Hospital facts for kids

A hospital is a special place where people go to get medical help when they are sick or hurt. It's like a big team of doctors, nurses, and other health experts working together with special equipment to make patients feel better.
The most common type is a general hospital. These hospitals can treat many different kinds of health problems, from accidents to sudden illnesses. They usually have an emergency department for urgent situations. A district hospital is often the main hospital in its area, with many beds for serious care and for patients who need to stay longer.
Some hospitals are very specialized. For example, there are children's hospitals just for kids, hospitals for older people, or hospitals focused on specific treatments like heart problems or broken bones. These specialized hospitals can be very good at what they do.
Many hospitals also help train future doctors and nurses. These are called teaching hospitals. Smaller places that offer medical care, but usually don't have patients stay overnight, are often called clinics. Hospitals get their funding from different sources, like government programs, health insurance, or generous donations from people and charities.
Contents
What's in a Name? The Word "Hospital"
The word "hospital" has a long history! It comes from the Latin word hospes, which meant a stranger or a guest. This is also where we get words like host, hospitality, and hotel.
During the Middle Ages, hospitals were not exactly like the ones we have today. They were often places that offered shelter to the poor, travelers, or people on religious journeys. They were truly "places of hospitality." Over time, these places evolved to focus more on medical care.
Different Kinds of Hospitals
Hospitals come in various types, each designed to help people in specific ways.
Staying or Visiting: Inpatients and Outpatients
When you visit a hospital just for a check-up, a test, or a quick treatment and then go home the same day, you are an "outpatient". If you need to stay overnight, or for several days or weeks, you become an "inpatient". Hospitals are unique because they can care for inpatients, unlike smaller clinics.
General Hospitals: Ready for Anything
The most common type is the general hospital, also known as an acute-care hospital. These hospitals are equipped to handle a wide range of illnesses and injuries. They almost always have an emergency department (sometimes called "accident & emergency") to treat urgent health problems right away. Larger cities might have several general hospitals.
District Hospitals: Local Care Hubs
A district hospital is usually the main healthcare center for a specific region or community. They have many beds for patients who need intensive care or who need to stay for a longer time to recover. These hospitals are vital for providing essential medical services to their local populations.
Specialized Hospitals: Focused Care



Specialized hospitals focus on one or a few related medical areas. Examples include:
- Children's hospitals: Just for kids!
- Hospitals for older people (sometimes called geriatric hospitals).
- Hospitals for specific conditions like cancer treatment, heart problems, or bone injuries.
- Rehabilitation hospitals: Where people go to recover after an injury or illness.
These hospitals can become very good at their specific treatments because their staff and equipment are all focused on that one area. For instance, a heart hospital might perform many heart surgeries, making their teams highly skilled.
Teaching Hospitals: Learning and Healing
A teaching hospital does two important things: it provides medical care to patients and also trains future doctors, nurses, and other health professionals. These hospitals are often connected to medical schools or nursing schools. Students get to learn by observing and assisting experienced medical teams, and these hospitals are often involved in medical research to discover new treatments.
Clinics: Quick Visits
Clinics are usually smaller than hospitals. They mainly offer "outpatient" services, meaning you visit for an appointment or treatment and then go home. Some clinics might have a few beds for short stays, but they don't offer the full range of services a hospital does.
Inside a Hospital: Departments and Teams
A hospital is like a small city, with many different sections working together.
Wards and Patient Rooms
Hospitals have different areas called "wards" where patients stay in hospital beds. There are also special units for very serious cases, like the intensive care unit (ICU), and rooms for operations, called operating theatres.
Special Medical Teams
Hospitals have many specialized departments, such as:
- The emergency department for urgent care.
- Departments for specific medical areas like cardiology (heart), surgery, or pediatrics (children's health).
- Outpatient departments for appointments and treatments where patients don't stay overnight.
Support Services
Behind the scenes, many other teams keep the hospital running smoothly:
- A hospital pharmacy prepares and gives out medicines.
- Radiology uses X-rays and other imaging to see inside the body.
- Pathology and medical laboratories analyze samples to help diagnose illnesses.
- Support teams handle things like medical records, technical support, cleaning, and security.
Nurses are a huge part of the hospital team. Each unit often has a nursing manager who makes sure patients receive excellent nursing care.
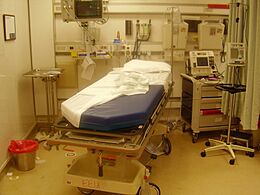
-
A resuscitation room bed after a trauma intervention, showing the highly technical equipment of modern hospitals.
Modern Care: Remote Monitoring
Thanks to new technology, some hospitals are now using "virtual wards." This means patients can be managed at home while still being closely monitored by the hospital team. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many patients in the UK used small devices to check their oxygen levels at home. Nurses and doctors could then check on them by phone or video calls. This allows more patients to recover comfortably at home while still getting the care they need.
A Look Back: The History of Hospitals
Hospitals have a fascinating history, changing a lot over thousands of years!
Ancient Beginnings
Long ago, around 400 AD, a Chinese monk traveling in India wrote about places that helped the sick. In ancient Sri Lanka, there were even "lying-in-homes" and hospitals around 400 BC! The ancient Greeks had temples dedicated to the healing god Asclepius, which offered medical advice and healing. The Romans had military hospitals for soldiers.
-
The Asklepeion of Kos, an ancient Greek healing center.
-
Ruins of a 2,000-year-old hospital in Anuradhapura, Sri Lanka.
Hospitals in the Middle Ages
When Christianity became widely accepted in the Roman Empire, more hospitals were built, often connected to churches. These early hospitals provided care and shelter.
In the Islamic world, the first general hospital was built in Baghdad in 805 AD. These "bimaristans" were advanced medical centers. They treated the poor, offered medical training, and even required doctors to have licenses. They were also forbidden by law from turning away patients who couldn't pay.
In China, during the Song dynasty, the government started creating public hospitals and dispensaries to help people.
Hospitals in Recent Centuries
In Europe, after the 1500s, hospitals began to change from being mainly religious charities to more secular (non-religious) institutions. In England, some of the first hospitals were supported by the king after churches stopped funding them.
The 1700s saw the rise of "voluntary hospitals," funded by private donations. These hospitals became important places for medical learning and discovery. Doctors and surgeons would work there and teach their knowledge to new students. The Pennsylvania Hospital in Philadelphia, founded in 1751, is one of the oldest public hospitals in the United States.



