Diospyros virginiana facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Diospyros virginiana |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
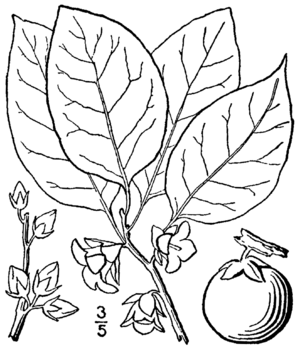
| Botanical details of buds, flowers and fruit | |
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ebenaceae |
| Genus: | Diospyros |
| Species: |
D. virginiana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Diospyros virginiana |
|
 |
|
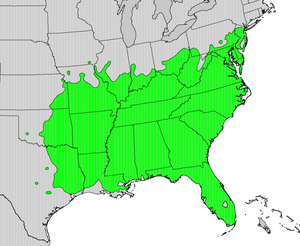
| Distribution map of the American persimmon | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Diospyros mosieri S.F.Blake |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Diospyros virginiana is a type of persimmon tree. It is often called the American persimmon or common persimmon. Other fun names for it include possumwood or sugar plum.
This tree grows naturally across a large part of the United States. You can find it from southern Connecticut all the way down to Florida. It also stretches west to states like Texas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Iowa.
Even though it grows wild, people have been growing this tree for a very long time. Native Americans started growing it for its tasty fruit and strong wood ages ago.
The American persimmon tree can grow up to 20 m (66 ft) (about 65 feet) tall. It likes soil that drains water well. In summer, the tree produces sweet-smelling flowers. To get fruit, you need both a male and a female tree. This is because the flowers are dioecious, meaning male and female parts are on separate plants.
Many types of American persimmon can grow fruit without needing pollination. This is called parthenocarpic fruit, and it means the fruit has no seeds. Insects and wind help pollinate the flowers. Trees usually start growing fruit when they are about 6 years old.
The fruit is round or oval. It is usually orange-yellow, but sometimes it can look a bit bluish. Each fruit is about 2 to 6 cm (3⁄4 to 2+1⁄4 in) (1 to 2.5 inches) wide. In the southern and midwestern U.S., people just call them persimmons or "'simmons". They are very popular in desserts and other foods.
Some types of American persimmon grown for sale include 'Early Golden', 'John Rick', 'Miller', 'Woolbright', and 'Ennis'. 'Ennis' is special because it grows seedless fruit. Another name for the American persimmon, 'date-plum', is also used for a different persimmon species found in South Asia, called Diospyros lotus.
Contents
What Does the American Persimmon Look Like?
The American persimmon is usually a small tree. It often grows to be 30 to 80 feet (9 to 24 m) (9 to 24 meters) tall. It has a short, thin trunk and branches that spread out. These branches often hang down, forming a wide or narrow, round-shaped top. Its roots are thick and can spread out to grow new trees. Sometimes, this tree grows more like a large bush.
The leaves are oval-shaped and have smooth edges. The flowers are separate male and female flowers on short stems. Male flowers have many stamens (the parts that make pollen). Female flowers are usually found alone and have an ovary that will become the fruit. The fruit stem is very short.
The fruit is round and about an inch or more wide. It is orange-yellow, sometimes with a bluish tint. It has a sweet, but also slightly bitter, pulp. At the bottom of the fruit, you can see the parts of the flower that stayed on as the fruit grew. When the fruit is unripe, it tastes very bitter. But after it gets soft, especially after a light frost, its flavor becomes much better.
- Bark: The bark is dark brown or dark gray. It has deep cracks that make it look like plates with a scaly surface. The smaller branches are thin and zigzag. The bark tastes bitter.
- Wood: The wood is very dark, especially the inner part called heartwood. The outer part, called sapwood, is yellowish-white. The wood is heavy, hard, strong, and has a very tight grain. The heartwood is a true type of ebony. It takes about 100 years for a tree to grow enough ebony wood to be useful.
- Winter Buds: The buds are small, about one-eighth of an inch long. They are covered in thick reddish or purple scales.
- Leaves: The leaves grow one after another on the stem. They are usually four to six inches (152 mm) long and oval-shaped. They are dark green and shiny on top, and paler underneath. In the fall, they sometimes turn orange or red, or they might just fall off without changing color.
