German Trade Union Confederation facts for kids
|
Deutscher Gewerkschaftsbund
|
|
 |
|
| Predecessor | General German Trade Union Federation |
|---|---|
| Founded | 12 October 1949 |
| Headquarters | Berlin, Germany |
| Location |
|
|
Members
|
6.0 million |
|
Key people
|
Yasmin Fahimi (SPD), president |
| Website | www.dgb.de |
The German Trade Union Confederation (DGB) is like a big team for eight different worker groups, called trade unions, in Germany. It helps over 6 million people who work. The DGB started in Munich on October 12, 1949.
The DGB helps its member unions work together. It talks to the government, political parties, and groups that represent employers. However, the DGB itself does not directly make deals about pay or working conditions. Its main job is to coordinate and support its member unions.
Union members choose people to represent them in different areas. These representatives form committees for 9 districts and 66 regions across Germany. Every four years, the DGB holds a big meeting called a federal congress. At this meeting, they decide on important goals for the unions. They also choose five leaders for the DGB. These leaders, along with the heads of the member unions, form the DGB's main committee. There is also a special group for young people called DGB-Jugend.
The DGB's main office is in Berlin. It is also part of bigger international groups, like the European Trade Union Confederation (ETUC) and the International Trade Union Confederation (ITUC).
Contents
History of German Trade Unions
Early Beginnings Until 1933
The very first big group of unions in Germany was founded on March 14, 1892. It was called the Generalkommission der Gewerkschaften Deutschlands. This group represented 57 national unions and some local ones, with about 300,000 members in total.
After World War I, unions had to start over. From June 30 to July 5, 1919, a new main union group was formed in Nuremberg. It was called the Allgemeiner Deutscher Gewerkschaftsbund (ADGB). This group had 52 unions and more than 3 million members. The ADGB is seen as an early version of today's DGB. Sadly, on May 2, 1933, all trade unions in Germany were shut down by the Nazis.
Rebuilding After World War II (1946–1949)
After World War II, German unions had to rebuild again. Different regional unions started forming in the parts of Germany controlled by the Western countries.
In the part of Germany controlled by the Soviet Union, the Freier Deutscher Gewerkschaftsbund (FDGB) was created in Berlin in February 1946. It was a group of 15 unions.
In the Western parts of Germany, several regional union groups were formed between 1946 and 1947. For example, the Deutscher Gewerkschaftsbund, DGB was founded in Bielefeld in April 1947.
Finally, from October 12 to 14, 1949, seven of these regional union groups in West Germany joined together. They formed the West German DGB, which included 16 different trade unions. This was the official start of the DGB we know today.
DGB After German Reunification
In 1990, when East and West Germany became one country again, the members of the FDGB from East Germany joined the DGB. In recent years, many of the DGB's member unions have merged with each other. This means that today, the DGB has only 8 main member unions. Some people thought this would make the unions stronger, but others worried it might weaken the DGB as the main organization.
Since 1990, the power of German trade unions has changed. They have had to accept lower real wages and changes to welfare support. For some years, the DGB and its member unions have been working to get a minimum wage for all workers in Germany.
DGB Member Unions Today
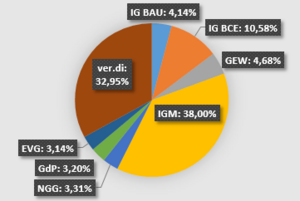
The DGB is made up of eight large unions. Here is a look at their membership numbers from 2017:
| Members of DGB unions 2017 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Union | Women | Men | In total | ||||
| IG Bauen-Agrar-Umwelt (Construction, Agriculture, Environment) | IG BAU | 67,069 | 26.35% | 187,456 | 73.65% | 254,525 | 4.25% |
| IG Bergbau, Chemie, Energie (Mining, Chemicals, Energy) | IG BCE | 137,012 | 21.49% | 500,611 | 78.51% | 637,623 | 10.64% |
| Gewerkschaft Erziehung und Wissenschaft (Education and Science) | GEW | 199,529 | 71.71% | 78,714 | 28.29% | 278,243 | 4.64% |
| IG Metall (Metalworkers) | IGM | 406,893 | 17.98% | 1,855,768 | 82.02% | 2,262,661 | 37.74% |
| Gewerkschaft Nahrung-Genuss-Gaststätten (Food, Beverages and Catering) | NGG | 83,741 | 41.89% | 116,180 | 58.11% | 199,921 | 3.33% |
| Gewerkschaft der Polizei (Police) | GdP | 46,032 | 24.86% | 139,121 | 75.14% | 185,153 | 3.09% |
| Eisenbahn- und Verkehrsgewerkschaft (Railway Workers) | EVG | 41,204 | 21.69% | 148,771 | 78.31% | 189,975 | 3.17% |
| Vereinte Dienstleistungsgewerkschaft (United Services Union) | ver.di | 1,038,221 | 52.24% | 949,115 | 47.76% | 1,987,336 | 33.15% |
| DGB in total | DGB | 2,019,701 | 33.69% | 3,975,736 | 66.31% | 5,995,437 | 100.00% |
Former Member Unions
Over the years, many unions have merged to form the larger unions that are part of the DGB today. For example, the German Postal Union and the Public Services, Transport and Traffic Union merged to become part of Ver.di.
DGB Presidents
The DGB has had several presidents since it was founded:
- 1949: Hans Böckler
- 1951: Christian Fette
- 1952: Walter Freitag
- 1956: Willi Richter
- 1962: Ludwig Rosenberg
- 1969: Heinz Oskar Vetter
- 1982: Ernst Breit
- 1990: Heinz-Werner Meyer
- 1994: Dieter Schulte
- 2002: Michael Sommer
- 2014: Reiner Hoffmann
- 2022: Yasmin Fahimi
How the DGB is Organized
The DGB is organized into different levels to help workers across Germany.
Districts and Regions
The DGB has 9 main districts, and within these districts, there are 66 smaller regions. This helps the DGB stay connected with workers all over the country.
- Baden-Württemberg: 4 regions
- Bayern: 14 regions
- Berlin/Brandenburg: 4 regions
- Hessen/Thüringen: 6 regions
- Niedersachsen/Bremen/Sachsen-Anhalt: 10 regions
- Nord (Niedersachsen/Bremen/Sachsen-Anhalt): 7 regions
- Nordrhein-Westfalen: 11 regions
- Sachsen: 4 regions
- West (Rheinland-Pfalz/Saarland): 6 regions
See also
 In Spanish: Federación Alemana de Sindicatos para niños
In Spanish: Federación Alemana de Sindicatos para niños
- List of labor unions
- Hans Böckler - first president of the confederation
Images for kids
 | George Robert Carruthers |
 | Patricia Bath |
 | Jan Ernst Matzeliger |
 | Alexander Miles |