Cytochrome facts for kids
Cytochromes are important proteins found in almost all living things, from tiny bacteria to humans. They play a big role in how our bodies make energy. Think of them as tiny workers that help move electricity (electrons) around inside cells. This movement helps create a special energy molecule called ATP, which is like the fuel our cells need to do everything.
Some cytochromes work alone, like cytochrome c. Others are part of larger teams called enzyme complexes. These teams help with chemical reactions that involve moving electrons, which are called redox reactions.
Contents
What Are Cytochromes?
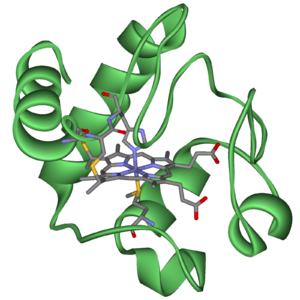
Cytochromes are a type of protein that contains a special group called a "haem" group. This haem group is what gives cytochromes their unique ability to handle electrons. It's similar to the haem group found in hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in our blood.
The main job of cytochromes is to help with electron transport. This is a series of steps where electrons are passed from one molecule to another, like a bucket brigade. Each time an electron is passed, a little bit of energy is released. This energy is then used to make ATP.
How Do Cytochromes Work?
The haem group inside cytochromes is key to their function. It contains an iron atom that can easily gain or lose electrons.
- When the iron atom gains an electron, it changes its electrical state.
- When it loses an electron, it changes back.
This back-and-forth change allows cytochromes to pick up electrons from one molecule and pass them on to another. This process is essential for many important jobs in the body, especially for making energy in places like mitochondria (the "powerhouses" of our cells) and chloroplasts (where plants make food using sunlight).
Discovering Cytochromes
Scientists first noticed cytochromes way back in 1884. They were described as "respiratory pigments" because they seemed to be involved in how living things breathe and use oxygen. At that time, other important pigments like myoglobin (which stores oxygen in muscles) were also being studied.
In the 1920s, a scientist named David Keilin rediscovered these special pigments. He gave them the name "cytochromes," which means "cellular pigments," because they are found inside cells. Keilin's work helped us understand that cytochromes are a type of haem protein and are vital for life.
Different Kinds of Cytochromes
Just like there are different types of cars, there are several kinds of cytochromes. Scientists can tell them apart by looking at how they absorb light, using a method called spectroscopy. The main differences between them come from slight variations in their haem groups.
In our cells, especially in mitochondria and chloroplasts, these different types of cytochromes often work together in teams. They are part of important metabolic pathways that help cells get energy and carry out other vital functions.
See also