa para niños
In Spanish: Taipán de la costa para niños
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |



