Euastacus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Euastacus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Euastacus spinifer | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Crustacea |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Order: | Decapoda |
| Family: | Parastacidae |
| Genus: | Euastacus Clark, 1936 |
| Type species | |
| Euastacus elongatus Clark, 1941
|
|
 |
|
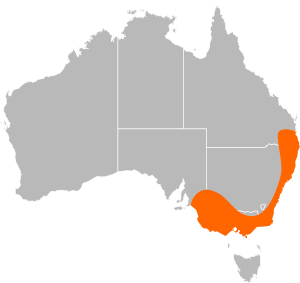
Euastacus is a group of freshwater crayfish often called "spiny crayfish." You can find them in the southeastern part of Australia. They belong to the same family, Parastacidae, as another type of Australian crayfish called Cherax. This family of crayfish only lives in the Southern Hemisphere.
Contents
What Makes Spiny Crayfish Special?
Euastacus crayfish are easy to tell apart from Cherax species. Euastacus have short, strong spikes on their claws and bodies. Cherax crayfish have smooth shells.
Many Euastacus species also grow much larger. For example, the Murray River crayfish (Euastacus armatus) is the second largest freshwater crayfish in the world! The biggest one is the Tasmanian giant freshwater crayfish (Astacopsis gouldi), which lives on the Australian island of Tasmania. Astacopsis is actually a very close relative of Euastacus.
Where Do Spiny Crayfish Live?
Australian freshwater crayfish often live in different kinds of places. Cherax species usually live in lowland rivers, swamps, and temporary waters. This includes areas like the Murray-Darling Basin.
On the other hand, Euastacus species only live in places with permanent water. They prefer upland rivers at higher altitudes. You can find them in the Murray-Darling Basin and many rivers flowing to the east and south coasts.
There are a few exceptions to this rule:
- The Murray River crayfish used to live along the entire Murray River. It also lived in many upland areas. Today, you can still find it in the middle parts of the Murray River.
- The Glenelg Spiny Crayfish (Eustacus bispinosus) lives in lowland areas of the Glenelg River system. It also lives in the Eight Mile Creek/Ewen Ponds system.
- The Gippsland Crayfish (Euastacus kershawi) lives in lowland parts of some streams in the Gippsland area.
Even when these Euastacus crayfish live in lowland areas, they need very clean water. They need good water flow, lots of oxygen, and low salt levels. Unlike Cherax (yabby) species, Euastacus crayfish cannot survive if their homes dry up.
Unique Homes and Long Lives
The Cherax genus lives in many more parts of Australia, including the southwest. But Euastacus crayfish are only found in southeastern Australia. Many Euastacus species are "endemic" to certain areas. This means they are found only in one river or creek catchment. Some Euastacus species also live in upland reservoirs.
Euastacus crayfish grow very slowly. They also live a very long time, possibly over 40 years for some species! They also take a long time to become old enough to have babies. Because of these traits, Euastacus species are easily harmed by changes in their environment. This also means they cannot support fishing where people catch and kill them.
Types of Spiny Crayfish
There are about 50 known species in the Euastacus group. Sadly, many of them are in danger. The IUCN Red List tracks how threatened species are.
- 17 species are critically endangered (CR) – this means they are at extremely high risk of disappearing.
- 17 species are endangered (EN) – they are at very high risk.
- 5 species are vulnerable (VU) – they are at high risk.
- 1 species is near threatened (NT) – they might become threatened soon.
- 8 species are least concern (LC) – they are not currently at risk.
- 1 species is data deficient (DD) – we don't have enough information about them.
- Euastacus armatus (Von Martens, 1866)

- Euastacus australasiensis (H. Milne-Edwards, 1837)

- Euastacus balanesis Morgan, 1988

- Euastacus bidawalis Morgan, 1986

- Euastacus bindal Morgan, 1989

- Euastacus bispinosus Clark, 1936

- Euastacus brachythorax Riek, 1969

- Euastacus clarkae Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus claytoni Riek, 1969

- Euastacus crassus Riek, 1969

- Euastacus dalagarbe Coughran, 2005

- Euastacus dangadi Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus diharawalus Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus diversus Riek, 1969

- Euastacus eungella Morgan, 1988

- Euastacus fleckeri (Watson, 1953)

- Euastacus gamilaroi Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus girurmulayn Coughran, 2005

- Euastacus gumar Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus guruhgi Coughran, 2005

- Euastacus guwinus Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus hirsutus (McCulloch, 1917)

- Euastacus hystricosus Riek, 1951

- Euastacus jagabar Coughran, 2005

- Euastacus jagara Morgan, 1988

- Euastacus kershawi Smith, 1912

- Euastacus maccai McCormack & Coughran, 2008

- Euastacus maidae (Riek, 1956)

- Euastacus mirangudjin Coughran, 2002

- Euastacus monteithorum Morgan, 1989

- Euastacus morgani Coughran & McCormack, 2011
- Euastacus neodiversus Riek, 1969

- Euastacus neohirsutus Riek, 1956

- Euastacus pilosus Coughran & Leckie, 2007

- Euastacus polysetosus Riek, 1951

- Euastacus reductus Riek, 1969

- Euastacus rieki Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus robertsi Monroe, 1977

- Euastacus setosus (Riek, 1956)

- Euastacus simplex Riek, 1956

- Euastacus spinichelatus Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus spinifer (Heller, 1865)

- Euastacus sulcatus Riek, 1951

- Euastacus suttoni Clark, 1941

- Euastacus urospinosus (Riek, 1956)

- Euastacus valentulus Riek, 1951

- Euastacus wiowuru Morgan, 1986

- Euastacus yanga Morgan, 1997

- Euastacus yarraensis (McCoy, 1888)

- Euastacus yigara Short & Davie, 1993



