Egyptian calendar facts for kids
The ancient Egyptian calendar was a special way the people of ancient Egypt kept track of time. It helped them know when to plant crops and when important festivals would happen. At first, their year had 365 days. It was divided into 12 months, and each month had 30 days.
Later, the Egyptians added five extra days to the end of the year. This happened around 3000 BC, during the time of the First Dynasty. These extra days were like special holidays.
Contents
How the Ancient Egyptian Calendar Worked
The Nile River and the Star Sirius
Ancient Egyptian astronomers noticed something important. The yearly flood of the Nile River usually happened around the same time they could first see the bright star Sirius in the morning sky, just before sunrise. This was a very important event for their farming.
Understanding the Calendar's "Drift"
Even with 365 days, the Egyptian calendar wasn't perfectly matched to the Earth's orbit around the sun. It would slowly "drift" by about one day every four years. This meant that over many years, the seasons would slowly shift in the calendar. However, this drift was so slow that it didn't cause big problems for people in their lifetime. For example, if someone lived to be 60 years old, the calendar would only be off by about 15 days.
Fixing the Egyptian Calendar
Early Attempts to Correct the Drift
Over time, people tried to make the calendar more accurate. In 238 BC, a rule called the Decree of Canopus suggested adding a sixth extra day every four years. This was an early attempt to create a "leap day" like we have today. However, this rule was mostly ignored by the people.
The Roman Emperor's Changes
Much later, in 30 BCE, the Roman Emperor Augustus made changes to the Egyptian calendar. He added a leap day every four years, just like the Julian calendar that was used in Rome at the time. This change helped to make the Egyptian calendar match the seasons more closely and brought it in line with the Roman way of telling time.
Images for kids
-
A section of the hieroglyphic calendar at the Kom Ombo Temple, showing the change from Month XII to Month I without mentioning the five extra days.
-
Astronomical ceiling from the Tomb of Senenmut (XVIII Dynasty, around 1479–1458 BC).
-
The Nile flood near Cairo around 1830.
-
Sirius (bottom) and Orion (right), seen from the Hubble Space Telescope.
-
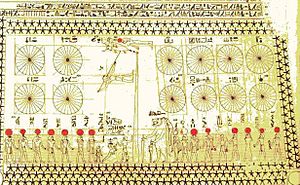
A Middle Kingdom star chart.
-
A hieroglyphic calendar at Elephantine.
-
An 11th-century Coptic calendar icon showing two months of saints.
See also
 In Spanish: Calendario egipcio para niños
In Spanish: Calendario egipcio para niños