Phobos (moon) facts for kids

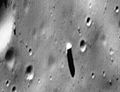
Enhanced-color view of Phobos obtained by Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on March 23 2008.
|
|
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Asaph Hall |
| Discovery date | August 18, 1877 |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Epoch J2000 | |
| Periapsis | 9235.6 km |
| Apoapsis | 9518.8 km |
| 9377.2 km | |
| Eccentricity | 0.0151 |
| 0.31891023 d (7 h 39.2 min) |
|
|
Average orbital speed
|
2.138 km/s |
| Inclination | 1.093° (to Mars's equator) 0.046° (to local Laplace plane) 26.04° (to the ecliptic) |
| Satellite of | Mars |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 26.8 × 22.4 × 18.4 km |
|
Mean radius
|
11.1 km (0.0021 Earths) |
| ~6100 km² (11.9 µEarths) |
|
| Volume | 5680 km³ (5.0 nEarths) |
| Mass | 1.072×1016 kg (1.8 nEarths) |
|
Mean density
|
1.887 g/cm³ |
| 0.0084–0.0019 m/s² (8.4-1.9 mm/s²) (860-190 µg) |
|
| 11.3 m/s (40 km/h) | |
| synchronous | |
|
Equatorial rotation velocity
|
11.0 km/h (at longest axis' tips) |
| 0° | |
| Albedo | 0.071 |
| Temperature | ~233 K |
| 11.3 | |
Phobos is the bigger of the two moons that orbit the planet Mars. It's the one closest to Mars. The other moon is called Deimos. An American astronomer named Asaph Hall found both Phobos and its sibling moon, Deimos, in 1877. He discovered them while looking at Mars from an observatory in Washington, D.C.
Phobos is a small moon that isn't perfectly round. It has an average size of about 11 km (7 mi) across. It is also seven times heavier than Deimos. Phobos gets its name from the Greek god Phobos. He was the son of Ares (the Greek name for Mars) and Aphrodite (Venus). Phobos was known as the god of horror or fear. This is where the word "phobia" comes from.
Phobos is very tiny compared to most other moons in our Solar System. It looks more like a lumpy potato than a round ball. At its widest, it is about 26 km across. At its narrowest, it is about 18 km across. This means it's roughly the size of a large city here on Earth.
Phobos is one of the darkest objects in the Solar System. It doesn't reflect much sunlight. The temperature on Phobos changes a lot. It can be about −4 °C (25 °F) on the side facing the Sun. But it drops to about −112 °C (−170 °F) on the shadowed side. The most famous feature on Phobos is a huge impact crater called Stickney. This crater covers a big part of the moon's surface. Scientists think that many grooves on Phobos were made by rocks. These rocks were thrown out when the asteroid hit and created the Stickney crater.
Contents
All About Phobos
How Phobos Orbits Mars
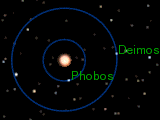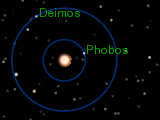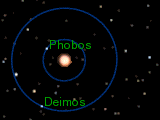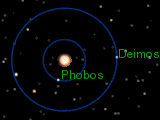
Scientists have studied Phobos's path around Mars very closely. It is known as "the best studied natural satellite in the Solar System" for its orbit. Phobos orbits Mars very closely, about 6,000 km (3,700 mi) from the Martian surface. This is closer to its planet than any other known moon.
Because it's so close, Phobos orbits Mars much faster than Mars spins. It completes one trip around Mars in just 7 hours and 39 minutes. This means that if you were on Mars, Phobos would appear to rise in the west. It would then move across the sky in about 4 hours and 15 minutes or less. Then it would set in the east. This happens twice every Martian day. A day on Phobos itself is about 7 hours and 40 minutes long.
What Phobos is Made Of
The features on Phobos are named after astronomers who studied it. They are also named after people and places from Jonathan Swift's book Gulliver's Travels.
Infrared images show that Phobos has material rich in carbon. This material is similar to what is found in certain meteorites called carbonaceous chondrites. Phobos's density is too low to be solid rock. This means it has many tiny holes inside it. Scientists think Phobos might even have a lot of ice hidden within it.
