Great Artesian Basin facts for kids
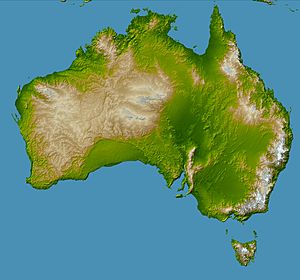
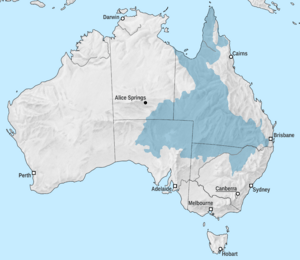
The Great Artesian Basin in Australia is the biggest and deepest underground water supply (called an aquifer or artesian basin) on Earth! It covers a huge area of about 1,711,000 square kilometers. That's about 22% of Australia's total land. This includes most of Queensland, the southeast part of the Northern Territory, the northeast part of South Australia, and northern New South Wales. In some places, the basin is as deep as 3,000 meters. It might hold about 64,900 cubic kilometers of groundwater, which is water stored underground. The water in the basin can be warm, ranging from 30°C to 100°C.
This basin is the only dependable source of freshwater for much of inland Australia. The Great Artesian Basin Coordinating Committee (GABCC) helps manage this important water source. They work with different government groups and local communities.
How the Basin Formed
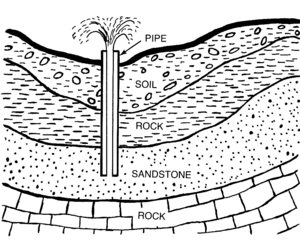
The water in the Great Artesian Basin is stored in a layer of sandstone. This sandstone was formed a very long time ago, during the Triassic, Jurassic, and Lower Cretaceous periods. Back then, much of Australia was under the sea.
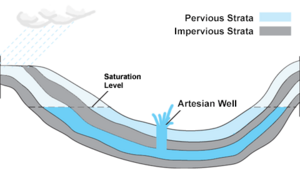
Over time, more layers of marine sedimentary rock (rock made from bits of sand, mud, and shells) formed on top of the sandstone. These top layers are like a lid, trapping the water in the sandstone below. This is what makes it an "artesian" basin – the water is under pressure.
The eastern side of the basin was lifted up when the Great Dividing Range mountains were formed. The other sides were shaped by the Central Eastern Lowlands and the Great Western Plateau to the west.
Water Flow and Age
Most of the water enters the basin from higher ground near the eastern edge, in Queensland and New South Wales. This water then slowly moves towards the south and west. A smaller amount of water also enters from the western side in central Australia, flowing towards the south and east.
Because the sandstone is permeable (meaning water can pass through it), the water slowly travels through tiny spaces between the sand grains. It moves very slowly, only about one to five meters each year.
Eventually, the water comes out through natural springs and seeps, mostly in the southern part of the basin. Scientists can figure out how old the groundwater is by studying things like carbon-14. Water in the northern parts of the basin (where it enters) can be several thousand years old. But in the southwestern areas (where it comes out), the water can be nearly 2 million years old!
Images for kids
-
Lightning Ridge bathing pools are supplied by water from the artesian basin.
-
A hot water bore hole into the Great Artesian Basin in Thargomindah.
-
Beel's Bore, Hariman Park near Cunnamulla.
See also
 In Spanish: Gran Cuenca Artesiana para niños
In Spanish: Gran Cuenca Artesiana para niños