East Japan Railway Company facts for kids
 |
|

Headquarters in Shibuya ward, Tokyo
|
|
|
Native name
|
東日本旅客鉄道株式会社
|
|---|---|
|
Romanized name
|
Higashi-Nihon Ryokaku Tetsudō kabushiki gaisha |
| Public | |
| Traded as |
|
| Industry | Rail transport |
| Predecessor | Japanese National Railways (JNR) |
| Founded | 1 April 1987, when JNR became a private company |
| Headquarters |
2-2-2 Yoyogi, Shibuya, Tokyo
,
Japan
|
|
Area served
|
Kanto and Tōhoku regions and parts of Niigata, Nagano, Yamanashi and Shizuoka |
|
Key people
|
Yuji Fukasawa (President) |
| Products | Suica (a rechargeable travel card) |
| Services | Passenger railways Bus transportation Other related services |
|
Number of employees
|
73,017 (as of 31 March 2013) |
| Subsidiaries | 83 companies, including Tokyo Monorail and J-TREC |
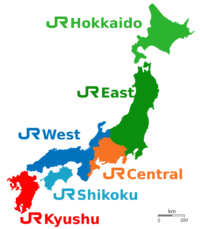
The East Japan Railway Company, also known as JR East, is the biggest passenger railway company in Japan. It is one of seven companies that make up the Japan Railways Group. In Japanese, the company is called JR Higashi-Nihon.
JR East's main office is in Yoyogi, Shibuya, Tokyo, right next to the famous Shinjuku Station. The company runs trains in the eastern part of Japan, including the busy Tokyo area and the entire Tōhoku region in the north. It is a major company listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
Contents
History of JR East
JR East was created on April 1, 1987. Before that, all of Japan's main railways were run by a single government-owned company called Japanese National Railways (JNR).
In 1987, the government decided to split JNR into several smaller, private companies. This process is called "privatization." JR East was one of these new companies. At first, the government still owned JR East, but by 2002, it had been completely sold to the public.
After the split, JR East took over running the train lines in and around Tokyo, the Tōhoku region, and nearby areas.
Train Lines and Services
JR East operates a huge network of train lines. These range from high-speed bullet trains to local trains that serve cities and towns. The company's lines are mainly in the Kanto (the area around Tokyo) and Tohoku regions.
Shinkansen: The Bullet Trains
JR East runs all of the Shinkansen (bullet train) lines that travel north from Tokyo. These amazing trains are known for their incredible speed and for always being on time.
The Shinkansen lines operated by JR East are:
- Tōhoku Shinkansen: Connects Tokyo with Shin-Aomori at the northern tip of Japan's main island.
- Jōetsu Shinkansen: Runs from Tokyo to Niigata.
- Hokuriku Shinkansen: Goes from Tokyo to Jōetsumyōkō. This line is shared with another company, JR West.
- Yamagata Shinkansen: Travels from Tokyo to Shinjo.
- Akita Shinkansen: Connects Tokyo and Akita.
JR East also operates many famous "limited express" trains that are fast and comfortable but not as fast as the Shinkansen. Some of these include the Narita Express, which connects Tokyo to Narita Airport, and the Azusa, which travels to the mountains in central Japan.
Famous Local Lines in Tokyo
JR East runs many of the most important train lines within Tokyo. These lines are used by millions of people every day.
- Yamanote Line: This is one of the most famous train lines in the world. It runs in a big loop around the center of Tokyo, stopping at major stations like Shinjuku, Shibuya, and Tokyo Station.
- Chūō-Sōbu Line: This line cuts across the center of the Yamanote Line loop, connecting eastern and western Tokyo.
- Keihin–Tōhoku Line: This line runs north-south through Tokyo, connecting the cities of Saitama, Kawasaki, and Yokohama.
- Saikyō Line: Another important north-south line that connects Tokyo with Saitama Prefecture.
Besides these, JR East has hundreds of other lines that serve cities, suburbs, and rural areas throughout eastern Japan.
Busiest Train Stations
Many of the world's busiest train stations are part of the JR East network. In 2017, the top five busiest JR East stations were:
- Shinjuku Station (778,618 passengers per day)
- Ikebukuro Station (566,516 passengers per day)
- Tokyo Station (452,549 passengers per day)
- Yokohama Station (420,192 passengers per day)
- Shinagawa Station (378,566 passengers per day)
These numbers only count passengers using the JR East lines at these stations. Many of these stations are also used by other train companies, so the total number of people passing through them is even higher!
Other JR East Activities
Besides running trains, JR East is involved in many other businesses.
Suica Smart Card
JR East created the Suica card, a rechargeable smart card. People can load money onto their Suica card and use it to pay for train rides by simply tapping it on a card reader. Suica can also be used to buy things at convenience stores and vending machines.
The Railway Museum
JR East helped create the East Japan Railway Culture Foundation. This non-profit organization runs the popular Railway Museum in Saitama. The museum has many real trains on display and teaches visitors about the history of railways in Japan.
Working for a Greener Future
JR East is working to reduce its impact on the environment. The company has a plan to cut its carbon emissions in half by 2030. To do this, they are making their trains more energy-efficient and developing new types of hybrid trains that use less power.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: East Japan Railway Company para niños
In Spanish: East Japan Railway Company para niños
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |