Darrell Figgis facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Darrell Figgis
|
|
|---|---|

1924 portrait of Figgis
|
|
| Teachta Dála | |
| In office June 1922 – 27 October 1925 |
|
| Constituency | Dublin County |
| Personal details | |
| Born | 17 September 1882 Rathmines, Dublin, Ireland |
| Died | 27 October 1925 (aged 43) Finsbury, Islington, London, England |
| Political party |
|
| Spouse | Millie Tate (1905–1924; her death) |
| Occupation |
|
Darrell Edmund Figgis (Irish: Darghal Figes; 17 September 1882 – 27 October 1925) was an Irish writer, activist, and politician. He was involved with Sinn Féin and later became an independent member of parliament in the Irish Free State.
Contents
Early Life of Darrell Figgis
Darrell Figgis was born in Rathmines, Dublin, Ireland, on September 17, 1882. His father, Arthur William Figges, was a tea merchant. When Darrell was a baby, his family moved to Calcutta, India. His father started a tea business there.
The family returned to Ireland when Darrell was ten years old. His father still spent a lot of time working in India. As a young man, Darrell worked in London for his uncle's tea business. During this time, he became very interested in books and writing.
Darrell Figgis's Literary Career
In 1910, Darrell Figgis joined the Dent publishing company. A famous writer named G. K. Chesterton helped him. Figgis lived in London for much of this time.
In 1913, he moved to Achill Island in Ireland. He wanted to write, learn the Irish language, and understand Irish culture better. Many people believed that true Irish culture was strongest on the western coast. After the Easter Rising in 1916, he left the publishing company. He then started his own firm. He republished old Irish books, including works by William Carleton.
Darrell Figgis's Political Life
Joining the Irish Volunteers and Gun-Running
Darrell Figgis joined the Irish Volunteers in Dublin in 1913. This group aimed to protect Ireland's right to self-government. He also helped set up a group of Volunteers in Achill, where he lived.
While in London, he met The O'Rahilly. He learned about people who sold weapons. Figgis became part of a group in London that planned to buy rifles for the Volunteers. This group included Molly and Erskine Childers, Mary Spring Rice, Alice Stopford Green, and Roger Casement.
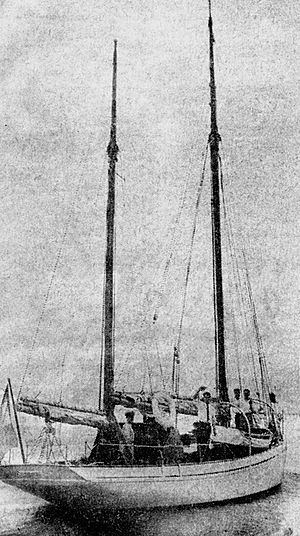
Figgis traveled with Erskine Childers to Germany to buy old army rifles. They then arranged for the rifles to be moved from a tugboat to two yachts, the Asgard and the Kelpie. The Asgard was sailed by the Childers, Mary Spring Rice, and two fishermen.
Figgis's job was to signal to the Asgard that it was safe to land. However, a big storm made it impossible for him to get out to sea. Luckily, the yachts still managed to reach their destinations safely. The Asgard sailed right into Howth harbour. This secret plan to bring weapons into Ireland was a success.
When the Volunteers were taking the rifles to Dublin, they met British soldiers and police. Figgis and Thomas MacDonagh tried to distract the officers. This allowed the Volunteers to quietly spread out with their new weapons.
Imprisonment and Political Changes
-
Piece 201-008; Darrell Figgis, Lectures, Howth Gun-Running, Internment (1918).pdf
Dublin Castle Records for Darrell Figgis
-
Piece 207-081; Darrell Figgis (1922).pdf
Military intelligence file for Darrell Figgis
Even though Figgis didn't take part in the 1916 Easter Rising, British authorities arrested him. He was held in Reading Gaol from 1916 to 1917. His wife, Millie, wrote letters to newspapers about his unfair imprisonment.
