Differential equation facts for kids
A differential equation is a special kind of equation used in math. It doesn't just involve numbers or simple variables like 'x' or 'y'. Instead, it includes how fast those variables are changing. Think of it like a puzzle where you know how something is changing, and you need to figure out what that "something" actually is.
The cool thing about differential equations is that their answer isn't just a number. The answer is usually a function, which is like a rule that tells you how different things are related. For example, it might tell you how a car's speed changes over time, or how heat spreads through an object.
These equations are super useful because in the real world, we often know how things are changing, but not exactly what they are. Differential equations help us find that missing information.
Contents
What Are the Types of Differential Equations?
Differential equations come in different types, depending on how many variables and how many "change rates" they involve.
First-Order Equations
If an equation only talks about one variable (like 'x') and how fast it changes (its derivative), it's called a first-order differential equation. It's the simplest kind.
Higher-Order Equations
Sometimes, an equation might involve the change of a change, or even more. These are called higher-order differential equations. They describe more complex changes.
Partial Differential Equations
If an equation has more than just one or two changing variables, it's called a partial differential equation. These are used when something depends on many different things at once, like temperature changing based on both time and location.
Coupled Equations
Sometimes, several differential equations work together to describe a single situation. These are known as coupled differential equations. They help explain how different parts of a system affect each other.
Solving Differential Equations
Some differential equations are easy to solve exactly, meaning you can find a perfect answer. Others are much harder. For these tough ones, people often use computer programs to find very close estimates.
Even though they can seem complicated, differential equations are vital for many experts. Most scientists, engineers, and mathematicians learn about them in college. Some mathematicians even spend their whole careers studying these challenging equations.
How Are Differential Equations Used?
Differential equations are used in many areas of science and engineering because they help describe how real things work and change.
- Physics: They describe how things move, like a swinging pendulum or the path of a rocket. They also explain oscillations, which are back-and-forth movements.
- Radioactive Decay: Scientists use them to calculate how fast radioactive materials break down over time.
- Newton's Laws: Isaac Newton's Second Law of Motion, which explains how force, mass, and acceleration are related, is a differential equation.
- Cooling: Newton's Law of Cooling uses these equations to predict how fast an object cools down.
- Waves: The wave equation describes how waves, like light or sound, travel.
- Fluids: The Navier–Stokes equations explain how fluids, like water or air, move and flow.
- Mechanics: The Hamiltonian equations are used in advanced mechanics to understand how systems behave.
People Who Studied Differential Equations
Many brilliant minds have contributed to our understanding of differential equations:
- Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi
- Hiroshi Umemura
- Israel Gelfand
- Peter Lax
- Ryogo Hirota
- Sofya Kovalevskaya
- Vladimir Arnold
Related pages
- Finite element method
- Numerical methods for ordinary differential equations
- Numerical methods for partial differential equations
Images for kids
-
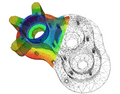
Visualization of heat transfer in a pump casing, created by solving the heat equation. Heat is being generated internally in the casing and being cooled at the boundary, providing a steady state temperature distribution.
See also
 In Spanish: Ecuación diferencial para niños
In Spanish: Ecuación diferencial para niños