Crotalus basiliscus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Crotalus basiliscus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Genus: | Crotalus |
| Species: |
C. basiliscus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalus basiliscus (Cope, 1864)
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Mexican west coast rattlesnake, also called Crotalus basiliscus, is a type of pit viper. It belongs to the Viperidae family of snakes. This snake lives only in western Mexico. Like all pit vipers, it is a venomous animal.
Its scientific name, basiliscus, comes from a Greek word meaning "king". This name hints at the snake's large size and strong venom. Currently, scientists do not recognize any different types (subspecies) of this snake.
Contents
- What Does the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Look Like?
- What Are Its Common Names?
- Where Does the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Live?
- What Kind of Habitat Does It Prefer?
- Is the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Endangered?
- How Does the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Behave?
- What Does the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Eat?
- How Strong Is Its Venom?
- How Is the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Classified?
- See also
What Does the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Look Like?

The Mexican west coast rattlesnake is one of the biggest rattlesnake species. Many of these snakes grow longer than 150 cm (4.9 ft), which is about 5 feet. The longest one ever recorded was 204.5 cm (6.71 ft) (about 6.7 feet) long.
This snake has a body that is quite thick and looks somewhat rectangular. Female snakes are considered adults when they reach at least 100 cm (3.3 ft) (about 3.3 feet) long and weigh 700 g (1.5 lb) (about 1.5 pounds).
Scales and Color Patterns
Around the middle of its body, this snake has 25 to 29 rows of scales that have a strong ridge (keel) down the middle. It also has 174 to 206 scales on its belly and 18 to 36 scales under its tail.
The snake's main color is brown or grayish. On top of this, it has 26 to 41 dark, diamond-shaped blotches. These blotches have lighter edges. Its head is usually a plain grayish-brown. However, the scales around its mouth are lighter, and it has a dark stripe behind its eyes. There are no clear patterns on its head or neck.
The tail can be gray with darker bands, or it might be a solid color without any distinct marks. The snake's belly is white or cream-colored. Young snakes are often reddish, but as they grow, adults turn an olive green color. In its natural home, this is the only rattlesnake that has diamond-shaped patterns on its back.
Sometimes, this snake lives in the same areas as another snake called C. molossus. When they live together, they sometimes have babies that are a mix of both species. It's usually easy to tell the two species apart, but identifying these mixed snakes can be tricky.
What Are Its Common Names?
People call C. basiliscus by several names. These include the Mexican west coast rattlesnake, Mexican green rattler, and Mexican west coast green rattlesnake. In Spanish, it is known as cascabel verde mexicana.
Where Does the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Live?
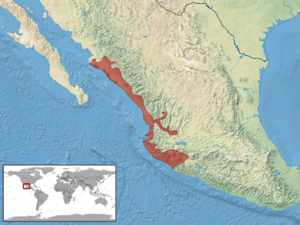
This rattlesnake, C. basiliscus, lives in western Mexico. Its range stretches from southern Sonora down to Michoacán. It mostly stays in the flat areas along the coast. The first place where this snake was officially found and described was near Colima, Mexico.
What Kind of Habitat Does It Prefer?
Around Colima, where many C. basiliscus snakes used to live, the land was mostly open. It had short grass and scattered groups of mesquite, acacia, and other thorny bushes. There were also many large cacti. The main home for C. basiliscus is tropical thorn forests. It can also be found in tropical deciduous forests.
Is the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Endangered?
The C. basiliscus species is listed as "Least Concern" on the IUCN Red List. This list helps track how endangered different species are. A species is called "Least Concern" if it is widespread, has a large population, or is not decreasing fast enough to be in a more threatened group. When scientists checked in 2007, the number of these snakes seemed to be stable.
How Does the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Behave?
In the lowlands, C. basiliscus is most active during the rainy summer months. Many of these snakes are seen crossing roads at night. However, some have also been spotted warming themselves in the sun early in the morning. People who keep these snakes say they can become calm quite quickly when in captivity.
What Does the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Eat?
Scientists have studied the stomachs of several C. basiliscus snakes. They found mammal hair, which likely came from rodents. This suggests that rodents are a common part of their diet.
How Strong Is Its Venom?
The Crotalus basiliscus is known for producing a lot of very strong venom. Because of this, large snakes of this species should be considered very dangerous.
Scientists have measured the average amount of dried venom this snake produces, which is about 297 milligrams. The venom contains special proteins called proteases.
There are special medicines called antivenoms that can help people bitten by this snake. Antivenom is made in Mexico and also in the US. It contains antibodies that can protect against bites from this snake.
How Is the Mexican West Coast Rattlesnake Classified?
Before 1989, scientists thought there were two types (subspecies) of C. basiliscus. One was C. b. basiliscus, and the other was C. b. oaxacus. However, in 1989, scientists decided that C. b. oaxacus was actually a type of C. molossus.
Sometimes, you might also hear about another subspecies called C. b. totonacus. This snake was found in northeastern Mexico. It was usually considered a type of C. durissus. But in 2004, scientists decided it was a completely separate species, now called Crotalus totonacus. This shows how scientists sometimes change how they classify animals as they learn more.
See also
 In Spanish: Serpiente de cascabel de la costa oeste de México para niños
In Spanish: Serpiente de cascabel de la costa oeste de México para niños