The Modern Hospital Takes Shape
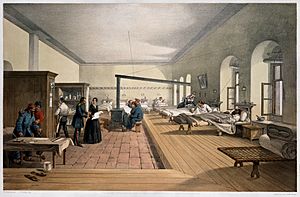
The 1800s were a time of great change. Florence Nightingale, a famous nurse, helped make hospitals much cleaner and safer during the Crimean War. She also started the first official nursing school in 1860, which trained nurses to work in hospitals and care for patients. Her work transformed hospitals from places where people often went to die, into places focused on healing and recovery.
By the late 1800s and early 1900s, medical breakthroughs like anesthesia (which makes surgery painless) and X-rays made hospitals even more important for treatment. Today, hospitals continue to evolve, using new technologies and focusing on patient safety and comfort.
Hospitals Today
Modern hospitals constantly measure how well they are doing, looking at things like how quickly patients are seen, how satisfied patients are, and how successful treatments are.
In the United States, the number of hospital stays has changed over the years, with more care now happening outside of traditional hospitals, like at home or in doctors' offices. Smaller hospitals, sometimes called "microhospitals," are also becoming more common.
The Catholic Church is a very large non-government provider of healthcare worldwide. It manages thousands of clinics, homes for the elderly, and hospitals, especially in developing countries.


How Hospitals Are Funded
Hospitals need a lot of money to operate, pay staff, and buy equipment. They get their funding from different places:
- Public Funding: Many hospitals, especially in countries like the United Kingdom with its National Health Service, are funded by the government through taxes. This means healthcare is often free for citizens when they need it.
- Health Insurance: In other countries, like the United States, people often have health insurance that helps pay for hospital costs.
- Private Payments: Some patients pay for their care directly, especially if they don't have insurance or want specific services.
- Charitable Donations: Many hospitals, especially non-profit ones, receive donations from individuals, charities, and organizations. Historically, many hospitals were started by religious groups or generous individuals.
In some places, laws require hospitals to provide emergency care to anyone, even if they can't pay.

Keeping Patients Safe and Healthy
Making sure patients receive high-quality and safe care is a top priority for hospitals around the world.
Checking for Quality
Hospitals often undergo special assessments, called "hospital accreditation", by independent groups. These groups check if the hospital meets high standards for patient care, safety, and cleanliness. For example, in England, hospitals are monitored by the Care Quality Commission.
Patient Safety
Hospitals work hard to prevent errors and infections. It's a big challenge, but they use many procedures and technologies to keep patients safe. For instance, they pay close attention to things like food safety, as good nutrition is important for recovery. They also focus on preventing infections that can sometimes happen in hospitals.
Hospital Buildings: Designed for Healing
Modern hospital buildings are carefully designed to help medical staff work efficiently and to keep patients comfortable and safe.
Smart Design for Care
Architects try to make it easy for staff to move around and for patients to be transported between different parts of the hospital. They also need to plan for heavy equipment like X-ray machines and for special systems like plumbing and waste disposal.
Comfort and Well-being
While some older hospitals might seem a bit confusing because they've grown over many years, newer designs often focus on making patients feel better. This includes:
- Allowing in more fresh air and natural light.
- Providing pleasant views from windows.
- Using calming colors.
- Creating spaces like hospital gardens, as being close to nature can improve mood and reduce stress.
Research shows that good hospital design can actually help patients recover faster! For example, having single-sex rooms helps ensure privacy and dignity.
Individual Rooms vs. Wards
There's a trend towards having more individual patient rooms instead of large communal "wards." While wards can be efficient for staff, individual rooms offer more privacy and can be less stressful for patients. However, building and running hospitals with all private rooms can be more expensive.
-
The medical center at the University of Virginia shows the growing trend for modern architecture in hospitals.
-
The National Health Service Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital in the UK, showing the utilitarian architecture of many modern hospitals.
-
A hospital chapel at Fawcett Memorial Hospital in Port Charlotte, Florida, offering a quiet space.
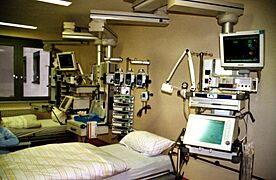
-
An intensive care unit (ICU) within a hospital, showing advanced medical equipment.
-
Tampere University Hospital in Tampere, Finland.
-
Lehigh Valley Hospital–Cedar Crest in Allentown, Pennsylvania, U.S.
See also
 In Spanish: Hospital para niños
In Spanish: Hospital para niños
- Burn center
- History of hospitals
- History of medicine
- Hospice
- Hospital network
- Lists of hospitals
- Trauma center
- Walk-in clinic
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |