Cultural diversity facts for kids
Cultural diversity means having many different cultures in one place or around the world. It's about celebrating what makes each culture special, instead of everyone being the same. Think of it like a big garden with many different kinds of flowers, all growing together. Cultural diversity also means that different cultures respect and understand each other. It's about including different ways of thinking and living in our communities and in the world.
Contents
What Cultural Diversity Means
Cultural diversity can mean a few important things:
- Protecting unique cultures: It's about making sure smaller or less common cultures are safe and can continue to thrive.
- Keeping cultures alive: This means helping cultures that might be in danger of disappearing.
- Valuing culture over money: Sometimes, cultural things like music or movies are seen just as products to sell. Cultural diversity helps us remember that culture is more than just business. It's about art, traditions, and ways of life.
- Cultural rights: This idea suggests that everyone has a right to their own culture, just like they have other human rights.
Cultural diversity is important in many areas:
- Economy: Having many different cultural goods and services available.
- Art: Seeing a wide variety of art styles and types.
- Participation: Different groups joining in a nation's culture.
- Heritage: Museums and other places showing many different cultural traditions.
- Multiculturalism: Many different ethnic groups and their traditions living together in a country.
Often, when countries talk about cultural diversity on a global level, they focus on the economic side. They want to protect their own cultural industries, like their film or music industries, from being taken over by bigger ones.

The UNESCO sees cultural diversity in a broad way. It includes lifestyles, values, traditions, and beliefs, not just art. UNESCO says that cultural diversity is as important for people as biodiversity (many different kinds of plants and animals) is for nature.
How We Measure Cultural Diversity
It's hard to measure cultural diversity exactly. One way is to count the number of different languages spoken in a region or worldwide.
Sadly, by this measure, the world's cultural diversity is shrinking fast. In the 1990s, a researcher named David Crystal found that about one language was disappearing every two weeks. If this continues, over 90% of the world's languages could be gone by the year 2100.
In 2003, a study ranked countries by how diverse they are in terms of ethnic groups, languages, and religions.
Cultural Diversity Around the World
The UNESCO has been working to protect cultural diversity since it started in 1945.
The World Day for Cultural Diversity for Dialogue and Development was created in 2002. It is celebrated every year on May 21. This day helps promote cultural diversity, understanding between cultures, and sustainable development.
In 2001, UNESCO released the Universal Declaration on Cultural Diversity. This important document said that cultural diversity includes everything that makes a society unique. This means lifestyles, values, traditions, and beliefs. The declaration also linked cultural diversity to human rights, like freedom of expression. It said that cultural diversity helps new ideas and creativity grow, and it drives both economic and personal development.
In 2005, UNESCO created the Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions (often called the "2005 Convention"). This agreement aims to protect cultural diversity from becoming too similar because of globalization. It says that linguistic diversity (many different languages) is a key part of cultural diversity.
The 2005 Convention also set up an International Fund for Cultural Diversity. This fund helps developing countries create cultural policies and support their own cultural industries. As of 2023, this fund has helped many projects in different countries.
What Affects Cultural Diversity
Many things can help or hurt cultural diversity, including actions by governments and individuals.
Globalization and Mass Media
Globalization means that countries and people around the world are becoming more connected. With new technology, information and money can move across borders very easily. This has changed how countries, businesses, and people interact.
The growth of mass media, like TV and the internet, has a big impact. While it can be good to share information, it can also make cultures too similar. When information spreads so easily, cultural meanings, values, and tastes might start to become the same everywhere. This could make the unique identity of people and societies weaker.
Artistic Freedom
Governments can either limit or protect artistic freedom. Limiting it means things like censorship (stopping artists from showing their work) or watching what artists do. Protecting it means letting artists express themselves freely and keeping them safe from harm.
Sadly, attacks against artists have increased in recent years. This includes online threats. Musicians and authors are often targets. Many groups are working to support artists' rights around the world.
Gender Equality in Creative Jobs
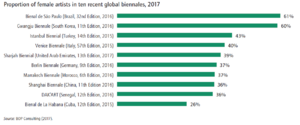
There is still a gap between men and women in creative jobs. Women often get paid less, have less access to funding, and are less likely to be in leadership roles. For example, in 2018, only 34% of Ministers for Culture were women. Women are often found in certain cultural fields, like arts education or book publishing.
Travel for Artists
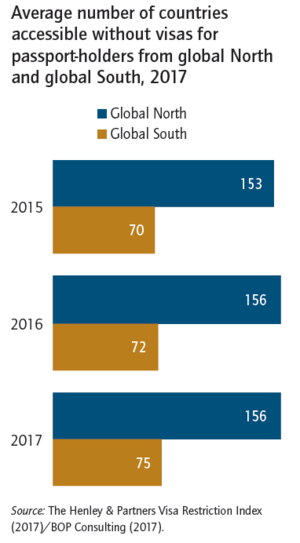
It can be hard for artists and creative people to travel, especially those from developing countries. Artists need to travel to perform, attend workshops, or meet other artists. Their ability to travel depends on their country's passport. For example, someone with a German passport can visit many more countries without a visa than someone with an Afghan passport. These travel limits often stop artists from sharing their work at international events.
How Culture is Managed
Countries that signed the 2005 Convention have made good progress in supporting digital art, helping creative businesses, and updating laws about copyright.
Trade in Cultural Goods
Some trade agreements between countries now include rules that help promote cultural diversity. This means they try to protect and support different cultural expressions, even when countries are trading goods and services.
Online Cultural Platforms
Online platforms that share culture can also help promote diversity. For example, Google Arts & Culture and Europeana aim to share stories and art from communities that might not have been widely known before. They work to show a wider range of cultural heritage.
Your Choices
Every person can help promote cultural diversity through their own choices. This includes sharing their own culture with others. The "Do One Thing for Diversity and Inclusion" campaign encourages people to explore music, books, art, and traditions from cultures they don't know. It also asks them to share their own culture with others.
An American lawyer, Juliette Passer, said that by interacting with different people and thinking about those experiences, we can better understand and appreciate differences.
Local Efforts for Diversity
Cities around the world are also working to promote cultural diversity. For example, in 2002, the city of Porto Alegre in Brazil held a meeting for culture. Mayors and cultural leaders from different cities came together. This led to the creation of "Culture 21" in 2004. This document helps cities include cultural diversity in their local plans and policies.
See also
 In Spanish: Diversidad cultural para niños
In Spanish: Diversidad cultural para niños
- Criticism of multiculturalism
- Cross-cultural communication
- Cultural agility
- Cultural Diversity Award (UNESCO)
- Cultural safety
- Foundation for Endangered Languages
- Heritage Day (South Africa)
- Intercultural dialogue
- Intercultural relations
- Melting pot
- Mondialogo
- Multiculturalism
- Social cohesion
- Social integration
- Subculture