Phobos has many craters from impacts. The biggest one is Stickney. It's about 9 km (5.6 mi) wide. This crater covers a large part of the moon's surface. The impact that made Stickney must have almost broken Phobos apart. This is similar to how the crater Herschel almost shattered Mimas, another moon.
Recent pictures from Mars Global Surveyor show that Phobos is covered in a layer of fine dust and small rocks. This layer is at least 100 meters thick. Scientists believe it was created by impacts from other space objects. It's a mystery how this material stays on Phobos, since it has almost no gravity. If you stood on Phobos, Mars would look huge in the sky. It would take up almost a quarter of the sky!
Does Phobos Have Air?
Phobos does not have an atmosphere (air). This is because it is too small and has very low gravity. It also doesn't have a magnetic field.
Phobos's Gravity
Because Phobos is so small, its gravity is extremely weak. It's only about 1/1000th as strong as Earth's gravity. Phobos is shaped like an uneven potato, measuring 27 km × 22 km × 18 km. It doesn't have enough mass to pull itself into a round shape.
If you weigh 68 kg (150 lb) on Earth, you would weigh only about 60 g (2 oz) on Phobos. That's like weighing as much as a small candy bar! This means you could lift incredibly heavy things. Someone who can carry 10 kg on Earth could carry three elephants on Phobos!
Phobos's gravity is so weak that it's easy to float away into space. You could even throw a tennis ball or a baseball, and it would fly right off Phobos and never come back.
Phobos is slowly getting closer to Mars. Its orbit is dropping about 1.8 meters every century. In about 50 million years, Phobos will reach a point called the Roche limit. This is the distance where Mars's gravity will be strong enough to pull Phobos apart. When Phobos breaks up, some pieces will fall onto Mars. Other pieces will likely form a ring around Mars. This ring could last for millions of years.
Exploring Phobos
Space Missions to Phobos
Many spacecraft have taken pictures of Phobos up close. Their main job was usually to photograph Mars. The first was Mariner 7 in 1969. Then came Viking 1 in 1977. Mars Global Surveyor took pictures in 1998 and 2003. Mars Express visited in 2004, 2008, and 2010. And Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter was there in 2007 and 2008. In 2005, the Spirit Rover on Mars even took pictures of Phobos and Deimos in the night sky.
The Soviet Union tried to send two probes to Phobos in 1988. This was part of the Phobos program. Phobos 1 was accidentally shut down and lost. Phobos 2 reached Mars in 1989. It sent back some data and images. But it stopped working just before it could study Phobos's surface closely.
The Russian Space Agency launched a mission called Fobos-Grunt in 2011. This mission aimed to bring a sample of Phobos back to Earth. It also carried a life science experiment. China's space agency also contributed a satellite to this mission. However, after reaching Earth orbit, Fobos-Grunt failed to travel to Mars. It crashed back to Earth in 2012.
The Martian Moons Exploration (MMX) is a robotic space probe from Japan. It is planned to launch in 2024. MMX will be the first mission to bring samples back from Phobos. It will land on Phobos once or twice to collect samples. It will also fly by Deimos and watch Mars's climate.
This mission will help scientists learn if Mars's moons are captured asteroids. Or if they formed from a large object hitting Mars.
Why Humans Might Visit Phobos
Because Phobos is so close to Mars and has very low gravity, it could be a useful stop for astronauts. It might act like a space station. Astronauts and supplies could transfer there before going to Mars. Then they could return to Earth from Phobos. It's very likely that if humans go to Mars, they will also visit Phobos.
Phobos might also have frozen water. This water could be very helpful for astronauts. They could drink it or use it to get oxygen for breathing.
Some scientists think Phobos should be an early target for a human mission to Mars. Landing on Phobos would be much easier and cheaper than landing on Mars itself. A spacecraft landing on Mars needs to be able to enter the atmosphere and return to orbit. This is very difficult for a human mission. But a lander for Phobos could be like those used for the Moon or asteroids.
Also, the amount of fuel needed to land on Phobos and return is less than for a trip to the Moon. This is partly because Phobos's gravity is so weak. Exploring Phobos could help us prepare for human missions to Mars. It would also be exciting and scientifically valuable on its own.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Fobos (satélite) para niños
In Spanish: Fobos (satélite) para niños