Glycoprotein facts for kids
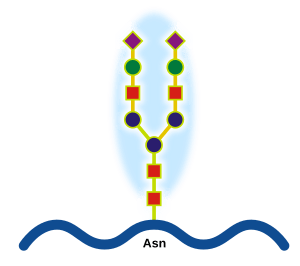
Imagine tiny building blocks inside your body. A glycoprotein is like a special building block made from two main parts: a protein and a carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are often like sugars. These molecules are super important for how your body works.
Glycoproteins help your body's immune system recognise different cells. This helps your body know what belongs and what doesn't. They are found in many living things, especially mammals (like humans!).
Some important glycoproteins you might hear about include:
- Antibodies: These are special proteins that help your immune system fight off germs. They react with things called antigens, which are like markers on invaders.
Certain hormones are also glycoproteins. Hormones are chemical messengers in your body. Some examples are:
- Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinising hormone (LH)
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Contents
What Glycoproteins Do
Glycoproteins have many important jobs in your body. They are like tiny workers that help cells communicate and protect themselves.
Cell Recognition
One of their main jobs is helping cells recognise each other. Think of them as ID badges on the surface of cells. This is very important for your immune system. It helps your body tell the difference between its own healthy cells and harmful invaders like viruses or bacteria.
Structure and Protection
Glycoproteins also help build and protect parts of your body. For example, they are found in the mucus that lines your nose and throat. This mucus helps trap germs and keep them from entering your body. They also help form the extracellular matrix, which is like the glue that holds cells together in tissues.
Hormones and Enzymes
As mentioned, some hormones are glycoproteins. These hormones control many body functions, like growth and metabolism. Some enzymes, which are proteins that speed up chemical reactions, are also glycoproteins.
Where Glycoproteins Are Found
You can find glycoproteins almost everywhere in your body. They are on the surface of most cells. They are also found in body fluids like blood and saliva.
In Blood
In your blood, glycoproteins play a role in blood clotting. They also help determine your blood type. The A, B, and O blood types are based on different glycoproteins found on the surface of your red blood cells.
In Viruses
Even viruses use glycoproteins! Viruses have glycoproteins on their outer surface. These help the virus attach to and enter host cells. For example, the influenza virus (which causes the flu) has glycoproteins that help it infect your cells.
How Glycoproteins Are Made
Glycoproteins are made inside cells through a process called glycosylation. This is when a carbohydrate (sugar) part is added to a protein. This process happens in special parts of the cell, like the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus.
The cell carefully adds the right sugar chains to the right proteins. This makes sure each glycoprotein has the correct shape and can do its specific job.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Glucoproteína para niños
In Spanish: Glucoproteína para niños