Han (Warring States) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Han
韓
*Gar |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 403 BC–230 BC | |||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| Status | State → Kingdom | ||||||||
| Capital | Yangzhai (before 375 BC) Xinzheng (after 375 BC) |
||||||||
| Religion | Chinese folk religion ancestor worship |
||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Hou → King | |||||||||
| Chancellor | |||||||||
| Historical era | Warring States period | ||||||||
| 403 BC | |||||||||
|
• Conquered by Qin
|
230 BC | ||||||||
| Currency | spade money other ancient Chinese coinage |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Han | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
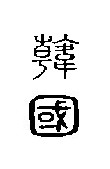
"State of Han" in small seal script (220 BC)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 韓國 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 韩国 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Han state was an important part of ancient China during a time called the Warring States period. This period lasted from about 475 BC to 221 BC. Historians sometimes spell its name as Hann to make sure people don't confuse it with the much later Han dynasty.
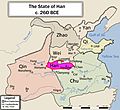
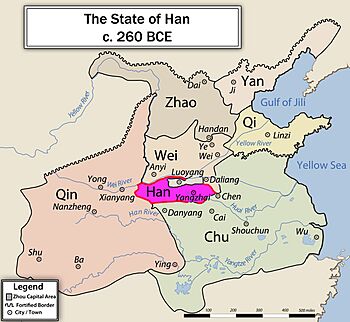
The Han state was located in central China. This area is now parts of Shanxi and Henan provinces. It was south and east of Luoyang, which was the capital of the Eastern Zhou dynasty. The rulers of Han came from the Ji family, a powerful group of nobles. They started as ministers in the state of Jin. Over time, they became even more powerful than Jin's own ruling family.
The breakup of the Jin state led to the creation of three new states: Han, Wei, and Zhao. This event, known as the Partition of Jin, marked the start of the Warring States period.
The Han state was quite small. It was in a mountainous area that wasn't very rich in resources. Its land also blocked the strong state of Qin from easily reaching the North China Plain. Han tried to make its government better. A wise leader named Shen Buhai helped improve how the state was run. He also made its army stronger. However, these changes were not enough. Han was the first of the seven main states to be conquered by Qin in 230 BC.
A huge battle happened in 260 BC when Qin invaded Han's Shangdang Commandery. This was the Battle of Changping. It is known as one of the bloodiest battles of the Warring States period. Up to 400,000 soldiers may have died there.
Contents
History of the Han State
How Han Began
The Han royal family was a branch of the royal family of the Jin state. This is written in an old book called the Records of the Grand Historian. The first important person from the Han clan was Wuzi of Han. He was the uncle of a ruler named Duke Wu of Jin.
Members of the Han family became important officials in the powerful Jin state. They were given land in a place called Hanyuan. This area is now Hancheng in Shaanxi province.
Growing Power in the Spring and Autumn Period
During the Spring and Autumn period, the Han family slowly gained more and more power within the Jin state. By 453 BC, a Han leader named Jing teamed up with leaders from the Wei and Zhao families. Together, they divided the Jin state among themselves.
This event, the Partition of Jin, is very important in Chinese history. It marks the end of the Spring and Autumn period and the start of the Warring States period. After this, Han became an independent state. In 403 BC, the King Lie of the Zhou dynasty officially recognized these new states. He gave their rulers the title of hou, which means "marquess".
The Warring States Period Challenges
In 375 BC, Han defeated a nearby state called Zheng. Zheng was founded by the Zhou dynasty in 806 BC. Han took over Zheng's land, making its own territory larger. Han also moved its capital to Zheng's former capital. This helped Han gain new ideas and people, including a young politician named Shen Buhai.
Han reached its strongest point under the rule of Marquess Xi. He made Shen Buhai his top advisor, known as a chancellor. Shen Buhai put in place new rules based on a philosophy called Legalism. These changes made the government work better and made the army stronger. Later, under King Xuanhui (who ruled from 332–312 BC), Han even declared itself an independent kingdom.
However, Han faced many difficulties during the Warring States period. After Jin was divided, Han was surrounded by very strong states. Chu was to the south, Qi to the east, Qin to the west, and Wei to the north. Han was the smallest of the seven main states. It had no easy way to expand its land or get more resources. Because of this, its more powerful neighbors often attacked it.
The Fall of Han
As Han grew weaker, it often needed help from other states to defend its land. For example, the states of Wei and Qi fought over control of Han. This led to the Battle of Maling, which showed that Qi was the strongest state in the east. In 260 BC, Qin invaded Han. This led to Zhao getting involved and the huge Battle of Changping.
In the later years of this era, Han tried a clever trick to weaken Qin. Han sent an engineer named Zheng Guo to Qin. He convinced Qin to build a very expensive canal. Han hoped this project would use up Qin's money and resources. However, the plan backfired! When the Zhengguo Canal was finished, it was incredibly useful. It helped Qin grow much more food and become even richer. This gave Qin the power to defeat all the other states. Han was the first state to fall to Qin in 230 BC.
A few years later, in 226 BC, some old nobles from Han tried to start a rebellion in the former capital, Xinzheng. But their rebellion failed. King An, the last king of Han, was killed that same year.
Much later, after the Han dynasty began, a general named Han Xin was made a "Prince" or "King of Han" by Liu Bang. He was moved to a different area. There, he joined forces with the Xiongnu people and led attacks against the Han Dynasty until he died.
Culture and Society
Before the state of Qin united all of China in 221 BC, each region had its own special customs and culture. However, the upper classes across China shared many common traditions. An old text called the Yu Gong (Tribute of Yu) describes China as having nine different regions. Each region had its own unique people and products. The main idea of this text is that these nine regions were brought together into one state. This happened as people traveled and sent their unique goods to the capital as tribute. Other old writings also talked about these different regional cultures and environments.
One of these texts was Wuzi (The Book of Master Wu). This was a military book written during the Warring States period. It was written to answer a question from Marquis Wu of Wei about how to deal with other states. Wu Qi, who wrote the book, believed that a government and its people were shaped by the land they lived in.
Important People from Han
- Han Fei: A famous thinker who followed the Legalist philosophy.
- Zhang Liang: A very important figure in the early Han dynasty.
- Zheng Guo: The smart engineer who designed the Zhengguo Canal for the state of Qin.
Han in Astronomy
In ancient Chinese astronomy, the Han state is represented by certain stars. One star, 35 Capricorni, is part of a group of stars called the "Twelve States." This group is in the "Girl" lunar mansion, which is part of the "Black Turtle" symbol. Han is also shown by the star Zeta Ophiuchi. This star is in a group called the "Right Wall," which is part of the "Heavenly Market" enclosure.
Images for kids
-
"State of Han" in small seal script (220 BC)
 | Valerie Thomas |
 | Frederick McKinley Jones |
 | George Edward Alcorn Jr. |
 | Thomas Mensah |