After his release, Figgis returned to Ireland. He became an Honorary Secretary of the Sinn Féin party. At a big Sinn Féin meeting, Éamon de Valera became the new President. Figgis was arrested again in 1918 because of false accusations about a "German Plot." He was sent back to England. In 1918, he became the editor of a newspaper called The Republic.
Irish War of Independence (1919–1921)
From 1919 to 1921, Figgis led a group that studied Ireland's resources and industries. During this time, he had disagreements with Michael Collins, who was a very important leader.
Once, while Figgis was at a Dáil Court meeting, British soldiers raided it. An officer threatened to hang Figgis and Peadar Kearney. But another officer stepped in, and they were set free.
The Truce and Political Divisions
Darrell Figgis supported the Anglo-Irish Treaty. This treaty created the Irish Free State. He disagreed with a plan by Collins and De Valera to unite Sinn Féin for the 1922 elections. Figgis believed this plan was not good for the country.
He encouraged other groups to put forward their own candidates in the elections. Because he went against Sinn Féin's policy, he was removed from the party. This showed how divided the political groups were at the time.
Attack by Republicans
On June 13, 1922, Dublin newspapers reported that Darrell Figgis had been attacked. Three men entered his home and assaulted him. His wife, Millie, was very shaken by the event. Later, a politician named Robert Briscoe said he was one of the attackers. This attack happened because of the strong political disagreements during that period.
Helping to Write the Constitution
After the Anglo-Irish Treaty was signed, a new constitution was needed for the Irish Free State. Arthur Griffith wanted Figgis to lead the group writing the constitution. However, Michael Collins disagreed and took the lead himself.
Collins and Figgis had different ideas, but they worked together on this important project. Other members of the committee also helped to shape the new constitution.
Elections and Later Life
In the 1922 and 1923 general elections, Darrell Figgis was elected as an independent Teachta Dála (member of parliament) for the Dublin County area.
While he was still a TD, he also ran for the Seanad Éireann (the upper house of parliament) in 1925, but he did not win.
Radio Broadcasting Inquiry
In December 1923, a committee was formed to decide how public radio broadcasting should work in the Irish Free State. One big question was whether the government should run the radio or if a private company should do it. Figgis joined this committee.
Later, a former business partner of Figgis, Andrew Belton, made accusations against him. Belton claimed that Figgis had promised to use his political influence to help him get government contracts. Figgis strongly denied these claims. He said they were made because Belton was upset that he didn't get special treatment. Figgis resigned from the committee, and another inquiry was started to look into the accusations.
Works by Darrell Figgis
- A Vision of Life (1909) poems [1]
- Shakespeare: A Study (1911) [2]
- The Crucibles of Time (1911) poems [3]
- Studies and Appreciations (1912) [4]
- Broken Arcs (1912) novel [5]
- Queen Tara (1913) play [6]
- Jacob Elthorne (1914) novel as Michael Ireland [7]
- The Mount of Transfiguration (1915) poems [8]
- AE (George W. Russell). A Study of a Man and a Nation (1916) [9]
- The Gaelic State in the Past & Future, or, "The Crown of a Nation" (1917)
- A Chronicle of Jails (1917)
- Bye-Ways of Study (1918) essays [10]
- Children of Earth (1918) novel as Michael Ireland
- The Historic Case for Irish Independence (1918) [11]
- Carleton's Stories of Irish Life (1918/9) by William Carleton, editor
- A Second Chronicle of Jails (1919)
- Bogach Bán (1922) poem
- The Economic Case for Irish Independence (1920) [12]
- Planning for the Future (1922) address to the Architectural Association of Ireland
- The House of Success (1922) novel as Michael Ireland
- The Irish Constitution Explained (Dublin: Mellifont Press, 1922 [13][14]
- The Return of the Hero (1923) novel, as Michael Ireland
- The Paintings of William Blake (1925)
- John Milton and Darrell Figgis [editor]
- Comus: A Mask with Eight Illustrations By William Blake (1926) John Milton, editor
- Recollections of the Irish War (1927) [15]