House of Representatives (Netherlands) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids House of RepresentativesTweede Kamer der Staten-Generaal |
|
|---|---|
| States General of the Netherlands | |
 |
|
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
|
Speaker
|
Martin Bosma, PVV
Since 14 December 2023 |
|
First Deputy Speaker
|
Tom van der Lee, GL–PvdA
Since 19 December 2023 |
|
Second Deputy Speaker
|
Thom van Campen, VVD
Since 23 May 2025 |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 150 |
 |
|
|
Political groups
|
Government (demissionary) (51)
Opposition (99) |
| Elections | |
| Open party-list proportional representation (D'Hondt method) | |
|
Last election
|
22 November 2023 |
|
Next election
|
29 October 2025 |
| Meeting place | |
 |
|
| Binnenhof, The Hague (closed due to ongoing renovations) |
|
 |
|
| Bezuidenhoutseweg 67, The Hague (temporary) |
|
The House of Representatives (called Tweede Kamer in Dutch) is a very important part of the government in the Netherlands. It's like the main team of lawmakers in the Dutch parliament, which is called the States General. The other part of the parliament is the Senate.
The House of Representatives has 150 members. These members are chosen by the people of the Netherlands through elections. The House is usually located in a historic building called the Binnenhof in The Hague. However, because the Binnenhof is being fixed up, the House has temporarily moved to another building nearby.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The official English name is "House of Representatives." But in Dutch, it's actually called the "Second Chamber of the States General." People often just say "Second Chamber" or even just "The Chamber."
A person who is a member of the House is called a (Tweede) Kamerlid in Dutch. This means "member of the (Second) Chamber."
What Does the House Do?
The House of Representatives has two main jobs. First, it's where new laws are discussed and created. Second, it checks on the work of the government, which is called the cabinet.
Making New Laws
Both the government and the House of Representatives can suggest new laws. When a new law is suggested, the House discusses it. If most members agree, the law then goes to the Senate for their approval.
Checking the Government
The House makes sure the government is doing its job well. If the House loses trust in a minister or the whole government, that minister or government must resign. This means they have to step down from their positions.
Members of the House can ask the government questions. They can also make "motions," which are like official requests. These motions ask the government to do something or to stop doing something. It's important to know that a person cannot be a member of both the parliament and the government at the same time.
Helping with European Union Decisions
The House of Representatives also helps with decisions made by the EU. Members discuss EU policies before important meetings. They also appoint special reporters who focus on EU topics. This helps the Netherlands have a say in how the EU works.
Choosing Important Officials
The House has a role in choosing some important people. For example, it helps select judges for the highest court in the Netherlands, the Supreme Court of the Netherlands. It also chooses the Dutch Ombudsman, who helps citizens with problems they have with the government.
How Are Members Chosen?
Members of the House of Representatives are usually elected for a four-year term. Elections can happen sooner if the government loses trust, if the ruling parties can't agree, or if a new government can't be formed after an election.
Who Can Vote?
To vote in a Dutch election, you must be at least 18 years old and a Dutch citizen. If you live in the Netherlands, you are automatically registered to vote. Dutch citizens living abroad can also register to vote.
People living in Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten can vote if they have lived in the Netherlands for at least ten years or work for the Dutch government.
How Voting Works
The Netherlands uses a system called party-list proportional representation. This means that parties get seats in the House based on the percentage of votes they receive. For example, if a party gets 10% of the votes, they will get about 10% of the 150 seats.
This system makes it very hard for one party to win enough seats to govern alone. Because of this, Dutch governments are almost always made up of a group of different parties working together. This is called a "coalition government."
Forming a Government
After an election, different political parties talk to each other to form a new government. This process can take a few months. The House of Representatives helps by appointing people to explore which parties could work together.
Once a group of parties agrees to form a government, they choose a formateur. This person leads the final talks and helps create the new government. The formateur then becomes the Prime Minister. All members of the new government must leave their seats in the House of Representatives.
Who Is in the House Now?
To be a member of the House of Representatives, a person must be over 18 and have a Dutch passport.
How the House Has Changed
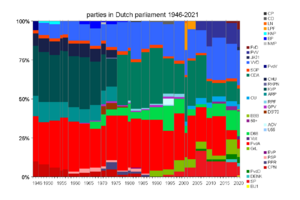
In the past, the House of Representatives had 100 seats. In 1956, this number was increased to 150, which is how many seats it has today.
The image below shows how the seats in the House have been divided among different parties since 1946. You can see how different parties have gained or lost seats over time. The lines show when new elections were held.
Current Members
The table below shows how the House of Representatives is made up after the 2023 Dutch general election.
| Group | Leader | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Party for Freedom | Geert Wilders |
|
|
| GroenLinks–PvdA | Frans Timmermans |
|
|
| People's Party for Freedom and Democracy | Dilan Yeşilgöz |
|
|
| New Social Contract | Nicolien van Vroonhoven |
|
|
| Democrats 66 | Rob Jetten |
|
|
| Farmer–Citizen Movement | Caroline van der Plas |
|
|
| Christian Democratic Appeal | Henri Bontenbal |
|
|
| Socialist Party | Jimmy Dijk |
|
|
| DENK | Stephan van Baarle |
|
|
| Party for the Animals | Esther Ouwehand |
|
|
| Forum for Democracy | Thierry Baudet |
|
|
| Reformed Political Party | Chris Stoffer |
|
|
| Christian Union | Mirjam Bikker |
|
|
| Volt Netherlands | Laurens Dassen |
|
|
| JA21 | Joost Eerdmans |
|
|
How Committees Work
The House of Representatives has special groups called "parliamentary committees." These committees focus on specific topics or areas of government. For example, there's usually a committee for each government ministry, like the Ministry of Finance or the Ministry of Education.
These committees discuss details about laws and policies. They help the main House meetings run more smoothly by doing a lot of the detailed work. There are currently fifteen standing committees.
See also
 In Spanish: Cámara de Representantes de los Estados Generales para niños
In Spanish: Cámara de Representantes de los Estados Generales para niños