Gallic War facts for kids
The Gallic Wars were a big series of military campaigns. They happened when Rome, led by the famous general Julius Caesar, fought against many different Gallic tribes. The main leader for the Gauls was Vercingetorix. These wars lasted for about eight years, from 58 BC to 50 BC.
Contents
What Was Gaul?
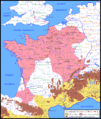
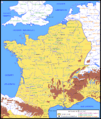
Gaul was a large area in ancient times. It covered much of what is now France, Belgium, and parts of Switzerland, Germany, and the Netherlands. Many different Celtic tribes lived there. They were known as the Gauls.
Why Did the Wars Start?
Julius Caesar was a powerful Roman general. He was the governor of a Roman province next to Gaul. In 58 BC, some Gallic tribes were moving near Roman lands. Caesar used this as a reason to start military action. He wanted to protect Rome's borders and its allies. He also wanted to gain fame and power for himself.
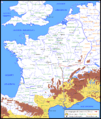
Early Campaigns (58–56 BC)
Caesar quickly began to conquer Gallic tribes.
- In 58 BC, he defeated the Helvetii and the Suebi. The Helvetii were trying to move through Roman territory. The Suebi were a Germanic tribe led by Ariovistus.
- In 57 BC, Caesar moved north. He fought against the Belgae, a group of strong tribes. He won many battles, like the Battle of the Sabis. This victory brought more of Gaul under Roman control.
- By 56 BC, Caesar had conquered most of western Gaul. He defeated the Veneti, a tribe known for their strong navy. He used special ships to win a big sea battle.
Crossing the Rhine and English Channel (55–54 BC)
Caesar wanted to show Rome's power.
- In 55 BC, he built a temporary bridge over the Rhine River. He led his army into Germania for a short time. This was to scare Germanic tribes from helping the Gauls.
- Later that year, he made his first trip to Britain. He wanted to punish British tribes for helping the Gauls.
- In 54 BC, Caesar returned to Britain with a larger army. He defeated some British tribes. But he did not conquer Britain fully. He made them agree to pay tribute to Rome.
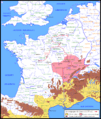
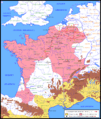
Gallic Revolts and Vercingetorix (53–52 BC)
The Gauls did not want to be ruled by Rome.
- In 53 BC, several tribes revolted. Caesar put down these uprisings. But the biggest challenge was still to come.
- In 52 BC, a young Gallic leader named Vercingetorix united many tribes. He was a brilliant general. He used tactics like burning crops and villages. This made it hard for the Romans to find food.
- Vercingetorix won a major victory against Caesar at the Battle of Gergovia. This was a big shock for the Romans.
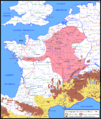
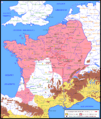
The Siege of Alesia (52 BC)
After Gergovia, Caesar chased Vercingetorix to the town of Alesia.
- Caesar began a huge siege. His army built two walls around Alesia. One wall kept the Gauls inside. The other wall protected the Romans from Gallic relief armies coming from outside.
- Vercingetorix and his people were trapped. They ran out of food.
- A massive Gallic army arrived to help Vercingetorix. But Caesar's army fought them off.
- Finally, Vercingetorix surrendered to Caesar. This was the turning point of the wars.
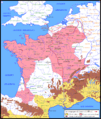
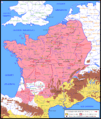
End of the Wars (51–50 BC)
After Alesia, the main fighting was over.
- In 51 BC, Caesar spent the year putting down the last small revolts. He made sure all of Gaul was under Roman control.
- By 50 BC, Gaul was fully conquered. It became a Roman province.
Results of the Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars had a huge impact.
- Caesar became incredibly famous and rich. His victories helped him gain power in Rome.
- Gaul became part of the Roman Empire. This brought Roman culture, laws, and language to the region.
- The wars showed the strength of the Roman army. They also showed Caesar's amazing skills as a military leader.
Images for kids
-
Caesar's Rhine Bridge, by John Soane (1814)
-
A page from an 1864 printing of the Commentarii, made by Parrish & Willingham, a Confederate publisher during the American Civil War
-
Denarius from 48 BC, thought to depict an allegory of Gaul with a carnyx on the obverse and Diana of Ephesus with a stag on the reverse
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra de las Galias para niños
In Spanish: Guerra de las Galias para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |