Combined gas law facts for kids
The combined gas law is a special rule in physics and chemistry that helps us understand how gases behave. It brings together three important laws about how the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas are connected.
Imagine you have a balloon. What happens if you squeeze it (change pressure)? What if you heat it up (change temperature)? What if it gets bigger or smaller (change volume)? The combined gas law helps explain these changes.
It's called "combined" because it uses ideas from three other gas laws:
- Charles's law says that if you keep the pressure the same, a gas's volume and temperature will change together. If you heat a gas, its volume gets bigger. If you cool it, its volume shrinks.
- Boyle's law says that if you keep the temperature the same, a gas's pressure and volume work opposite to each other. If you squeeze a gas (increase pressure), its volume gets smaller. If you let it expand (decrease pressure), its volume gets bigger.
- Gay-Lussac's law says that if you keep the volume the same, a gas's pressure and temperature will change together. If you heat a gas in a closed container, its pressure goes up. If you cool it, its pressure goes down.
The combined gas law shows how all three of these things—pressure, volume, and temperature—are related at the same time.
Contents
Understanding the Formula
The combined gas law can be written as a simple formula:
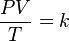
Let's break down what each letter means:
- P is the pressure of the gas. Think of how hard the gas pushes on its container.
- V is the volume of the gas. This is how much space the gas takes up.
- T is the temperature of the gas. It must be measured in kelvin, which is a special temperature scale used in science.
- k is a constant. This means it's a number that doesn't change for a specific amount of gas.
So, the formula tells us that if you multiply the pressure by the volume and then divide by the temperature, you will always get the same number (k) for that gas.
If you want to compare the same gas in two different situations (like before and after heating it), you can use this version of the formula:
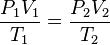
Here, the numbers "1" and "2" just mean "situation 1" and "situation 2." This formula is very useful for solving problems where a gas changes its conditions.
How It Connects to Other Laws
The combined gas law is a step towards understanding the ideal gas law. If you add Avogadro's law to the combined gas law, you get the ideal gas law. Avogadro's law talks about how the amount of gas (number of particles) affects its volume.
Real-World Uses
The combined gas law helps explain how many everyday things work. It's used in:
- Air conditioners and refrigerators: These devices change the pressure and volume of gases to cool things down.
- Cloud formation: As warm, moist air rises, its pressure drops, causing it to expand and cool, which forms clouds.
- Engines and other machines that use gases.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ley general de los gases para niños
In Spanish: Ley general de los gases para niños