- Flowers: The flowers bloom in May or June when the leaves are partly grown. Male and female flowers are usually on separate trees. The flowers are greenish-yellow or creamy white.
- Fruit: The fruit is a juicy berry. It can have one to eight seeds, or sometimes none. It is crowned with the remains of the flower's style and sits in the enlarged flower base. The fruit is round and pale orange, often with a red blush. It might have a slight powdery coating. When it ripens, it turns yellowish-brown after freezing. The flesh is bitter when green but becomes sweet and delicious when ripe.
Where Does the American Persimmon Grow?
This tree is very common in the South Atlantic and Gulf states of the U.S. It grows largest in the area around the Mississippi River. It is found along the coast from Connecticut to Florida. West of the Appalachian Mountains, it grows in southern Ohio, southeastern Iowa, and southern Missouri. When it reaches Louisiana, eastern Kansas, and Oklahoma, it can become a very tall tree, sometimes reaching one hundred fifteen feet high.
Scientists have found old remains of persimmon trees in rocks from Greenland and Alaska. They have also found them in older rock layers in Nebraska.
Some scientists think the American persimmon was eaten by large animals like mammoths that lived in North America thousands of years ago. A study in 2015 showed that when persimmon seeds passed through the stomach of modern elephants, they sprouted faster. This supports the idea that ancient elephant-like animals helped spread persimmon seeds before they died out.
How People and Animals Use Persimmons
Birds, raccoons, skunks, deer, wild hogs, flying squirrels, and opossums all enjoy eating the persimmon fruit.
The fruit is well-known for its special qualities. It is a round berry that can have different numbers of seeds, from eight to none. It ripens in late autumn and is pale orange with a red side. It often has a slight powdery coating. People in the South sometimes trick newcomers into tasting an unripe persimmon. Its very bitter taste is quite a shock! The bitterness comes from a substance called tannin. During the American Civil War, the seeds were even used as buttons.
The fruit has a lot of vitamin C. The unripe fruit is extremely bitter. But the ripe fruit can be eaten raw, cooked, or dried. The fruit pulp can be used to make pie, pudding, jam, and molasses. You can make a tea from the leaves. The roasted seeds can even be used as a coffee substitute. Other popular treats include persimmon pie, persimmon pudding, or persimmon candy.
The fruit can also be fermented with hops, cornmeal, or wheat bran to make a type of beer or brandy. The wood is heavy, strong, and has a very tight grain. It is often used for woodturning, which is shaping wood on a spinning machine.
Growing Persimmon Trees
The American persimmon tree prefers light, sandy soil that drains water well. However, it can also grow in rich, southern lowland areas.
The fruit from different persimmon trees can vary a lot in size and taste. Some trees in the South produce fruit that tastes delicious even without a frost. But trees right next to them might produce fruit that never becomes good to eat.
The tree was brought to England before 1629 and is grown there, but its fruit rarely ripens fully. It is easy to grow from seeds. You can also grow new trees from its stolons, which are underground stems that produce new plants. The tree is strong enough to grow in southern England and the Channel Islands.
It's a common idea that persimmon fruit needs frost to ripen and soften. This process is called bletting. However, some types, like 'pieper' and 'NC21' (also known as 'supersweet'), lose their bitterness easily and become very sweet when they are just slightly soft. This happens even in the British climate. On the other hand, some types, like the large-fruited 'yates', stay bitter even when they are completely soft. Frost actually damages the cells inside the fruit, causing it to rot instead of ripen. Only fruit that is already fully ripe and soft can handle some frost. When this happens, it might dry out and become even sweeter, which is probably where the idea about frost came from. The same is true for the Oriental persimmon (Diospyros kaki).
Is Persimmon Fruit Safe to Eat?
Eating too much unripe persimmon fruit can sometimes cause a problem called a diospyrobezoar. This is when indigestible parts of the persimmon pulp get stuck in your intestines, most often in your stomach. It's best to eat persimmons only when they are fully ripe and soft.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Caqui de Virginia para niños
In Spanish: Caqui de Virginia para niños






