Glebe Island facts for kids
Glebe Island is a historic area in Sydney Harbour, Australia. It used to be a very important port where things like cars and other goods arrived. Even though it's still called an "island," it's actually connected to the land now. It's surrounded by White Bay, Johnstons Bay, and Rozelle Bay. Bridges like the Glebe Island Bridge and the Anzac Bridge connect it to nearby areas like Pyrmont and Rozelle.
Contents
History of Glebe Island
From Island to Mainland

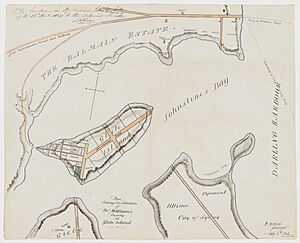
Glebe Island was once a rocky piece of land. You could only reach it from the Balmain shore when the tide was low. In the 1840s, a special road called a causeway was built to connect it. This made it easier to get to the island.
In 1841, a surveyor named William Wells planned to divide the Balmain end of the island into lots for houses. However, this plan never happened.
Early Abattoirs and Bridges

Between 1850 and 1854, a famous architect named Edmund Blacket designed stone buildings for a public abattoir (a place where animals are prepared for meat) on the island. These buildings had a special design, similar to old Norman castles.
In 1862, the Pyrmont Bridge Company built a wooden bridge. This bridge connected Glebe Island to Pyrmont and then to the city. This made it much easier to transport goods and people.
The abattoirs were very busy. In 1882, over half a million sheep and many thousands of cattle, pigs, and calves were processed there. However, people living nearby complained about the smell and other issues.
On June 28, 1903, a new bridge opened. It was designed by Percy Allan, a skilled engineer. This new Glebe Island Bridge was a swing bridge. This means a part of it could swing open to let ships pass through. It was a very advanced design for its time. Later, in 1906, Glebe Island officially became part of the Municipality of Balmain.
Wharves and Silos for Grain
Starting in 1912, the Sydney Harbour Trust began planning to build large wharves (docks) around Glebe Island. Also in 1912, it was decided to close the abattoirs and build a new one at Homebush Bay.
By 1915, a quarry master named Robert Saunders was hired to flatten the island. This was to make space for the new wharves. His workers dumped a lot of rock and soil to create more land for the docks. They also carefully cut out high-quality stone, likely used for other buildings.
Glebe Island quickly became a successful port for the Harbour Trust. Wharves were built on three sides of the flattened island. The fourth side was connected to the Rozelle shoreline. This was part of a big project to reclaim (fill in) parts of Rozelle Bay and White Bay.
Glebe Island also became home to a large grain elevator and tall concrete silos. These were used to store huge amounts of wheat, starting in 1921. By 1958, the terminal could hold 7.5 million bushels of wheat, which is about 202,500 tonnes. During World War II, a large part of the island was used as a main supply depot for the United States Army in Sydney.
From Industry to Future Plans
The bulk handling of grain continued until 1990. After that, the wheat terminal moved to Port Kembla. The wharves were then changed to handle containerised cargo (goods packed in large metal boxes). Some of the old silos were knocked down. However, 16 of them were kept and used by Cement Australia to store bulk cement. These silos are now considered important historical structures.
In the 1990s, a new, very tall, cable-stayed bridge was built above the older Glebe Island Bridge. This new bridge, which opened in 1995, was also first called Glebe Island Bridge. In 1998, it was renamed the Anzac Bridge to honour Australian and New Zealand soldiers. Until 2008, Glebe Island was a major place for importing cars into Australia.
Today, there are many ideas for what to do with the disused Glebe Island site. In 2008, there was a suggestion to build a tennis centre there for the Australian Open tournament. This idea didn't last long. In 2009, it was announced that the White Bay Cruise Terminal would be renovated. This would allow it to become a cruise ship terminal, helping to ease pressure on other busy terminals in Sydney. This plan has caused some debate among local residents due to concerns about traffic.
On New Year's Eve 2011–12, the large empty space at Glebe Island was used for a big televised concert. It offered a great view of the Sydney Harbour Bridge fireworks. The old Glebe Island Bridge was added to the heritage list in 2013. This supports calls to keep it as a way for people to walk or cycle.
In August 2013, construction began on a temporary exhibition centre called Sydney Exhibition Centre @ Glebe Island. It opened in February 2014 and provided 20,000 square metres of space for large shows. This centre was used while the main Sydney Convention & Exhibition Centre was being rebuilt. The temporary centre was removed in 2017. In 2018, plans were announced for a new complex to handle building materials.
Glebe Island is part of the New South Wales Government's Bays Precinct urban renewal program. This program aims to redevelop and improve the areas around Sydney's bays.