Phobos-Grunt facts for kids
| Phobos-Grunt Фобос-Грунт |
|
|---|---|
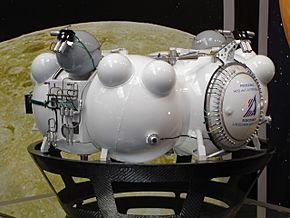 A model of Phobos-Grunt's base section |
|
| Organization: | Russian Federal Space Agency |
| Mission type: | Orbiter, lander, sample return |
| Flyby of: | Phobos |
| Satellite of: | Mars |
| Launch date: | 8 November 2011 |
| Launch vehicle: | Zenit rocket |
| Launch site: | Baikonur Cosmodrome |
| Mass: | 8120 kg |
Quick facts for kids edit |
|
Phobos-Grunt (also known as Fobos-Grunt) was a Russian spacecraft that did not have a crew. Its main goal was to travel to Phobos, a moon of the planet Mars. The mission planned to bring a small piece of Phobos's soil back to Earth.
Scientists wanted Phobos-Grunt to orbit Mars and study it closely. It was designed to look at Mars' atmosphere, dust storms, and the space environment around it. After studying Mars, the spacecraft was supposed to land on Phobos. The plan was to collect a 200 gram (about 7 ounces) soil sample.
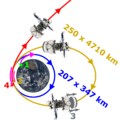
This mission was the first time Russia tried to send a spacecraft to another planet since the Mars 96 mission. Phobos-Grunt launched on November 8, 2011, from the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It was carried into space by a Zenit rocket. Two other things were launched with it: the Chinese spacecraft Yinghuo-1 and the Living Interplanetary Flight Experiment.
The name Phobos-Grunt (Russian: Фобос-Грунт) means Phobos-Soil in Russian.
Contents
The Mission's Goals
Phobos-Grunt had several important scientific goals. It aimed to learn more about Mars and its moon, Phobos.
Studying Mars
The spacecraft was meant to orbit Mars. From there, it would study the planet's thin atmosphere. It would also look at the huge dust storms that happen on Mars. Scientists hoped to understand how these storms form and move.
Phobos-Grunt also planned to study the plasma and radiation around Mars. Plasma is a superheated gas, and radiation is energy that travels through space. Understanding these helps us learn about the space environment.
Landing on Phobos
After orbiting Mars, Phobos-Grunt was supposed to land on Phobos. Phobos is a small, potato-shaped moon of Mars. The spacecraft had a special arm to collect a sample of the moon's soil. This soil sample, weighing 200 grams, would then be sent back to Earth. Studying a piece of Phobos up close could tell us a lot about its history. It could also give clues about how moons and planets form.
The Launch and Journey
The launch of Phobos-Grunt was a big event. It marked Russia's return to interplanetary missions.
Launch Details
Phobos-Grunt launched on November 8, 2011. It lifted off from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The powerful Zenit rocket carried it into space.
Two other payloads were on board. One was the Chinese spacecraft Yinghuo-1, which was also going to orbit Mars. The other was the Living Interplanetary Flight Experiment. This experiment carried tiny living things to see how they would survive in space.
What Happened Next
After launch, the spacecraft was supposed to fire its engines. This would send it on its way to Mars. However, the engines did not fire as planned. Phobos-Grunt got stuck in Earth's orbit. Engineers tried for weeks to fix the problem. Sadly, they could not regain control of the spacecraft.
On January 15, 2012, Phobos-Grunt fell back to Earth. Most of it burned up in the atmosphere. Some small pieces likely landed in the Pacific Ocean. This meant the mission to Phobos was not successful.
Images for kids
-
Modules -- A: lander, B: return module, C: reentry vehicle (not shown). Major components -- 1: solar panels, 2: reaction wheels, 3: landing gear, 4: robotic sample arm (second arm not shown), 6: sample transfer container, 7: attitude control thrusters, 8 and 10: fuel and helium tanks, 9: return module solar panels. Scientific instruments (some instruments are not visible from this angle or are not present on the model) -- a: Termofob thermodetector, b: GRAS-F seismogravimeter; c: METEOR-F cosmic dust detector, d: GAP (Gas Analytic Package) pyrolizer/thermal-differential analyzer, e: GAP chromatograph; f: GAP mass spectrometer, g: LAZMA mass spectrometer, h: MANAGA mass spectrometer, i: FPMS dust detector
-
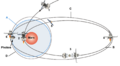
Phobos-Grunt around Mars: (1) Arrival of Phobos-Grunt, (2) Insertion maneuver in orbit around Mars, (3) Drop of the Fregat stage and separation of the probe and Yinghuo-1, (4) Maneuver for to raise the periapsis, (5) Yinghuo 1 starts his mission on the first orbit, (6) Maneuver to place himself in an orbit close to that of Phobos; (A) Orbit of Phobos, (B) Orbit of insertion of Phobos-Grunt and Yinghuo-1, (C) Orbit with raised periapsis, (D) Quasi-synchronous orbit with Phobos.
See also
 In Spanish: Fobos-Grunt para niños
In Spanish: Fobos-Grunt para niños